Full updates ensure your software includes the latest features and security patches, enhancing performance and protecting your data. Regularly applying updates prevents vulnerabilities and keeps your system running smoothly. Discover how to manage full updates effectively by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
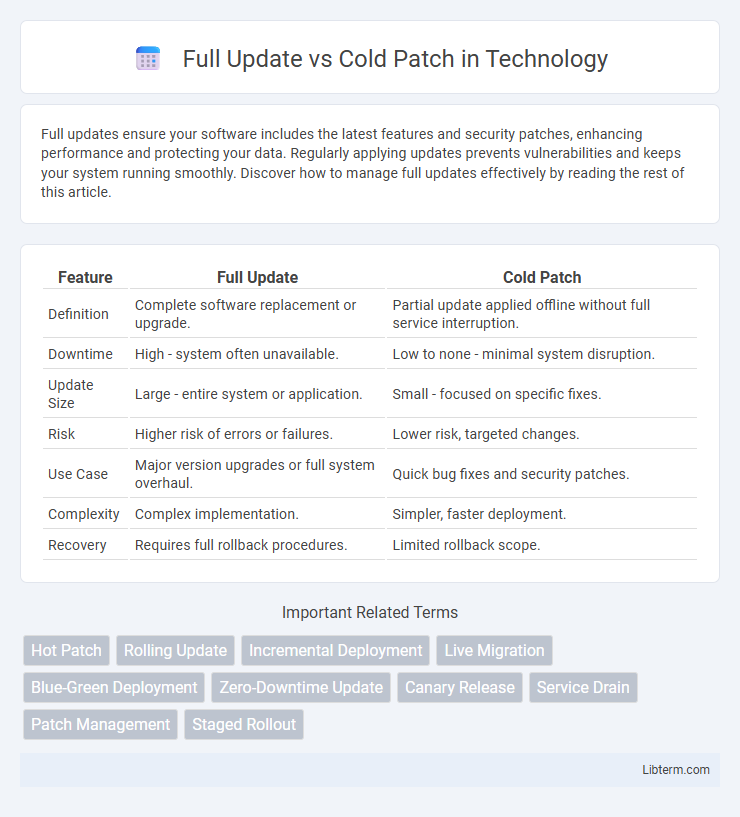
| Feature | Full Update | Cold Patch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete software replacement or upgrade. | Partial update applied offline without full service interruption. |
| Downtime | High - system often unavailable. | Low to none - minimal system disruption. |
| Update Size | Large - entire system or application. | Small - focused on specific fixes. |
| Risk | Higher risk of errors or failures. | Lower risk, targeted changes. |
| Use Case | Major version upgrades or full system overhaul. | Quick bug fixes and security patches. |
| Complexity | Complex implementation. | Simpler, faster deployment. |
| Recovery | Requires full rollback procedures. | Limited rollback scope. |
Introduction to Full Updates and Cold Patches
Full updates replace the entire software or system components, ensuring all files and configurations are up to date, which can improve stability and security but requires more time and resources. Cold patches apply targeted fixes or updates while the system is offline or in a minimal state, reducing the risk of conflicts and errors during the update process. Both methods serve different operational needs depending on the urgency and scope of the software maintenance required.
Defining Full Update: Scope and Process
A full update involves replacing or upgrading all software components, often requiring system downtime to ensure a complete installation and integration of new features or security patches. This process typically includes backing up data, uninstalling the previous version, installing the new version from scratch, and performing thorough testing to confirm system stability. The scope of a full update encompasses comprehensive changes, which may affect configurations, dependencies, and user settings to deliver enhanced functionality and reliability.
Understanding Cold Patch: Purpose and Application
Cold patch is a repair method designed for quick, temporary fixes on asphalt surfaces, often used in pothole remediation without the need for heating equipment. This technique involves applying pre-mixed asphalt material directly to the damaged area, allowing it to bond and harden at ambient temperatures. Cold patch is ideal for emergency repairs and areas with limited access to hot mix asphalt plants, providing a cost-effective, immediate solution to maintain road safety and prevent further pavement deterioration.
Key Differences Between Full Update and Cold Patch
Full Update involves completely replacing or overwriting the existing software or system files, ensuring all components are refreshed and up to date, while Cold Patch applies incremental changes or fixes without fully shutting down or reinstalling the system. Full Update requires more time and system downtime but guarantees a comprehensive refresh, whereas Cold Patch minimizes disruption by targeting specific issues with smaller data sets. Key differences include the extent of file replacement, impact on system availability, and update duration, with Full Update providing thoroughness and Cold Patch emphasizing efficiency.
Advantages of Implementing Full Updates
Full updates ensure comprehensive software integrity by providing complete replacement of all program files, eliminating risks associated with partial or incremental changes. This method enhances system stability and security through thorough patching of vulnerabilities and bugs. Additionally, full updates reduce compatibility issues by standardizing the installation process across all devices.
Benefits and Limitations of Cold Patching
Cold patching offers the advantage of quick, temporary road repairs without the need for heating equipment, making it highly effective for emergency fixes and low-traffic areas. However, its limitations include reduced durability and strength compared to full updates, leading to a shorter lifespan and potential surface degradation under heavy traffic or extreme weather conditions. While cost-effective and convenient for immediate use, cold patching typically requires follow-up maintenance or a more permanent full update to ensure long-term road integrity.
Impact on System Downtime and Performance
Full updates require system shutdowns, leading to longer downtime but ensure comprehensive software improvements and security patches, enhancing overall system performance post-installation. Cold patches apply fixes without the need for full shutdowns, minimizing downtime but may provide limited performance improvements and patch scope. Balancing downtime impact and performance gains depends on the criticality of updates and operational requirements.
Security Implications: Full Update vs Cold Patch
Full Update processes replace the entire system or software version, ensuring all security vulnerabilities are comprehensively addressed and system integrity is maintained, significantly reducing the risk of exploitation. Cold Patch applies targeted fixes to specific security issues without rebooting the system, allowing for immediate protection but potentially leaving latent vulnerabilities from unpatched components. Evaluating the trade-offs between full kernel or software reboots and rapid vulnerability mitigation is critical for maintaining robust security posture in dynamic IT environments.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a full update and a cold patch depends largely on the scope of the changes and system downtime tolerance. Full updates are ideal for comprehensive improvements or critical security fixes requiring complete system reboot and data integrity assurance. Cold patches suit minor bug fixes or performance tweaks where immediate deployment with minimal disruption is critical, but they may lack the thoroughness of a full update.
Best Practices for Effective Patch Management
Full update involves replacing or upgrading an entire software component to the latest version, ensuring comprehensive bug fixes and security enhancements, whereas cold patch applies selective fixes without rebooting the system. Best practices for effective patch management recommend scheduling full updates during planned maintenance windows to minimize downtime while using cold patches for critical, immediate fixes to reduce operational disruption. Combining thorough testing, timely deployment, and clear rollback procedures enhances reliability and security in patch management strategies.
Full Update Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com