Logical delete preserves data by marking records as inactive instead of physically removing them from the database, ensuring data integrity and auditability. This approach enhances system reliability, allows for easy data recovery, and supports compliance with regulatory requirements. Explore the full article to understand how implementing logical delete can benefit your data management strategy.
Table of Comparison
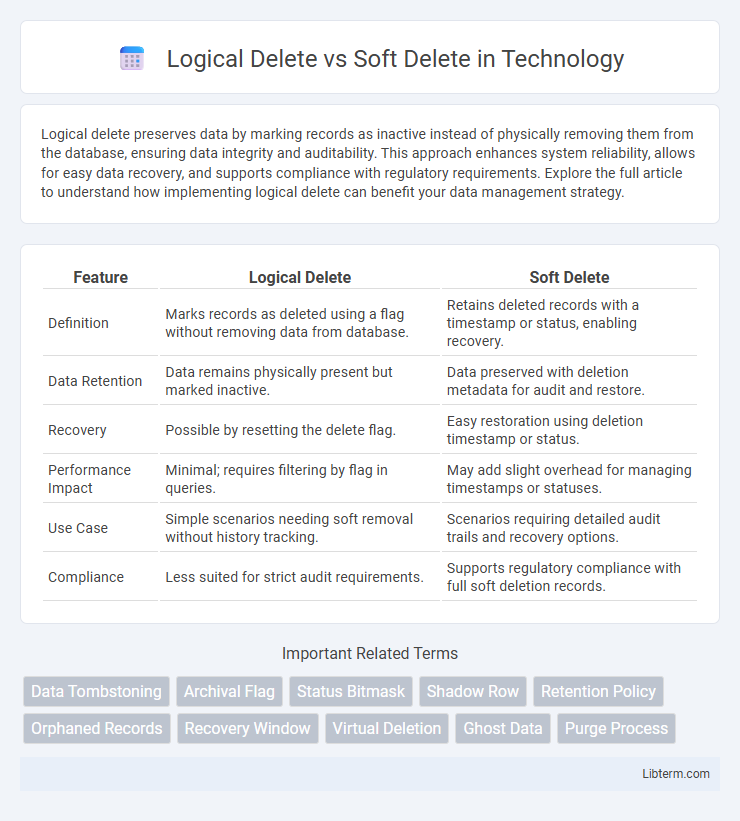
| Feature | Logical Delete | Soft Delete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marks records as deleted using a flag without removing data from database. | Retains deleted records with a timestamp or status, enabling recovery. |
| Data Retention | Data remains physically present but marked inactive. | Data preserved with deletion metadata for audit and restore. |
| Recovery | Possible by resetting the delete flag. | Easy restoration using deletion timestamp or status. |
| Performance Impact | Minimal; requires filtering by flag in queries. | May add slight overhead for managing timestamps or statuses. |
| Use Case | Simple scenarios needing soft removal without history tracking. | Scenarios requiring detailed audit trails and recovery options. |
| Compliance | Less suited for strict audit requirements. | Supports regulatory compliance with full soft deletion records. |
Introduction to Logical Delete vs Soft Delete
Logical delete and soft delete are data management techniques used to mark records as deleted without physically removing them from the database. Logical delete typically involves setting a flag or status indicating the record is inactive, enabling easy recovery and auditing. Soft delete extends this by preserving the data for longer-term retention, often incorporating additional metadata such as deletion timestamp and user information for comprehensive data lifecycle tracking.
Definition of Logical Delete
Logical delete refers to the process of marking a record as deleted in a database without physically removing it, often by setting a flag or status attribute. This method preserves the data for auditing, recovery, or historical purposes while preventing it from appearing in regular queries. Logical delete contrasts with soft delete, which may involve additional mechanisms like archiving or moving data to a separate storage area.
Definition of Soft Delete
Soft Delete is a data management technique where records are marked as deleted without physically removing them from the database, preserving data integrity and enabling easy recovery. Logical Delete shares similarities but often refers to a broader concept of flagging data as inactive or hidden instead of permanently erasing it. This approach supports audit trails, compliance requirements, and minimizes accidental data loss by maintaining historical records.
Key Differences Between Logical and Soft Delete
Logical delete marks data as inactive or hidden by setting a status flag without removing the record from the database, preserving the original data for auditing or recovery. Soft delete often involves moving the data to a separate storage or marking it with a deletion timestamp, enabling easier restoration while keeping the data out of active queries. Key differences include logical delete relying primarily on status flags within the same table, whereas soft delete may utilize either flags or separate archival storage, influencing recovery processes and query performance.
Use Cases for Logical Delete
Logical delete is ideal for audit-sensitive applications where retaining historical data is crucial, such as financial systems and compliance tracking. It enables record visibility to authorized users without permanently removing data, supporting data recovery and regulatory reporting. Use cases include order management systems and healthcare records where tracking changes without data loss ensures transparency and integrity.
Use Cases for Soft Delete
Soft delete is essential in applications requiring data recovery and auditing, allowing records to be marked as deleted without permanent removal from the database. Common use cases include user management systems where accounts can be temporarily deactivated, e-commerce platforms retaining order histories for customer service, and content management systems preserving article versions for compliance purposes. This approach enhances data integrity and provides flexibility for restoring unintended deletions while maintaining audit trails.
Advantages of Logical Delete
Logical delete offers significant advantages by preserving data integrity and enabling easy audit trails, as records remain in the database with status indicators rather than being physically removed. This approach improves compliance with data retention policies and facilitates recovery of accidentally deleted information without complex restoration procedures. Businesses benefit from enhanced data analytics and historical reporting since logical deletion maintains complete datasets over time.
Advantages of Soft Delete
Soft delete preserves data by marking records as inactive rather than removing them, enabling easy recovery and audit trails. This approach enhances data integrity and supports compliance with regulatory requirements by retaining historical information. Soft delete also improves application stability by preventing accidental data loss and facilitating seamless rollback operations.
Best Practices for Implementing Deletion Strategies
Best practices for implementing deletion strategies emphasize using soft delete to preserve data integrity and enable recovery by marking records as inactive rather than removing them physically. Logical delete, often implemented via flags or status fields, allows for audit trails and complies with regulatory data retention requirements, minimizing accidental data loss. Ensuring proper indexing on deletion indicators and incorporating cleanup routines for archiving or purging outdated data optimizes system performance and maintains data relevance.
Choosing the Right Deletion Method for Your Application
Choosing the right deletion method for your application depends on data retention requirements and performance considerations; logical delete marks records as inactive without removing them, enabling easy recovery and audit trails, while soft delete typically involves hiding data without physical deletion. Applications requiring historical tracking or regulatory compliance benefit from logical deletes, whereas soft deletes suit scenarios prioritizing user experience with minimal data exposure. Evaluating factors such as database size, query performance, and compliance policies helps determine the optimal approach for managing deleted data.
Logical Delete Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com