Latency refers to the delay between a user's action and a system's response, critically affecting performance in gaming, streaming, and real-time communications. Lower latency enhances user experience by providing faster, more seamless interactions, essential for applications requiring instant feedback. Explore this article to understand how latency impacts your digital activities and ways to minimize it effectively.
Table of Comparison
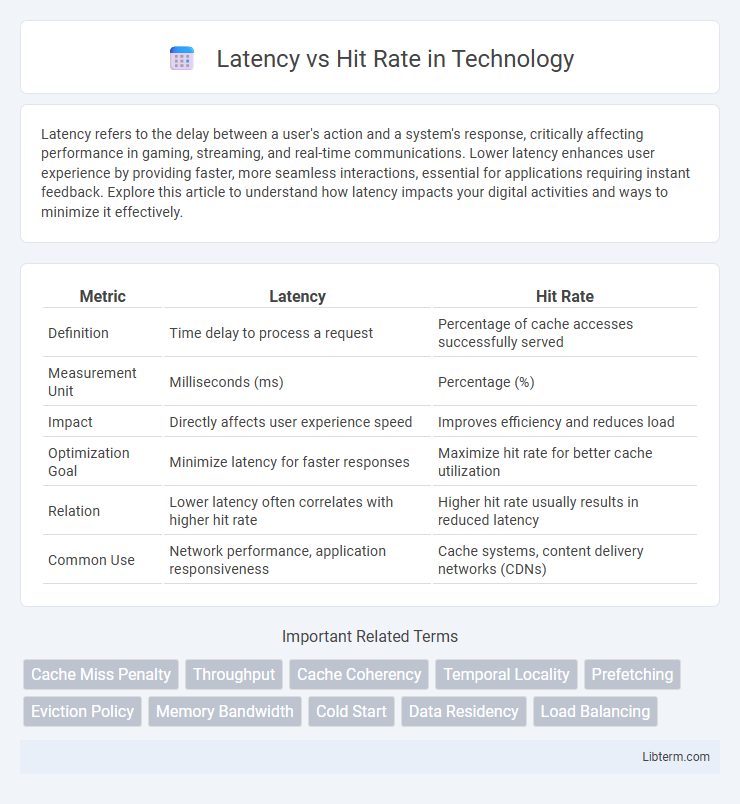
| Metric | Latency | Hit Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Time delay to process a request | Percentage of cache accesses successfully served |
| Measurement Unit | Milliseconds (ms) | Percentage (%) |
| Impact | Directly affects user experience speed | Improves efficiency and reduces load |
| Optimization Goal | Minimize latency for faster responses | Maximize hit rate for better cache utilization |
| Relation | Lower latency often correlates with higher hit rate | Higher hit rate usually results in reduced latency |
| Common Use | Network performance, application responsiveness | Cache systems, content delivery networks (CDNs) |
Understanding Latency in Computing
Latency in computing refers to the time delay between a request and the corresponding response, significantly impacting system performance and user experience. Hit rate measures how often requested data is found in a cache, directly affecting latency by reducing access times when the hit rate is high. Optimizing cache hit rates lowers latency, enhancing overall speed and efficiency in memory-intensive applications.
Defining Hit Rate in Caching Systems
Hit rate in caching systems measures the percentage of data requests successfully served from the cache without accessing the slower primary storage. High hit rates reduce latency by minimizing the time needed to retrieve data, enhancing overall system performance. Optimizing hit rate involves balancing cache size, replacement policies, and workload characteristics to maintain efficient data accessibility.
The Relationship Between Latency and Hit Rate
Latency and hit rate are inversely related in caching systems, where a higher hit rate significantly reduces latency by serving more requests from faster cache memory instead of slower main storage. Improving hit rate through optimized cache algorithms or increased cache size decreases the average access time and boosts system performance. Monitoring the hit rate helps predict latency trends, enabling targeted interventions to minimize delays and enhance responsiveness.
Factors Affecting Latency
Latency is influenced by cache hit rate, where a higher hit rate reduces the need to access slower memory layers, significantly lowering response time. Factors affecting latency include cache size, block size, and associativity, which determine how efficiently data is stored and retrieved. Memory hierarchy design, access patterns, and workload characteristics also play critical roles in shaping overall latency performance.
Factors Influencing Hit Rate
Cache hit rate is influenced primarily by factors such as cache size, block size, and replacement policies. Larger cache sizes typically increase hit rates by accommodating more data, while optimal block sizes reduce miss penalties by fetching relevant adjacent data. Replacement policies like Least Recently Used (LRU) or First-In-First-Out (FIFO) critically affect the retention of frequently accessed data, thereby maximizing cache efficiency and reducing latency.
Impact of Low Hit Rate on Latency
A low hit rate significantly increases latency by causing more frequent accesses to slower memory levels or disk storage, resulting in longer data retrieval times. Cache inefficiencies force the system to bypass fast cache memory and rely on main memory or even secondary storage, which dramatically slows down response time. Optimizing hit rate is crucial for minimizing latency and ensuring high system performance in memory hierarchy architectures.
Strategies to Improve Hit Rate
Improving cache hit rates involves optimizing data locality through techniques such as prefetching frequently accessed data and implementing adaptive caching algorithms like Least Recently Used (LRU) or Least Frequently Used (LFU). Employing multi-level cache hierarchies and fine-tuning cache size and associativity can significantly reduce cache misses and latency. Monitoring workload patterns and dynamically adjusting cache policies enhance hit rate efficiency, resulting in improved overall system performance.
Techniques for Reducing Latency
Techniques for reducing latency in cache systems include implementing prefetching algorithms that predict and load data before it is requested, thereby decreasing access time. Using multi-level caches with optimized hit rates ensures frequently accessed data is available closer to the processor, significantly cutting down retrieval delays. Employing adaptive replacement policies such as Least Recently Used (LRU) or machine learning-based predictors can fine-tune cache performance by maximizing hit rate and minimizing latency in real-time.
Balancing Latency and Hit Rate for Optimal Performance
Balancing latency and hit rate is crucial for optimizing cache performance, enabling faster data retrieval while minimizing resource consumption. High hit rates reduce the need for time-consuming data fetches from the main storage, directly lowering latency and improving system responsiveness. Tuning cache size and eviction policies helps maintain an equilibrium where latency is minimized without sacrificing a high hit rate, ensuring efficient workload handling.
Real-World Applications: Latency vs Hit Rate
In real-world applications, latency directly impacts user experience by determining the response time of data retrieval systems, while hit rate measures the efficiency of cache performance in delivering requested data. High hit rates in caching systems reduce latency by minimizing the need to access slower storage layers, thus improving application speed and responsiveness. Balancing latency and hit rate is crucial for optimizing performance in content delivery networks, databases, and web services where timely data access is essential.
Latency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com