Amazon SWF (Simple Workflow Service) enables developers to build, run, and scale background jobs that require coordination across distributed components, ensuring reliable execution of complex workflows. It manages state, checkpoints, and retries, allowing your applications to automatically recover from failures and maintain consistent progress. Discover how SWF can streamline your application workflows in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
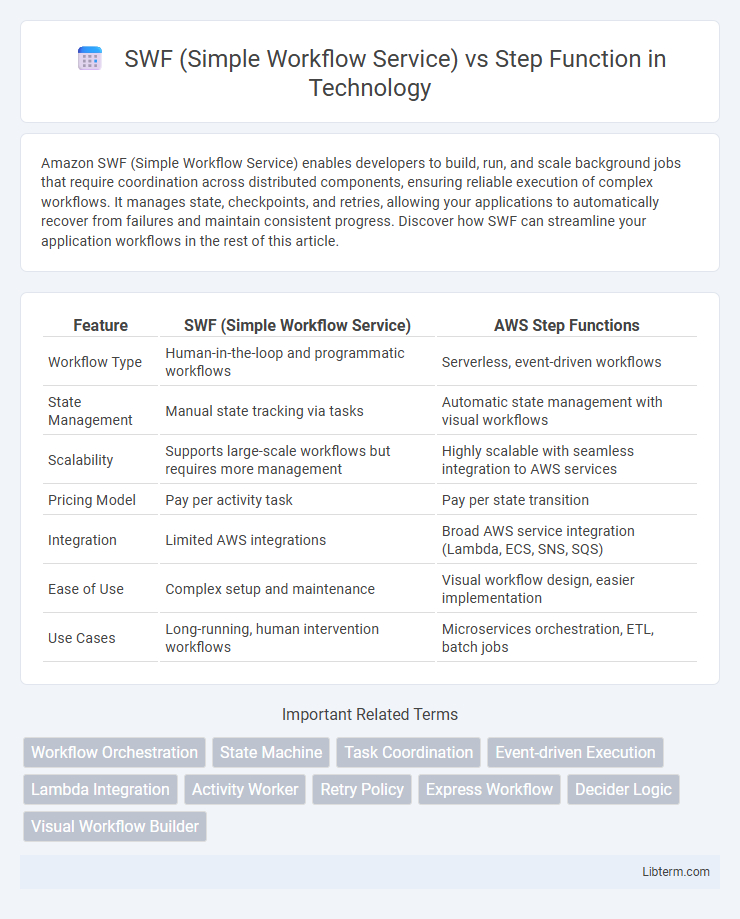
| Feature | SWF (Simple Workflow Service) | AWS Step Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Type | Human-in-the-loop and programmatic workflows | Serverless, event-driven workflows |
| State Management | Manual state tracking via tasks | Automatic state management with visual workflows |
| Scalability | Supports large-scale workflows but requires more management | Highly scalable with seamless integration to AWS services |
| Pricing Model | Pay per activity task | Pay per state transition |
| Integration | Limited AWS integrations | Broad AWS service integration (Lambda, ECS, SNS, SQS) |
| Ease of Use | Complex setup and maintenance | Visual workflow design, easier implementation |
| Use Cases | Long-running, human intervention workflows | Microservices orchestration, ETL, batch jobs |
Introduction to SWF and Step Functions
AWS Simple Workflow Service (SWF) is a fully managed state tracker and task coordinator designed for building distributed applications with complex workflows, providing reliable task execution and automatic retries. AWS Step Functions offers a serverless orchestration service that enables users to build and visualize workflows using state machines with integrated error handling, service integrations, and parallel processing capabilities. Both services support coordinating distributed components but differ in abstraction, with SWF requiring more manual coordination and Step Functions providing a more visual and declarative approach to workflow design.
Core Concepts and Workflow Models
Amazon SWF (Simple Workflow Service) employs a task-oriented workflow model where developers manage tasks, deciders, and workers explicitly to coordinate processes through activities and decision logic. AWS Step Functions use a state machine model with JSON-based Amazon States Language, enabling declarative definition of workflows including parallel, sequential, and error-handling states. Step Functions offer built-in integration with AWS services and visual workflow execution, while SWF requires custom implementation for state management and coordination.
