Community Cloud offers a shared infrastructure tailored for organizations with common goals, enhancing collaboration and security while reducing costs. Its customizable features support seamless data sharing and regulatory compliance across industries such as healthcare, finance, and government. Explore this article to discover how Community Cloud can transform your organization's cloud strategy.
Table of Comparison
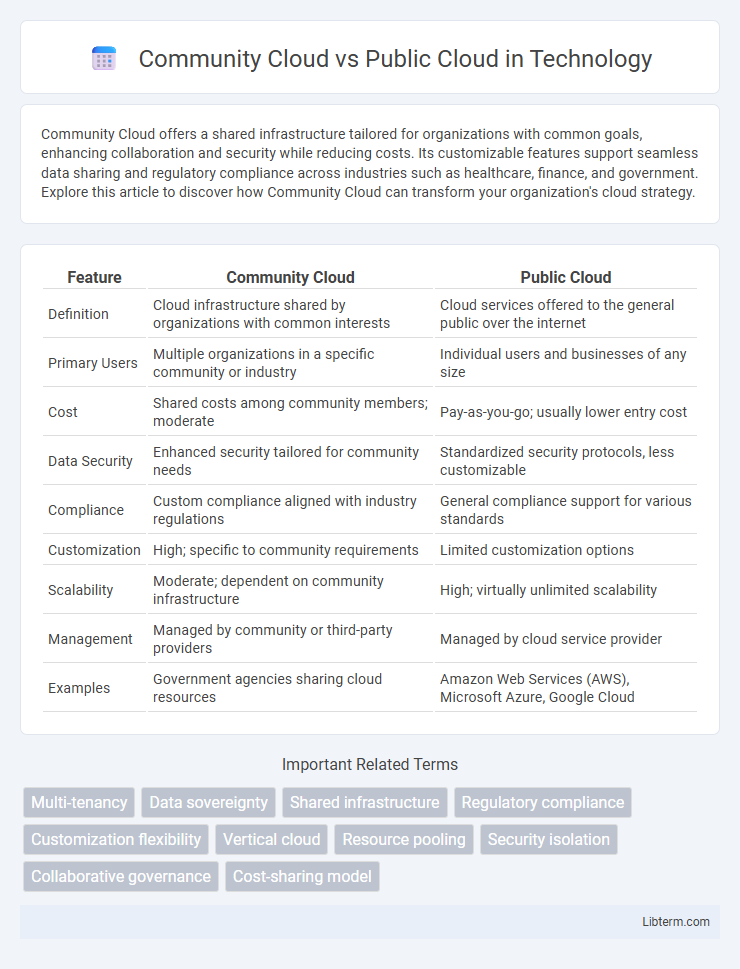
| Feature | Community Cloud | Public Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud infrastructure shared by organizations with common interests | Cloud services offered to the general public over the internet |
| Primary Users | Multiple organizations in a specific community or industry | Individual users and businesses of any size |
| Cost | Shared costs among community members; moderate | Pay-as-you-go; usually lower entry cost |
| Data Security | Enhanced security tailored for community needs | Standardized security protocols, less customizable |
| Compliance | Custom compliance aligned with industry regulations | General compliance support for various standards |
| Customization | High; specific to community requirements | Limited customization options |
| Scalability | Moderate; dependent on community infrastructure | High; virtually unlimited scalability |
| Management | Managed by community or third-party providers | Managed by cloud service provider |
| Examples | Government agencies sharing cloud resources | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud |
Introduction to Community Cloud and Public Cloud
Community Cloud is a collaborative cloud environment shared by organizations with common goals, regulatory requirements, or mission objectives, offering enhanced privacy and security tailored to sector-specific needs such as healthcare or finance. Public Cloud, provided by third-party vendors like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform, delivers scalable resources over the internet accessible to multiple customers, optimizing cost-efficiency and rapid deployment. Both models differ in control, customization, and compliance, with Community Cloud focusing on shared governance and Public Cloud emphasizing broad accessibility and elastic scaling.
