Load balancing efficiently distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed, enhancing reliability and performance. It improves response times and increases the availability of your services by preventing bottlenecks and server failures. Explore the rest of the article to understand how implementing effective load balancing can optimize your infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
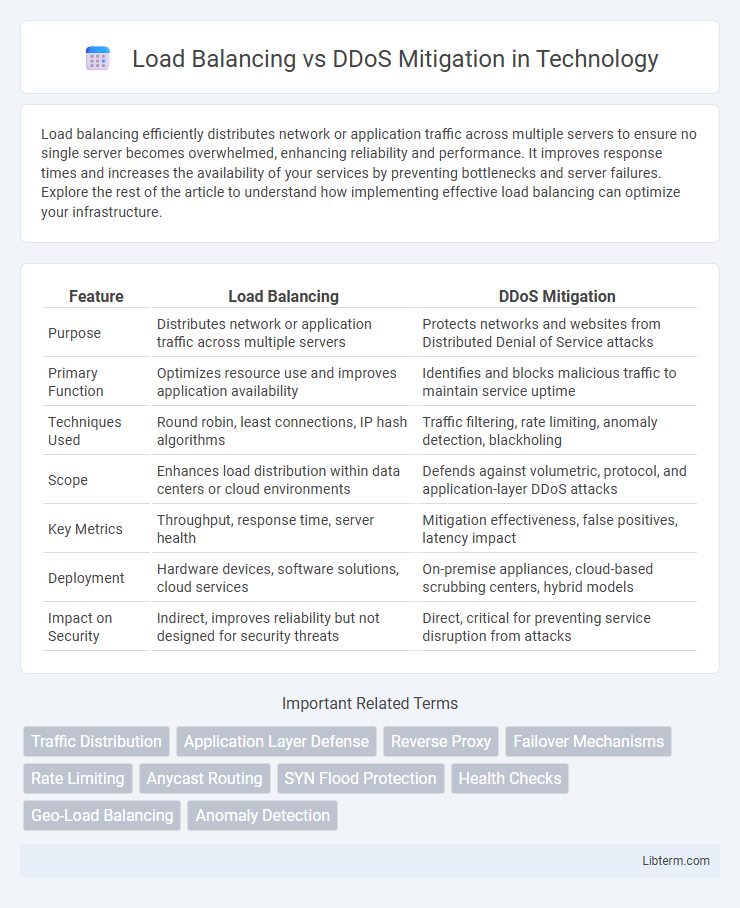
| Feature | Load Balancing | DDoS Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers | Protects networks and websites from Distributed Denial of Service attacks |
| Primary Function | Optimizes resource use and improves application availability | Identifies and blocks malicious traffic to maintain service uptime |
| Techniques Used | Round robin, least connections, IP hash algorithms | Traffic filtering, rate limiting, anomaly detection, blackholing |
| Scope | Enhances load distribution within data centers or cloud environments | Defends against volumetric, protocol, and application-layer DDoS attacks |
| Key Metrics | Throughput, response time, server health | Mitigation effectiveness, false positives, latency impact |
| Deployment | Hardware devices, software solutions, cloud services | On-premise appliances, cloud-based scrubbing centers, hybrid models |
| Impact on Security | Indirect, improves reliability but not designed for security threats | Direct, critical for preventing service disruption from attacks |
Understanding Load Balancing: Definition and Purpose
Load balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure optimal resource use, minimize response time, and avoid server overload. It enhances system reliability by preventing any single server from becoming a bottleneck and supports scalability in handling increased traffic volumes. Unlike DDoS mitigation, which specifically targets and blocks malicious traffic, load balancing optimizes performance and availability in normal operational conditions.
What is DDoS Mitigation? Core Concepts Explained
DDoS mitigation refers to the process and techniques used to protect networks and servers from Distributed Denial of Service attacks, which aim to overwhelm resources and disrupt normal traffic. Core concepts include traffic filtering, rate limiting, and anomaly detection to identify and block malicious traffic while allowing legitimate requests. In contrast to load balancing, which distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use and prevent overload, DDoS mitigation specifically targets security threats to maintain service availability under attack conditions.
