Cloud computing offers scalable and flexible resources that empower businesses to deploy applications and store data efficiently without heavy upfront investments. With enhanced security measures and global accessibility, cloud solutions optimize operational workflows and enable seamless collaboration. Explore the full article to understand how cloud computing can transform your business infrastructure and drive innovation.
Table of Comparison
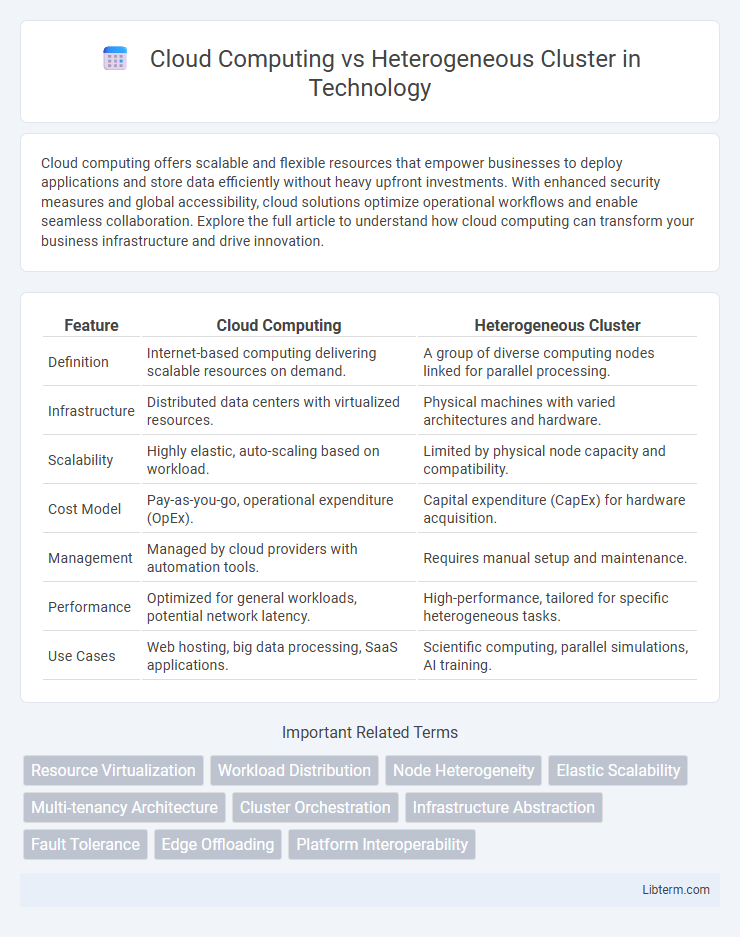
| Feature | Cloud Computing | Heterogeneous Cluster |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internet-based computing delivering scalable resources on demand. | A group of diverse computing nodes linked for parallel processing. |
| Infrastructure | Distributed data centers with virtualized resources. | Physical machines with varied architectures and hardware. |
| Scalability | Highly elastic, auto-scaling based on workload. | Limited by physical node capacity and compatibility. |
| Cost Model | Pay-as-you-go, operational expenditure (OpEx). | Capital expenditure (CapEx) for hardware acquisition. |
| Management | Managed by cloud providers with automation tools. | Requires manual setup and maintenance. |
| Performance | Optimized for general workloads, potential network latency. | High-performance, tailored for specific heterogeneous tasks. |
| Use Cases | Web hosting, big data processing, SaaS applications. | Scientific computing, parallel simulations, AI training. |
Introduction to Cloud Computing and Heterogeneous Clusters
Cloud computing delivers on-demand access to shared computing resources, enabling scalable storage, processing power, and software services over the internet with minimal management effort. Heterogeneous clusters consist of interconnected computers with diverse hardware architectures and varying performance capabilities, optimized for specific workloads by leveraging different processor types and accelerators. Understanding the fundamentals of cloud computing highlights its flexibility and scalability, while heterogeneous clusters emphasize performance optimization through resource diversity.
