An Organization Validation Certificate (OV) confirms your business's legitimacy by verifying its identity through official documents, enhancing trust for website visitors. OV certificates enable strong encryption, ensuring secure data exchange between you and your users. Discover how utilizing an OV certificate can protect your online presence and boost customer confidence in the full article.
Table of Comparison
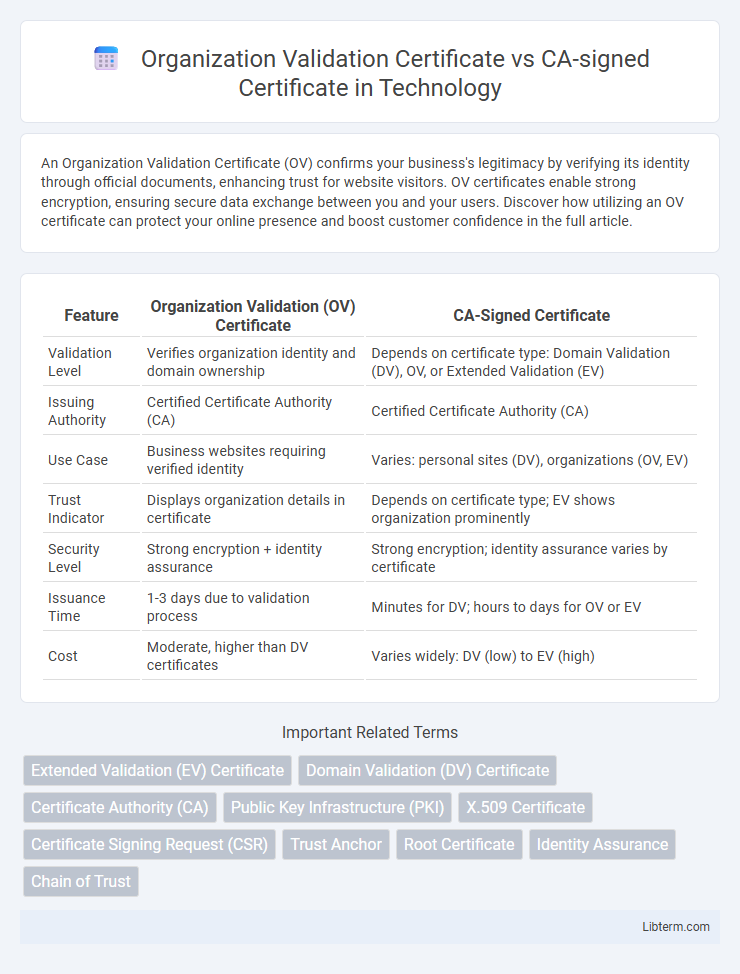
| Feature | Organization Validation (OV) Certificate | CA-Signed Certificate |
|---|---|---|
| Validation Level | Verifies organization identity and domain ownership | Depends on certificate type: Domain Validation (DV), OV, or Extended Validation (EV) |
| Issuing Authority | Certified Certificate Authority (CA) | Certified Certificate Authority (CA) |
| Use Case | Business websites requiring verified identity | Varies: personal sites (DV), organizations (OV, EV) |
| Trust Indicator | Displays organization details in certificate | Depends on certificate type; EV shows organization prominently |
| Security Level | Strong encryption + identity assurance | Strong encryption; identity assurance varies by certificate |
| Issuance Time | 1-3 days due to validation process | Minutes for DV; hours to days for OV or EV |
| Cost | Moderate, higher than DV certificates | Varies widely: DV (low) to EV (high) |
Introduction to Organization Validation Certificates
Organization Validation (OV) Certificates provide an intermediate level of security by verifying the legitimacy of the organization behind a website, ensuring that the business is a legally registered entity. These certificates require a Certificate Authority (CA) to perform rigorous checks on the organization's identity, offering users assurance that the website is trustworthy beyond simple domain control verification. OV certificates are preferred by businesses seeking to establish credibility and enhance customer confidence without the extensive vetting process of Extended Validation (EV) certificates.
What is a CA-Signed Certificate?