Key Differences Between Load Balancing and DDoS Mitigation
Load balancing distributes network traffic evenly across multiple servers to optimize resource use, enhance performance, and ensure availability, while DDoS mitigation specifically focuses on detecting and blocking malicious traffic aimed at overwhelming and disrupting services. Load balancing primarily addresses normal traffic management to prevent server overload, whereas DDoS mitigation is designed to defend against large-scale, targeted cyberattacks intended to cause service denial. The key difference lies in load balancing's role in traffic distribution versus DDoS mitigation's focus on security and attack prevention.
How Load Balancers Handle Traffic Distribution
Load balancers optimize traffic distribution by intelligently routing incoming requests across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed, ensuring high availability and improved application responsiveness. They use algorithms such as round-robin, least connections, or IP hash to evenly distribute workloads, enhancing resource utilization and minimizing latency. Unlike DDoS mitigation tools focused on identifying and blocking malicious traffic, load balancers primarily maintain performance and reliability under normal traffic loads rather than combating attack patterns.
Techniques and Strategies in DDoS Mitigation
DDoS mitigation employs techniques such as traffic filtering, rate limiting, and anomaly detection to identify and block malicious traffic before it reaches the network infrastructure. Strategies include deploying scrubbing centers, implementing behavior-based algorithms, and leveraging cloud-based mitigation services to absorb and disperse attack traffic effectively. Load balancing complements these efforts by distributing legitimate traffic across multiple servers, enhancing resilience and ensuring service availability during attack scenarios.
Load Balancing as Part of an Overall Security Strategy
Load balancing distributes network traffic evenly across multiple servers to enhance application availability and performance, reducing the risk of server overload during high-demand periods. As part of an overall security strategy, load balancing complements DDoS mitigation by preventing single points of failure and maintaining service continuity under attack conditions. Integrating load balancers with intrusion detection systems and firewall rules creates a robust defense framework that supports both traffic management and threat protection.
DDoS Mitigation Tools and Technologies Compared
DDoS mitigation tools like Arbor Networks, Cloudflare, and Akamai leverage advanced traffic filtering, rate limiting, and behavior analysis to detect and block malicious traffic effectively. In contrast, load balancing solutions primarily distribute legitimate network traffic across servers for optimal resource use but lack specialized capabilities for filtering attack traffic. Combining DDoS mitigation technologies with load balancing infrastructure enhances protection by ensuring high availability while preventing service disruption from volumetric and application-layer attacks.
When to Use Load Balancing vs. DDoS Mitigation
Load balancing is ideal when distributing network traffic efficiently across multiple servers to optimize resource use, maximize throughput, and ensure high availability during normal or high traffic loads. DDoS mitigation should be deployed specifically when defending against malicious, volumetric, or application-layer attacks aimed at overwhelming network resources and disrupting service. Use load balancing for performance optimization and scalability, while reserving DDoS mitigation for active defense against cyber threats and traffic floods.
Integrating Load Balancing and DDoS Protection Solutions
Integrating load balancing with DDoS mitigation enhances network resilience by distributing traffic evenly across servers while simultaneously filtering malicious requests. This approach leverages real-time traffic analysis and adaptive routing to maintain optimal performance during attack scenarios, reducing downtime and preserving user experience. Combining these solutions ensures scalable capacity management and proactive defense against volumetric and application-layer DDoS attacks.
Best Practices for Ensuring Uptime and Security
Effective load balancing disperses network traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload, ensuring consistent uptime and optimal performance. DDoS mitigation employs traffic filtering and rate limiting to identify and block malicious attacks, protecting system availability and integrity. Combining both strategies with real-time monitoring and automated response mechanisms enhances resilience against disruptions and maintains continuous, secure service delivery.
Load Balancing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com