Architecture Overview
AWS Simple Workflow Service (SWF) uses a centralized decider-worker architecture where deciders manage workflow logic and workers execute tasks, enabling fine-grained control of workflow state and task execution. AWS Step Functions adopt a serverless state machine model based on Amazon States Language, supporting visual workflows with built-in error handling, state transitions, and parallel execution capabilities. While SWF requires explicit coordination between components, Step Functions abstract orchestration, reduce operational overhead, and provide seamless integration with other AWS services through event-driven workflows.
Supported Use Cases
AWS Simple Workflow Service (SWF) supports long-running, complex business processes with human interaction and manual task coordination, making it ideal for legacy applications and workflows that require precise control over state transitions. AWS Step Functions excels in orchestrating modern, serverless applications with microservices, event-driven workflows, and parallel execution, offering native integration with AWS Lambda and scalable automation. Step Functions are particularly suited for real-time data processing, automated deployments, and high-throughput event handling where state management and fault tolerance are critical.
Integration with AWS Services
Step Functions offer seamless integration with over 200 AWS services, including Lambda, DynamoDB, ECS, and SNS, enabling automated orchestration and event-driven workflows. SWF supports integration primarily through custom worker applications and API calls but lacks native bindings with modern AWS services, making it less efficient for complex, service-based workflows. Step Functions also provide built-in error handling and state management tailored for AWS environments, enhancing reliability and scalability compared to SWF.
Scalability and Performance
AWS Step Functions offer superior scalability compared to SWF by supporting high-volume, concurrent executions with automatic scaling across distributed systems. Step Functions provide enhanced performance through state machine automation and integrated error handling, minimizing latency in complex workflow orchestration. SWF, while reliable for smaller-scale workflows, requires manual scaling and management, which can introduce bottlenecks in large-scale, high-throughput environments.
Error Handling and Retry Strategies
AWS Simple Workflow Service (SWF) offers error handling through decider logic, requiring manual implementation for retries and failure management, allowing fine-grained control but increasing complexity. AWS Step Functions provide built-in error handling and automatic retry capabilities with configurable parameters like interval seconds, maximum attempts, and backoff rates, simplifying robust workflow management. Step Functions support catching specific errors and triggering fallback states, enhancing resilience without extensive custom coding compared to SWF.
Pricing Comparison
AWS Simple Workflow Service (SWF) pricing is based on the number of workflow executions, activity tasks, and decision tasks, with costs incurred per thousand tasks and workflow executions, which can accumulate in complex workflows. AWS Step Functions uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model charging per state transition, making it cost-effective for workflows with fewer, larger states but potentially expensive with high-frequency or granular state transitions. Choosing between SWF and Step Functions depends on the workflow complexity and task granularity, with Step Functions often preferred for serverless orchestration and SWF for long-running, lower-frequency workflows.
Security and Compliance Features
AWS Step Functions offer enhanced security and compliance features compared to Simple Workflow Service (SWF), including fine-grained IAM policies that control state machine execution and activity-level permissions. Step Functions integrate seamlessly with AWS CloudTrail for detailed auditing and logging, supporting compliance with standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOC. SWF supports basic access control and logging but lacks the advanced encryption and governance capabilities inherent in Step Functions for enterprise-grade security.
Choosing Between SWF and Step Functions
Choosing between AWS SWF (Simple Workflow Service) and AWS Step Functions depends on the complexity and scale of your workflow orchestration needs. SWF is suited for long-running, complex business processes requiring fine-grained control over task coordination and state management, ideal for legacy systems and custom deciders. Step Functions offer serverless orchestration with native integration to AWS services, visual workflow support, and scalability, making it preferable for modern microservices architectures, event-driven applications, and simplified state machine management.
SWF (Simple Workflow Service) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com