Service scalability ensures your business can efficiently handle increased workloads without compromising performance or quality. Implementing scalable systems allows seamless growth and adaptability to fluctuating customer demands. Explore the rest of this article to discover strategies for optimizing service scalability in your organization.
Table of Comparison
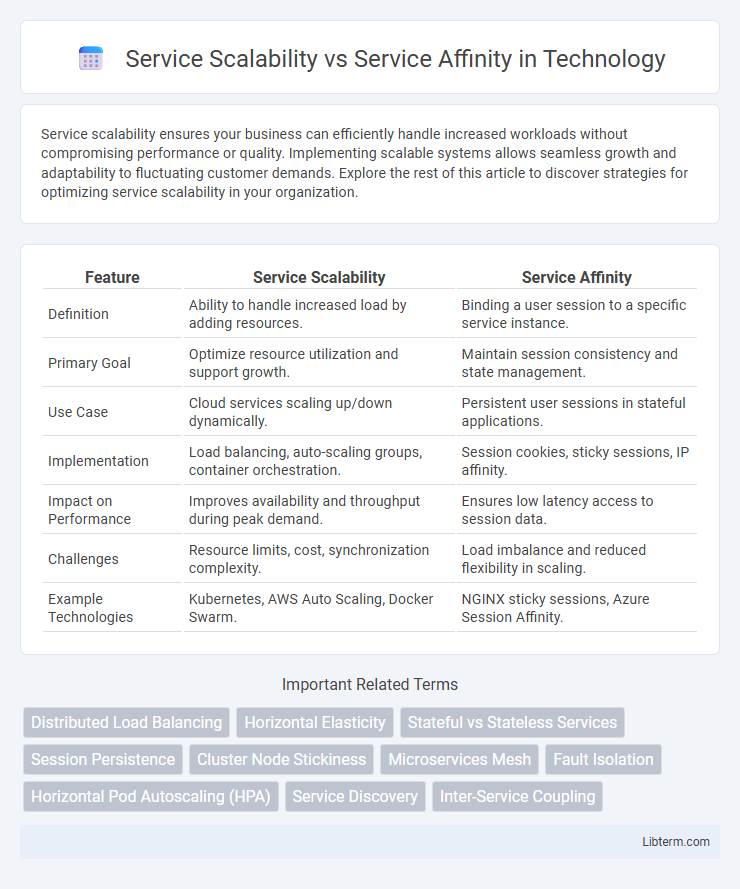
| Feature | Service Scalability | Service Affinity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to handle increased load by adding resources. | Binding a user session to a specific service instance. |
| Primary Goal | Optimize resource utilization and support growth. | Maintain session consistency and state management. |
| Use Case | Cloud services scaling up/down dynamically. | Persistent user sessions in stateful applications. |
| Implementation | Load balancing, auto-scaling groups, container orchestration. | Session cookies, sticky sessions, IP affinity. |
| Impact on Performance | Improves availability and throughput during peak demand. | Ensures low latency access to session data. |
| Challenges | Resource limits, cost, synchronization complexity. | Load imbalance and reduced flexibility in scaling. |
| Example Technologies | Kubernetes, AWS Auto Scaling, Docker Swarm. | NGINX sticky sessions, Azure Session Affinity. |
Understanding Service Scalability
Service scalability refers to the ability of a system or application to handle increasing workloads by efficiently allocating resources such as CPU, memory, and network bandwidth. It involves horizontal scaling, which adds more instances or nodes, and vertical scaling, which upgrades hardware capacity to maintain consistent performance under growing demand. Effective service scalability ensures high availability, reduces latency, and supports seamless user experiences during traffic spikes or business growth.
Defining Service Affinity
Service affinity refers to the design principle where client requests consistently interact with the same service instance, ensuring session persistence and stateful interactions. This approach improves user experience by maintaining context and reducing latency but can limit scalability by creating bottlenecks on specific instances. Understanding service affinity helps balance load distribution and resource allocation for optimized service performance.
Key Differences Between Scalability and Affinity
Service scalability refers to the system's ability to handle increasing workloads by adding resources, ensuring performance consistency under high demand. Service affinity denotes the preference or requirement for a client's requests to be directed to the same server or instance, maintaining session continuity. The key difference lies in scalability focusing on resource adaptability and load management, whereas affinity emphasizes session persistence and user-specific routing.
Importance of Scalability in Modern Architectures
Service scalability ensures that applications efficiently handle increased loads by dynamically allocating resources, which is crucial for maintaining performance and cost-effectiveness in cloud-native and microservices architectures. In contrast, service affinity, where requests are consistently routed to the same server or instance, can limit flexibility and scalability by creating bottlenecks and single points of failure. Emphasizing scalability allows modern systems to achieve high availability, fault tolerance, and seamless user experiences regardless of fluctuating demand.
Role of Affinity in Service Deployment
Service affinity plays a crucial role in service deployment by ensuring that specific workloads consistently interact with designated instances, optimizing resource allocation and improving performance through reduced latency. This localized binding supports efficient state management and session persistence, which is essential for applications requiring continuous context awareness. While service scalability emphasizes distributing workloads across multiple instances, affinity prioritizes stability and reliability by maintaining session proximity within the deployment environment.
Benefits of Highly Scalable Services
Highly scalable services enable systems to handle increased workloads efficiently by dynamically distributing resources and balancing traffic, ensuring consistent performance under varying demand. These services improve fault tolerance and availability by allowing seamless resource addition or removal without downtime. Scalability reduces operational costs and enhances customer satisfaction by supporting growth and maintaining responsiveness across diverse environments.
Challenges Caused by Service Affinity
Service affinity creates challenges in scalability by binding user sessions to specific servers, leading to uneven load distribution and resource bottlenecks. This dependency complicates failover and maintenance processes, as traffic cannot be easily rerouted without disrupting ongoing sessions. Consequently, service affinity increases latency and reduces overall system resilience during peak demand or hardware failure.
Strategies to Balance Scalability and Affinity
Strategies to balance service scalability and service affinity involve dynamic load balancing techniques that distribute client requests while maintaining session consistency through affinity cookies or token-based mechanisms. Employing stateless service designs combined with session replication or centralized session stores enhances scalability without sacrificing affinity. Leveraging container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes ensures efficient scaling and affinity management by automatically rescheduling pods based on affinity rules and resource availability.
Best Practices for Scalable and Affinity-aware Services
Service scalability requires designing stateless components and leveraging load balancers to distribute traffic evenly, ensuring consistent performance under increased demand. Service affinity demands session persistence techniques, such as sticky sessions or affinity tokens, to route requests to the same backend instance for stateful interactions. Best practices combine auto-scaling groups with intelligent service discovery to maintain responsiveness while honoring affinity constraints for user sessions.
Future Trends in Service Scalability and Affinity
Future trends in service scalability emphasize automated elasticity through AI-driven resource allocation, enabling systems to dynamically adjust capacity based on real-time demand patterns. Service affinity is evolving with microservices architectures adopting context-aware affinity models that maintain session persistence while facilitating load balancing and fault tolerance. Emerging technologies such as edge computing and 5G networks further enhance scalability and affinity by reducing latency and enabling localized service affinity for improved user experience.
Service Scalability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com