Modular architecture breaks down complex systems into smaller, independent modules, enhancing flexibility and scalability in design. This approach simplifies maintenance and allows for easier upgrades by isolating changes within specific components. Explore the rest of this article to understand how modular architecture can transform your projects and optimize performance.
Table of Comparison
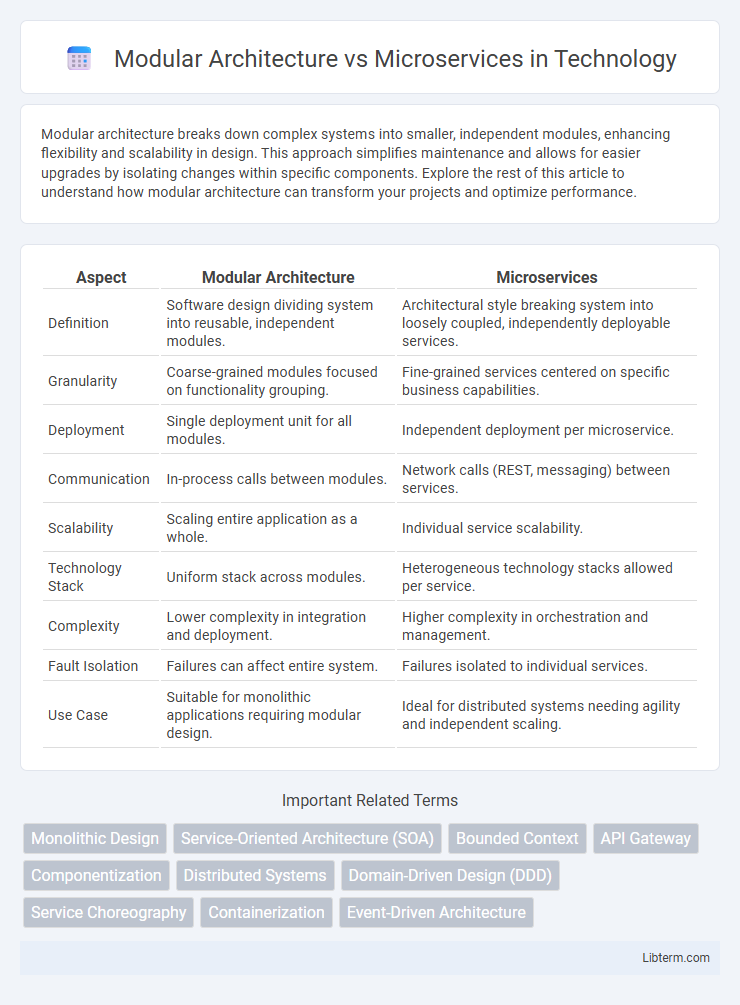
| Aspect | Modular Architecture | Microservices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software design dividing system into reusable, independent modules. | Architectural style breaking system into loosely coupled, independently deployable services. |
| Granularity | Coarse-grained modules focused on functionality grouping. | Fine-grained services centered on specific business capabilities. |
| Deployment | Single deployment unit for all modules. | Independent deployment per microservice. |
| Communication | In-process calls between modules. | Network calls (REST, messaging) between services. |
| Scalability | Scaling entire application as a whole. | Individual service scalability. |
| Technology Stack | Uniform stack across modules. | Heterogeneous technology stacks allowed per service. |
| Complexity | Lower complexity in integration and deployment. | Higher complexity in orchestration and management. |
| Fault Isolation | Failures can affect entire system. | Failures isolated to individual services. |
| Use Case | Suitable for monolithic applications requiring modular design. | Ideal for distributed systems needing agility and independent scaling. |
Introduction to Modular Architecture and Microservices
Modular architecture organizes software into distinct, self-contained modules that encapsulate specific functionality, promoting maintainability and scalability. Microservices architecture breaks applications into independently deployable services that communicate over networks, enhancing agility and enabling continuous delivery. Both approaches emphasize decomposition but differ in granularity and deployment strategies, with modular architecture focusing on internal code organization and microservices on distributed system design.
Core Principles of Modular Architecture
Modular architecture emphasizes the division of software into independent, interchangeable modules that encapsulate specific functionality and communicate through well-defined interfaces, enhancing maintainability and scalability. Each module is designed to be self-contained, promoting reuse and enabling parallel development while minimizing dependencies. This approach contrasts with microservices by focusing on high cohesion within modules rather than distributed service deployments, optimizing internal system organization and component interaction.
Defining Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture is a software design approach where applications are composed of small, independent services that communicate through APIs, enabling scalable and flexible development. Each microservice focuses on a specific business capability, deployed and maintained autonomously to enhance fault isolation and faster delivery cycles. This architecture contrasts with modular architecture by emphasizing distributed, loosely coupled services rather than monolithic modules within a single application.
Key Differences Between Modular Architecture and Microservices
Modular architecture divides a software system into cohesive, loosely coupled modules within a single unified application, emphasizing internal code organization and maintainability. Microservices architecture, however, decomposes an application into independent, deployable services that communicate over a network, focusing on scalability, fault isolation, and technology heterogeneity. Key differences include deployment scope--modules run as part of the same process, whereas microservices operate as separate processes--and operational management, where microservices require complex orchestration tools unlike simpler modular systems.
Advantages of Modular Architecture
Modular architecture enhances system maintainability by breaking down complex software into manageable, reusable components, which accelerates development and simplifies debugging processes. It promotes flexibility, allowing teams to update or replace individual modules without impacting the entire system, reducing downtime and deployment risks. This architecture also improves collaboration across teams by defining clear module boundaries, facilitating parallel work streams and efficient resource allocation.
Benefits of Adopting Microservices
Microservices architecture enhances scalability by allowing individual services to be developed, deployed, and scaled independently, reducing system downtime and improving resource utilization. It promotes fault isolation, ensuring that failures in one microservice do not impact the entire application, thus increasing system resilience. Continuous integration and deployment become more efficient, enabling faster innovation cycles and better alignment with agile development practices.
Challenges in Implementing Modular Architecture
Implementing modular architecture poses challenges such as managing inter-module dependencies, ensuring consistent communication protocols, and maintaining modular boundaries to prevent tight coupling. Developers often face difficulties in version control and deployment coordination across multiple modules, which can slow down development cycles. Scalability can be hindered if modules are not designed with clear interfaces and independence, leading to increased complexity in testing and debugging.
Common Pitfalls in Microservices Adoption
Microservices adoption often faces challenges such as increased system complexity due to distributed services, which complicates debugging and monitoring processes. Data consistency and transaction management can become problematic since microservices typically use decentralized databases, leading to potential synchronization issues. Teams also struggle with establishing effective communication protocols and managing service dependencies, resulting in deployment delays and integration errors.
Choosing the Right Architecture for Your Project
Choosing the right architecture between modular architecture and microservices depends on project scale, complexity, and deployment needs. Modular architecture offers a structured way to organize code within a single deployable unit, ideal for smaller teams and monolithic applications. Microservices provide independent, scalable services that enhance flexibility and fault isolation, making them suitable for large, distributed systems requiring continuous integration and delivery.
Future Trends in Software Architecture
Future trends in software architecture increasingly emphasize the integration of modular architecture and microservices to enhance scalability and maintainability. Modular architecture promotes reusable, independently deployable components, while microservices focus on fine-grained services communicating via APIs, enabling continuous delivery and rapid innovation. Advances in container orchestration, service mesh technologies, and domain-driven design are driving the evolution of these architectures to support complex, distributed systems with improved resilience and agility.
Modular Architecture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com