An API key is a unique identifier used to authenticate requests associated with your project for usage tracking and security purposes. It controls access to the API, ensuring only authorized users can interact with the services and helps protect against misuse or abuse. Discover more about how API keys work and how to manage them effectively by reading the rest of the article.
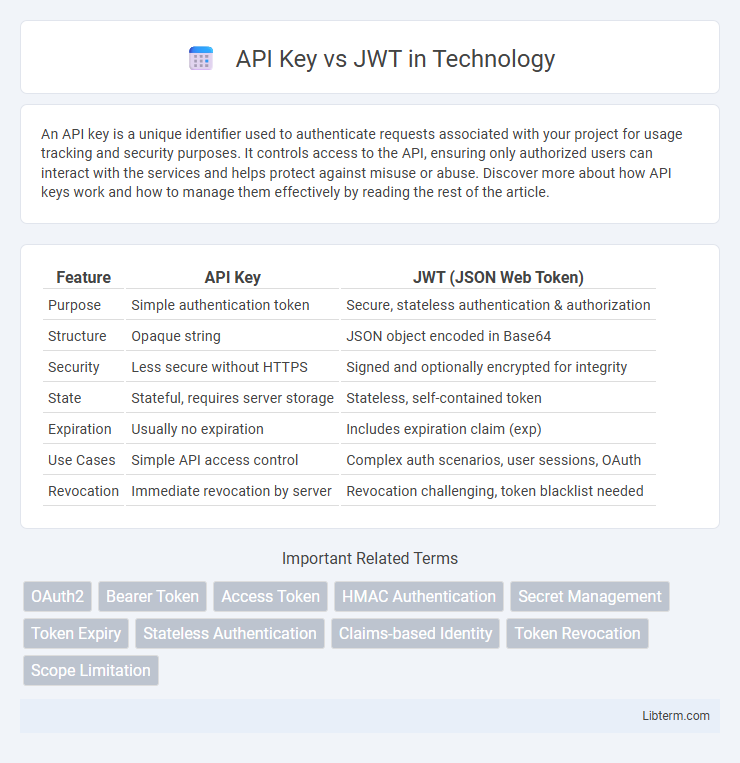
Table of Comparison
| Feature | API Key | JWT (JSON Web Token) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Simple authentication token | Secure, stateless authentication & authorization |
| Structure | Opaque string | JSON object encoded in Base64 |
| Security | Less secure without HTTPS | Signed and optionally encrypted for integrity |
| State | Stateful, requires server storage | Stateless, self-contained token |
| Expiration | Usually no expiration | Includes expiration claim (exp) |
| Use Cases | Simple API access control | Complex auth scenarios, user sessions, OAuth |
| Revocation | Immediate revocation by server | Revocation challenging, token blacklist needed |
Introduction to API Key and JWT
API Key is a simple authentication token used to identify clients accessing an API, often passed in request headers or URLs for access control. JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, self-contained token that securely transmits information between parties, including claims and user identity, enabling stateless authentication and authorization. Both methods serve to authenticate API requests, but JWT offers enhanced security and flexibility through token expiration and payload data.
What is an API Key?
An API key is a unique identifier used to authenticate a client or application accessing an API, typically a long alphanumeric string that grants access to specific resources or services. It is commonly used to track and control how the API is being used, such as monitoring usage limits and preventing unauthorized access. Unlike JWT (JSON Web Token), an API key does not carry embedded user information or claims, making it simpler but less secure for complex authentication scenarios.
What is JWT (JSON Web Token)?
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe token format used for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object, commonly utilized in authentication and authorization protocols. It consists of three parts: a header, payload, and signature, enabling verification of the token's integrity and authenticity without server-side session storage. JWTs support stateless authentication in RESTful APIs by embedding claims about the user or client, making them efficient for scalable and distributed systems.
Core Differences Between API Key and JWT
API Key and JWT differ fundamentally in security and functionality; API Keys are simple tokens used for identifying the client, whereas JWTs (JSON Web Tokens) carry encoded claims that verify user identity and permissions. API Keys lack inherent expiration and cannot convey user roles or scopes, making them less secure compared to JWTs, which have embedded expiration times and support granular access control. JWTs enable stateless authentication with trust established by a signature, while API Keys primarily serve as static credentials without built-in mechanisms for validation or revocation.
Security Considerations: API Key vs JWT
API keys provide a simple authentication method but lack granular control and can be vulnerable to interception or misuse if not stored securely. JWTs (JSON Web Tokens) enhance security by embedding claims and expiration information, enabling stateless authentication with signature verification to prevent tampering. Proper implementation of JWTs includes securing the signing secret and using HTTPS to mitigate token theft and replay attacks, making them more robust for complex security requirements.
Use Cases: When to Use API Key vs JWT
API keys are best suited for simple access control in server-to-server communication or services where user identity verification is not critical. JWTs excel in scenarios requiring secure, stateless authentication with embedded user claims and role-based access control, such as user login systems and microservices architecture. Use API keys for limited permission access and straightforward API consumption; choose JWTs for complex authentication workflows demanding scalability and token expiration management.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
API keys offer simplicity and faster validation since they are static tokens, resulting in lower latency for each request, which suits low-latency, high-throughput environments. JWTs contain embedded user data and claims, enabling stateless authentication and reducing server-side session storage requirements, which improves scalability in distributed systems. However, JWT verification involves cryptographic checks that introduce slightly higher computational overhead compared to straightforward API key validation.
Implementation Best Practices
API keys should be stored securely in environment variables and transmitted over HTTPS to prevent interception, with usage limited by scopes and expiry times for enhanced security. JWTs require robust signing algorithms like RS256 and careful management of token expiration and refresh mechanisms to maintain authentication integrity. Implementing role-based access control and validating tokens on every API request ensures both API key and JWT methods uphold secure and efficient authentication practices.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes to avoid when using API keys include exposing them in client-side code or repositories, leading to unauthorized access and security breaches. JWTs are often misused by not validating token signatures properly or neglecting to implement token expiration, resulting in potential token forgery and session hijacking. Ensure API keys are rotated regularly and JWTs are securely signed with robust algorithms like RS256 to maintain optimal access control and data integrity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Authentication Method
API keys offer simple, static credentials suited for basic authentication and limited access control, making them ideal for less complex applications. JWTs provide secure, scalable authentication with embedded user claims and expiration, enabling fine-grained authorization and stateless sessions for dynamic, distributed systems. Selecting between API key and JWT depends on the application's security requirements, complexity, and need for detailed user context.
API Key Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com