Effective delegation enhances productivity by distributing tasks based on team members' strengths and expertise. It empowers your team, fosters trust, and optimizes workflow, ensuring projects are completed efficiently. Discover how mastering delegation can transform your leadership and drive success in the full article.
Table of Comparison
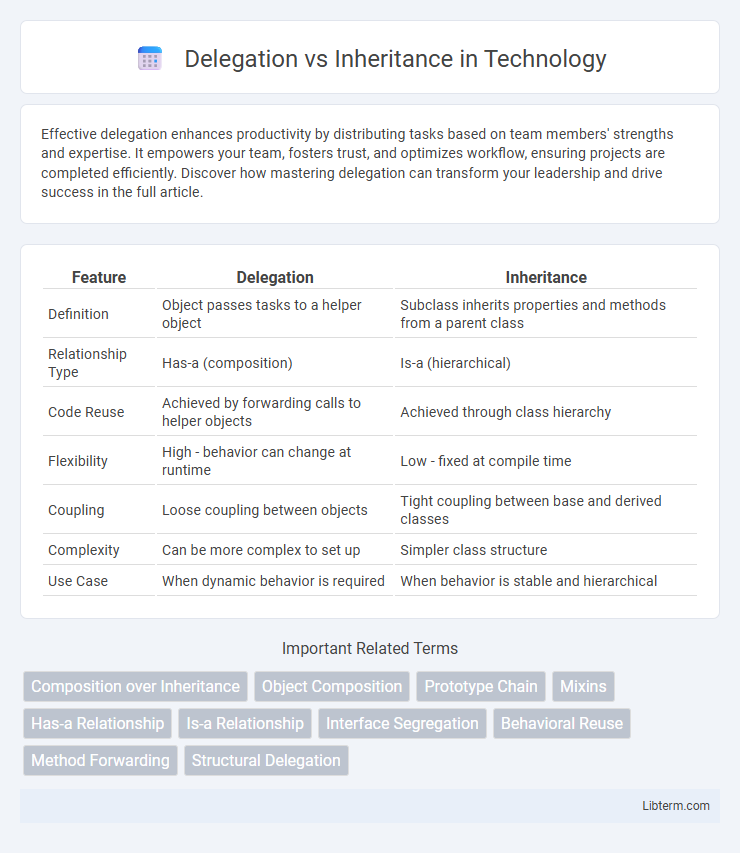
| Feature | Delegation | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Object passes tasks to a helper object | Subclass inherits properties and methods from a parent class |
| Relationship Type | Has-a (composition) | Is-a (hierarchical) |
| Code Reuse | Achieved by forwarding calls to helper objects | Achieved through class hierarchy |
| Flexibility | High - behavior can change at runtime | Low - fixed at compile time |
| Coupling | Loose coupling between objects | Tight coupling between base and derived classes |
| Complexity | Can be more complex to set up | Simpler class structure |
| Use Case | When dynamic behavior is required | When behavior is stable and hierarchical |
Understanding Delegation and Inheritance
Delegation involves an object relying on another to provide a specified behavior, promoting composition over class hierarchy and enabling dynamic method resolution at runtime. Inheritance establishes an "is-a" relationship where a subclass inherits properties and methods from a parent class, facilitating code reuse and polymorphism through static type hierarchies. Understanding delegation emphasizes flexible, runtime behavior sharing, while inheritance focuses on compile-time hierarchical relationships and type extension.
Core Principles of Object-Oriented Design
Delegation in object-oriented design enables an object to hand off tasks to a helper object, promoting flexibility and composition over rigid class hierarchies. Inheritance establishes a parent-child relationship where subclasses inherit properties and behaviors, enabling code reuse and polymorphism but often leading to tight coupling. Core principles such as encapsulation, modularity, and the open-closed principle are supported by choosing delegation to enhance maintainability, while inheritance facilitates extensibility through hierarchical organization.
What is Inheritance?
Inheritance is a core concept in object-oriented programming where a class derives properties and behaviors from a parent class, enabling code reuse and the creation of hierarchical relationships. It allows subclasses to inherit methods and attributes, promoting extensibility and polymorphism within software design. This mechanism simplifies maintenance by centralizing common functionality in a base class while supporting specialization through derived classes.
What is Delegation?
Delegation is a design pattern where an object handles a request by passing it to a second helper object, enabling flexible code reuse without establishing a strict hierarchical relationship. Unlike inheritance, delegation allows behavior sharing at runtime by forwarding method calls, enhancing modularity and reducing tight coupling. This approach supports dynamic composition, making it ideal for scenarios requiring adaptable behavior or multiple traits without rigid class structures.
Key Differences Between Delegation and Inheritance
Delegation involves an object relying on another object to provide a specified set of functionalities, promoting composition and flexible runtime behavior, while inheritance establishes a static, hierarchical relationship where a subclass inherits properties and methods from a superclass. Delegation supports dynamic method resolution and better encapsulation, enabling objects to change their behavior by delegating responsibilities to different helper objects. Inheritance can lead to tight coupling and less reusable code due to its fixed structure, whereas delegation enhances modularity and reduces dependency by favoring object collaboration over class hierarchy.
Pros and Cons of Inheritance
Inheritance allows code reuse and promotes hierarchical relationships by enabling new classes to inherit properties and methods from existing ones, simplifying maintenance and extension. However, it can lead to tight coupling between parent and child classes, making systems fragile and difficult to refactor when the superclass changes. Overuse of inheritance may also result in complex hierarchies that hinder flexibility and violate encapsulation principles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Delegation
Delegation enhances flexibility by allowing objects to delegate responsibilities to helper objects, promoting code reuse without the tight coupling seen in inheritance hierarchies. It avoids the pitfalls of deep inheritance chains, such as fragility and difficulty in maintaining or extending code, but can increase complexity due to the need for managing multiple object interactions. However, delegation may introduce runtime overhead and requires careful design to ensure clear responsibility distribution and efficient communication between objects.
Use Cases: When to Choose Delegation or Inheritance
Delegation is ideal for scenarios requiring dynamic behavior changes at runtime, such as extending functionality without modifying existing classes or adhering to the composition-over-inheritance principle to promote code reuse and flexibility. Inheritance suits cases where a clear hierarchical relationship exists, enabling polymorphism and method overriding to share common behavior among related classes, especially in static type hierarchies like GUI component frameworks. Choosing delegation over inheritance reduces tight coupling and fragility in complex systems, particularly when multiple behaviors need to be combined or altered independently.
Best Practices for Applying Delegation and Inheritance
Best practices for delegation emphasize composition over inheritance, promoting flexible and maintainable code by delegating tasks to helper objects rather than extending classes unnecessarily. Inheritance should be applied when there is a true "is-a" relationship, ensuring subclasses only override or extend behavior without violating the Liskov Substitution Principle. Combining delegation with interface implementation encourages loose coupling and enhances code reusability across different components.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Delegation offers flexibility by enabling objects to share behavior without rigid hierarchical constraints, making it ideal for dynamic or evolving systems. Inheritance provides a clear, structured way to reuse code when a strict "is-a" relationship exists, ensuring consistent behavior across related classes. Choosing between delegation and inheritance depends on the specific design requirements, with delegation favored for composition and extensibility, and inheritance suited for straightforward, hierarchical relationships.
Delegation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com