A CA-signed certificate is a digital certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) that verifies the authenticity of a website or organization by confirming its ownership and enabling secure HTTPS connections. Unlike self-signed certificates, CA-signed certificates are widely recognized by browsers, ensuring trust and preventing security warnings for users. These certificates use public key infrastructure (PKI) to encrypt data and provide identity validation at various levels, including Domain Validation (DV), Organization Validation (OV), and Extended Validation (EV).
Key Features of Organization Validation Certificates
Organization Validation (OV) Certificates provide a higher level of trust by verifying the organization's identity through government business registry checks and operational existence validation. OV certificates include detailed organizational information in the certificate, such as the company's name, physical address, and domain ownership, enhancing credibility with users. These certificates utilize stronger encryption standards and offer secure, authenticated connections, making them ideal for businesses requiring verified legitimacy without the extensive vetting of Extended Validation (EV) certificates.
Characteristics of CA-Signed Certificates
CA-signed certificates are issued by trusted Certificate Authorities after verifying the applicant's identity, ensuring a higher level of trust and security for online transactions. These certificates provide encryption, authentication, and data integrity, crucial for websites handling sensitive information like e-commerce platforms and financial services. The validation process involves rigorous checks, making CA-signed certificates essential for establishing user confidence and compliance with industry standards.
Validation Process: OV vs CA-Signed Certificates
Organization Validation (OV) Certificates require thorough verification of the organization's identity, including legal, physical, and operational existence checks, ensuring that the entity requesting the certificate is legitimate. CA-signed Certificates, often referring to Domain Validation (DV) certificates, primarily validate control over the domain via email or DNS verification without extensive organizational scrutiny. The OV process offers a higher trust level by confirming an organization's authenticity, whereas CA-signed DV certificates provide faster issuance but limited assurance about the organization's identity.
Security Benefits Comparison
Organization Validation (OV) Certificates provide enhanced security by verifying the organization's identity through rigorous vetting, reducing the risk of phishing and man-in-the-middle attacks. CA-signed certificates, including Domain Validation (DV) certificates, authenticate domain ownership but lack the robust organizational verification, offering a lower level of trust for users. OV certificates ensure visitors receive clear information about the business entity, increasing confidence and mitigating social engineering threats more effectively than standard CA-signed certificates.
Trust Levels: OV Certificates vs CA-Signed Certificates
Organization Validation (OV) certificates provide a higher trust level than standard CA-signed certificates by verifying the organization's identity through thorough vetting processes. CA-signed certificates without OV validation primarily ensure domain ownership but do not authenticate the organization behind the website, offering limited trust assurance. OV certificates display verified company information in the certificate details, enhancing user confidence and reducing the risk of phishing attacks.
Use Cases and Applications
Organization Validation (OV) certificates are ideal for businesses seeking to establish verified identity and trustworthiness on websites handling sensitive transactions, such as e-commerce platforms and customer portals. CA-signed certificates, including Domain Validation (DV) and Extended Validation (EV) certificates, cater to a range of applications from personal blogs to large enterprises requiring enhanced security assurance and brand recognition. OV certificates provide moderate validation, suitable for organizations handling moderate-risk data, while CA-signed certificates vary in validation levels to match use cases from basic encryption to stringent identity verification in regulated industries.
Cost and Maintenance Differences
Organization Validation (OV) Certificates typically cost more than standard CA-signed Domain Validation (DV) Certificates due to the additional validation process verifying the organization's identity. Maintenance for OV Certificates involves periodic re-validation of the business details, which can increase administrative workload and renewal complexity compared to CA-signed DV Certificates that require minimal upkeep. Choosing OV Certificates enhances trust with extended validation but demands higher expenses and ongoing management compared to the relatively low-cost, low-maintenance nature of CA-signed DV Certificates.
Choosing the Right Certificate for Your Organization
Choosing the right certificate between an Organization Validation (OV) Certificate and a CA-signed Certificate depends on the level of trust and validation your organization requires; OV Certificates provide verified business identity to users and are ideal for organizations seeking to establish credibility without the higher cost and longer issuance time of Extended Validation (EV) Certificates. CA-signed Certificates offer a broad range of validation levels, including domain validation (DV), OV, and EV, allowing organizations to select certificates that match their security needs and budget while benefiting from recognition by all major browsers. Evaluate factors such as the desired assurance level, user trust, and compliance requirements to determine the optimal certificate type that aligns with your organization's security strategy.
Organization Validation Certificate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com