Core Concepts: Definitions and Key Components
Cloud computing refers to delivering computing services like servers, storage, databases, and networking over the internet, enabling scalable and flexible resource access. Key components include virtualization, distributed systems, and service models such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Heterogeneous clusters consist of interconnected computers with diverse hardware architectures or operating systems working collaboratively, emphasizing high-performance computing and resource optimization through coordination of CPUs, GPUs, and specialized accelerators.
Architecture Comparison: Cloud vs Heterogeneous Cluster
Cloud computing architecture relies on virtualized resources distributed across multiple data centers, enabling scalable and flexible on-demand services. Heterogeneous cluster architecture integrates diverse hardware components, such as CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs, tightly coupled to optimize performance for specialized workloads. The cloud offers abstraction and elasticity through software-defined infrastructure, whereas heterogeneous clusters emphasize hardware-level customization and parallel processing efficiency.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Cloud computing offers elastic scalability and on-demand resource provisioning, enabling dynamic performance adjustments based on workload requirements. Heterogeneous clusters, composed of diverse hardware architectures, provide optimized performance for specialized tasks but require complex workload scheduling to balance computational capabilities. Evaluating performance and scalability involves assessing cloud's flexibility against heterogeneous clusters' tailored efficiency for specific applications.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
Cloud computing offers scalable and flexible resource allocation, enabling cost-efficient pay-as-you-go models that minimize upfront infrastructure expenses. Heterogeneous clusters allow for tailored hardware utilization, optimizing performance by combining diverse processors and accelerators to match specific workloads. Organizations achieve superior resource optimization by leveraging cloud elasticity for variable demand while using heterogeneous clusters to maximize computational efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Flexibility and Customization Capabilities
Cloud computing offers high flexibility through scalable resources and on-demand services, enabling quick adaptation to varying workloads without physical infrastructure changes. Heterogeneous clusters provide advanced customization by integrating diverse hardware components tailored for specific computational tasks, optimizing performance for specialized applications. Combining cloud elasticity with heterogeneous cluster customization allows organizations to achieve both dynamic resource allocation and precise hardware optimization.
Security and Compliance Differences
Cloud computing often relies on multi-tenant architectures with centralized security controls, offering comprehensive compliance certifications such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR to ensure data protection. Heterogeneous clusters, composed of diverse hardware and software environments, present unique security challenges due to inconsistent patching and varied security policies, making compliance management more complex and fragmented. While cloud providers invest heavily in automated compliance monitoring and advanced encryption, heterogeneous clusters require customized security frameworks and manual audits to meet regulatory standards.
Typical Use Cases and Industry Applications
Cloud computing excels in scalable web services, big data analytics, and on-demand application hosting across industries such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce due to its elastic resource allocation and cost efficiency. Heterogeneous clusters, leveraging diverse hardware like CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs, are typically employed for scientific simulations, machine learning training, and high-performance computing tasks in sectors including aerospace, automotive, and life sciences. Both paradigms address computational demands differently, with cloud computing favoring flexibility and global accessibility, while heterogeneous clusters emphasize performance optimization and specialized workloads.
Deployment and Management Challenges
Cloud computing offers scalable deployment with centralized management through automated orchestration tools, reducing operational complexity and enabling rapid resource provisioning. In contrast, heterogeneous clusters present deployment challenges due to diverse hardware architectures requiring specialized configuration and tuning for compatibility and performance optimization. Managing heterogeneous clusters demands sophisticated monitoring and workload scheduling to handle variability in processing capabilities, whereas cloud platforms provide unified dashboards and APIs that simplify resource allocation and maintenance.
Future Trends and Evolving Technologies
Cloud computing is advancing with the integration of edge computing, serverless architectures, and AI-driven resource management, enhancing scalability and real-time processing capabilities. Heterogeneous clusters evolve by incorporating diverse hardware accelerators such as GPUs, FPGAs, and TPUs to optimize performance for specialized workloads, particularly in AI and big data analytics. Future trends include seamless interoperability between cloud infrastructures and heterogeneous clusters, enabling hybrid environments that maximize computational efficiency and energy consumption.
Cloud Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com