Key Features of Community Cloud
Community Cloud offers a shared infrastructure tailored for organizations with common goals, ensuring enhanced collaboration, security, and compliance specific to their industry or regulatory needs. It provides customizable access controls, data sovereignty, and resource sharing among members, optimizing costs while maintaining privacy compared to Public Cloud. This environment supports collective governance and specialized workloads, making it ideal for sectors like healthcare, government, and finance requiring strict compliance and joint data management.
Key Features of Public Cloud
Public Cloud offers scalable and cost-effective infrastructure managed by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, facilitating rapid deployment and global accessibility. It provides multi-tenant environments with shared resources, enabling flexible pay-as-you-go pricing models that minimize upfront capital expenditure. Key features include automated updates, robust security protocols, extensive API integrations, and compliance certifications like ISO 27001 and GDPR.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Community Cloud offers enhanced security and compliance by restricting access to a specific group of organizations with shared regulatory requirements, making it ideal for industries like healthcare and finance that demand strict data governance and privacy controls. Public Cloud provides scalable resources but may pose challenges in meeting stringent compliance standards due to multi-tenant environments and broader access controls. Security frameworks such as HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC 2 are more easily enforced in Community Cloud settings, reducing risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access compared to typical Public Cloud deployments.
Cost Comparison: Community Cloud vs Public Cloud
Community Cloud typically involves shared infrastructure among organizations with similar needs, resulting in moderate upfront costs and predictable operational expenses; Public Cloud offers pay-as-you-go pricing with no initial investment, providing cost efficiency for scalable workloads. While Community Cloud can reduce costs through resource sharing and tailored services, Public Cloud's elasticity often leads to lower expenses for variable demand and smaller-scale users. The choice depends on workload stability, budget constraints, and compliance requirements affecting total cost of ownership.
Customization and Control
Community Cloud offers greater customization and control by allowing organizations with shared interests to tailor infrastructure, policies, and security settings to specific compliance requirements and operational needs. Public Cloud provides limited customization as resources and configurations are standardized to serve multiple unrelated users, prioritizing scalability and cost-efficiency over granular control. Enterprises requiring stringent data governance and specialized application environments often prefer Community Cloud for its enhanced ability to accommodate unique regulatory and collaboration demands.
Scalability and Performance
Community Cloud offers scalable resources shared among organizations with similar requirements, ensuring optimized performance tailored to specific industry needs. Public Cloud provides vast scalability through extensive global data centers, supporting dynamic workloads with high availability and rapid resource provisioning. Performance in Community Cloud is often more predictable due to controlled user environments, while Public Cloud excels in handling large-scale applications with variable demand and elastic resource allocation.
Ideal Use Cases for Community Cloud
Community Cloud is best suited for organizations with shared concerns such as regulatory compliance, security requirements, or collaborative projects, often seen in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government. It provides a customizable environment that supports specific industry standards and data privacy needs, enabling seamless communication and resource sharing within the community. Public Cloud, by contrast, offers broad scalability and cost efficiency for businesses seeking flexible, on-demand computing resources without the need for specialized compliance.
Ideal Use Cases for Public Cloud
Public Cloud is ideal for startups and businesses with scalable workloads that require rapid provisioning and cost-effective infrastructure without the need for extensive customization. It suits organizations prioritizing global accessibility, high scalability, and on-demand resource availability, such as e-commerce platforms, SaaS providers, and agile development teams. Enterprises leveraging Public Cloud benefit from managed services, pay-as-you-go pricing, and integration with advanced tools like AI and big data analytics.
Choosing the Right Cloud Model for Your Organization
Community Cloud offers a shared infrastructure tailored for organizations with common goals, regulatory requirements, or security concerns, ensuring enhanced collaboration and compliance. Public Cloud provides scalable, cost-effective resources managed by third-party providers, ideal for organizations seeking flexibility and broad service options without the burden of infrastructure management. Choosing the right cloud model depends on factors like data sensitivity, compliance needs, collaboration demands, and budget constraints to align IT strategies with organizational goals.
Community Cloud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com