Table replication ensures that your data is consistently duplicated across multiple database servers, enhancing availability and fault tolerance. This process supports real-time data synchronization, minimizing downtime and data loss in distributed systems. Explore the rest of the article to understand how table replication can optimize your database performance and reliability.
Table of Comparison
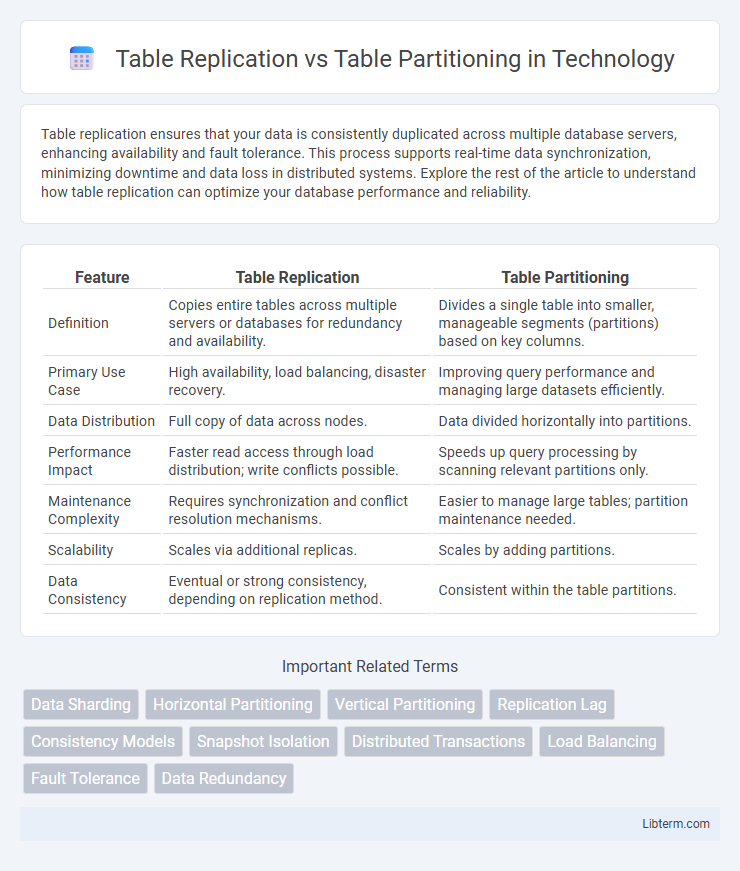
| Feature | Table Replication | Table Partitioning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Copies entire tables across multiple servers or databases for redundancy and availability. | Divides a single table into smaller, manageable segments (partitions) based on key columns. |
| Primary Use Case | High availability, load balancing, disaster recovery. | Improving query performance and managing large datasets efficiently. |
| Data Distribution | Full copy of data across nodes. | Data divided horizontally into partitions. |
| Performance Impact | Faster read access through load distribution; write conflicts possible. | Speeds up query processing by scanning relevant partitions only. |
| Maintenance Complexity | Requires synchronization and conflict resolution mechanisms. | Easier to manage large tables; partition maintenance needed. |
| Scalability | Scales via additional replicas. | Scales by adding partitions. |
| Data Consistency | Eventual or strong consistency, depending on replication method. | Consistent within the table partitions. |
Introduction to Table Replication and Table Partitioning
Table replication involves creating and maintaining exact copies of a database table across multiple servers to enhance data availability, fault tolerance, and load balancing. Table partitioning divides a large table into smaller, manageable segments called partitions, based on key ranges or columns, which improves query performance and data maintenance. Both techniques optimize database efficiency but target different operational goals: replication focuses on redundancy and distribution, while partitioning enhances manageability and access speed.
Key Concepts: What is Table Replication?
Table replication involves creating and maintaining exact copies of a database table across multiple servers or locations to ensure data availability, fault tolerance, and load balancing. Each replicated table is synchronized to reflect changes made in any copy, facilitating distributed querying and disaster recovery. This method contrasts with table partitioning, which divides a single table into smaller, manageable segments within the same database for performance optimization.
Key Concepts: What is Table Partitioning?
Table partitioning divides a large database table into smaller, manageable segments based on a partition key, improving query performance and maintenance efficiency. This technique optimizes data management by enabling faster data access, easier archiving, and selective backup processes. Partitioning types include range, list, hash, and composite partitions, tailored to specific data distribution needs.
Core Differences: Table Replication vs Table Partitioning
Table replication involves copying and maintaining identical data sets across multiple database nodes to enhance data availability and fault tolerance. Table partitioning divides a single large table into smaller, manageable segments based on a specified key, improving query performance and maintenance efficiency. Replication focuses on data redundancy and consistency across systems, while partitioning optimizes storage and access within a single database instance.
Use Cases for Table Replication
Table replication is ideal for use cases requiring high availability, disaster recovery, and load balancing across multiple geographic locations, ensuring data consistency and fault tolerance. It supports real-time data synchronization for reporting and analytics without impacting the performance of the primary database. This approach benefits distributed applications that demand low latency access to identical datasets across different nodes or data centers.
Use Cases for Table Partitioning
Table partitioning is ideal for managing large datasets by splitting tables into smaller, more manageable segments based on key columns like date or region, enhancing query performance and maintenance efficiency. It is commonly used in data warehousing, time-series data management, and scenarios requiring fast access to subsets of data for analytics or ETL processes. Partitioning reduces query latency, improves data loading speeds, and facilitates easier data archiving and purging in environments such as financial services, retail analytics, and IoT data management.
Performance Impacts: Replication vs Partitioning
Table replication improves read performance by distributing data copies across multiple nodes, enabling parallel query execution and higher availability, but may introduce write latency due to synchronization overhead. Table partitioning enhances query efficiency by dividing large datasets into smaller, manageable segments, reducing I/O and improving maintenance operations without duplicating data. Replication suits workloads with frequent read requests requiring fault tolerance, while partitioning optimizes performance for large tables with range- or key-based data access patterns.
Scalability Considerations for Each Technique
Table replication enhances scalability by distributing read workloads across multiple database instances, reducing latency and improving availability in high-traffic environments. Table partitioning improves scalability by dividing a large table into smaller, manageable segments, which accelerates query performance and simplifies maintenance by allowing operations on specific partitions. While replication scales read operations horizontally, partitioning optimizes both read and write operations by localizing data access within partitions.
Data Consistency and Maintenance Challenges
Table replication ensures data consistency by maintaining multiple synchronized copies of the entire table across different databases or servers, which simplifies read scalability but requires complex conflict resolution mechanisms during writes. Table partitioning divides a single table into smaller, manageable segments based on key ranges or hashes, improving query performance and maintenance by isolating partitions, yet it demands careful handling to maintain consistency during insert, update, or delete operations across partitions. Maintenance challenges in replication include synchronization lag and conflict detection, while partitioning involves rebalancing partitions and managing partition pruning to avoid data inconsistency and performance degradation.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Database
Table replication enhances data availability and fault tolerance by duplicating entire tables across multiple servers, ideal for read-heavy workloads and disaster recovery scenarios. Table partitioning improves query performance and manageability by dividing large tables into smaller, more manageable segments based on key values, which is beneficial for large datasets with frequent range queries. Assess your workload characteristics, data size, and consistency requirements to choose between replication for high availability and partitioning for efficient data management.
Table Replication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com