Continuous Delivery enhances software development by automating the release process, ensuring faster and more reliable deployments. This approach reduces risks associated with manual releases while enabling your team to deliver high-quality updates promptly. Discover how implementing Continuous Delivery can transform your development workflow in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
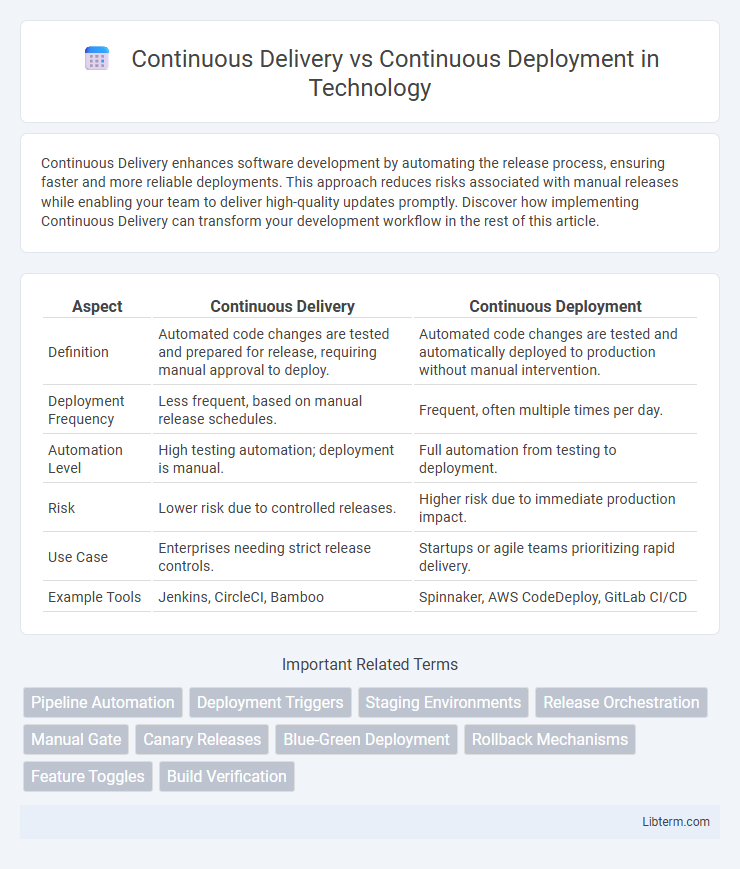
| Aspect | Continuous Delivery | Continuous Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated code changes are tested and prepared for release, requiring manual approval to deploy. | Automated code changes are tested and automatically deployed to production without manual intervention. |
| Deployment Frequency | Less frequent, based on manual release schedules. | Frequent, often multiple times per day. |
| Automation Level | High testing automation; deployment is manual. | Full automation from testing to deployment. |
| Risk | Lower risk due to controlled releases. | Higher risk due to immediate production impact. |
| Use Case | Enterprises needing strict release controls. | Startups or agile teams prioritizing rapid delivery. |
| Example Tools | Jenkins, CircleCI, Bamboo | Spinnaker, AWS CodeDeploy, GitLab CI/CD |
Introduction to Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment
Continuous Delivery is a software development practice where code changes are automatically built, tested, and prepared for release to production, enabling reliable and frequent updates. Continuous Deployment extends this process by automatically deploying every code change that passes automated testing directly to production, eliminating manual intervention. Both practices aim to accelerate software release cycles while maintaining high quality and stability.
Defining Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery is a software development practice where code changes are automatically built, tested, and prepared for release to production but require manual approval before deployment. This approach ensures that the software is always in a deployable state, reducing integration risks and enabling faster release cycles. Emphasizing automated testing and staging environments, Continuous Delivery enhances reliability and accelerates feedback loops.
Defining Continuous Deployment
Continuous Deployment is an advanced software development practice where code changes are automatically released to production after passing all stages of the pipeline, without manual approval. It relies on robust automated testing and monitoring tools to ensure deployment quality and system stability. Emphasizing rapid delivery and immediate user feedback, Continuous Deployment shortens release cycles and enhances agile development processes.
Key Differences Between Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment
Continuous Delivery ensures that code changes are automatically tested and prepared for deployment to production but requires manual approval before release, while Continuous Deployment automates the entire process, deploying every change that passes automated tests directly to production. Key differences include the level of automation in release, with Continuous Delivery involving human intervention and Continuous Deployment enabling fully automated release pipelines. Both practices aim to accelerate software delivery, improve quality, and reduce risk by integrating automated testing and continuous integration methodologies.
Advantages of Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery enhances software quality by ensuring code changes are automatically tested and ready for release, reducing deployment risks. It enables faster feedback loops from stakeholders, improving collaboration and alignment with business goals. The approach provides a controlled release process, allowing teams to decide the optimal timing for deploying new features or fixes.
Advantages of Continuous Deployment
Continuous Deployment accelerates software release cycles by automatically deploying every code change that passes automated tests, ensuring rapid delivery of new features and bug fixes. This approach enhances product quality and customer satisfaction through immediate feedback and faster iterations. It also reduces manual errors and operational overhead, enabling development teams to focus more on innovation and less on deployment logistics.
Common Challenges and Risks
Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment share challenges such as managing complex automation pipelines, ensuring consistent environment configurations, and maintaining robust testing frameworks to prevent defective code from reaching production. Risks include potential introduction of bugs due to insufficient test coverage, difficulty in rollback processes, and increased pressure on monitoring systems to detect and mitigate issues rapidly. Both methodologies require strong collaboration between development and operations teams to address these hurdles effectively and ensure reliable software releases.
Best Practices for Implementation
Implementing Continuous Delivery requires rigorous automated testing, consistent environment configurations, and a robust approval workflow to ensure code changes are production-ready but manually released. Best practices for Continuous Deployment emphasize fully automated pipelines with comprehensive monitoring, rollback mechanisms, and feature flag integration to enable seamless live updates without human intervention. Both approaches benefit from version control discipline, incremental deployments, and clear documentation to maintain reliability and accelerate software delivery cycles.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Team
Choosing the right approach between Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment depends on your team's risk tolerance, automation maturity, and release frequency needs. Continuous Delivery enables teams to validate code changes through automated testing before manual release approval, ideal for environments requiring strict quality control. Continuous Deployment fully automates the release process, accelerating delivery cycles and increasing deployment frequency but demands robust testing frameworks to minimize production risks.
Conclusion: Which Strategy Fits Your Organization?
Continuous Delivery suits organizations aiming for reduced deployment risks and manual control over releases, providing flexibility without automating every release step. Continuous Deployment fits teams prioritizing rapid, automated delivery and continuous feedback, enabling faster innovation and quicker market response. Selecting the right approach depends on factors like risk tolerance, team maturity, regulatory requirements, and the desired speed of software delivery.
Continuous Delivery Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com