Service mesh technology enhances microservices communication by providing secure, reliable, and observable interactions within distributed systems. It manages service-to-service traffic with features like load balancing, authentication, and telemetry without requiring changes to application code. Explore the rest of the article to understand how implementing a service mesh can optimize Your infrastructure and improve scalability.
Table of Comparison
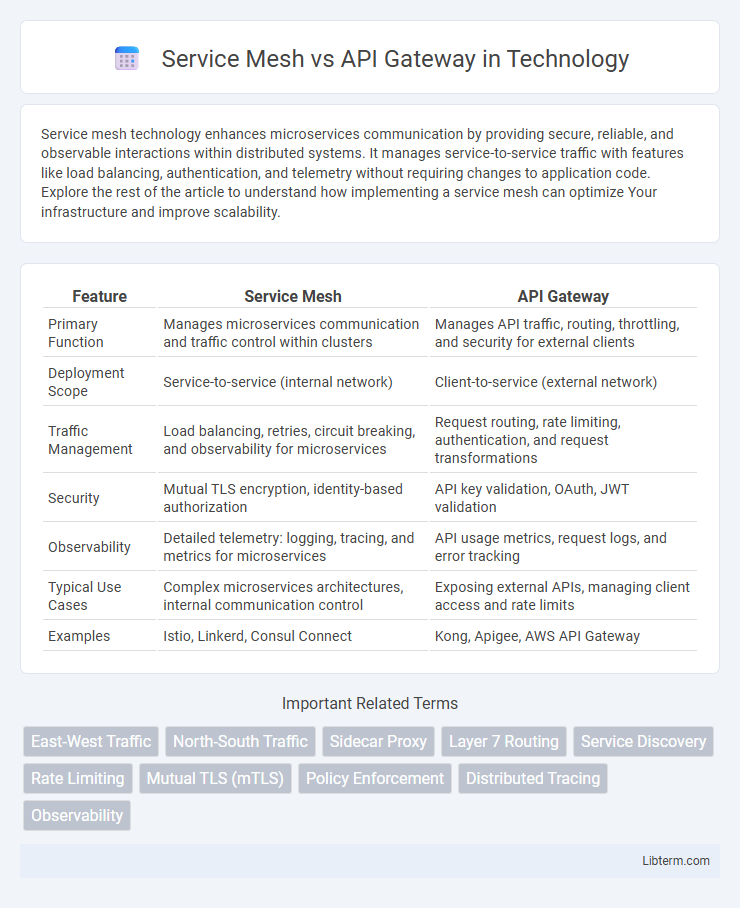
| Feature | Service Mesh | API Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages microservices communication and traffic control within clusters | Manages API traffic, routing, throttling, and security for external clients |
| Deployment Scope | Service-to-service (internal network) | Client-to-service (external network) |
| Traffic Management | Load balancing, retries, circuit breaking, and observability for microservices | Request routing, rate limiting, authentication, and request transformations |
| Security | Mutual TLS encryption, identity-based authorization | API key validation, OAuth, JWT validation |
| Observability | Detailed telemetry: logging, tracing, and metrics for microservices | API usage metrics, request logs, and error tracking |
| Typical Use Cases | Complex microservices architectures, internal communication control | Exposing external APIs, managing client access and rate limits |
| Examples | Istio, Linkerd, Consul Connect | Kong, Apigee, AWS API Gateway |
Introduction to Service Mesh and API Gateway
Service Mesh and API Gateway both manage communication in microservices architectures but serve distinct roles. A Service Mesh provides fine-grained control, observability, and security for internal service-to-service communication through lightweight proxies embedded alongside application code. In contrast, an API Gateway acts as a single entry point for external client requests, handling tasks like request routing, authentication, rate limiting, and API composition.
Core Functions of Service Mesh
Service mesh core functions include fine-grained traffic management, secure service-to-service communication through mutual TLS, and comprehensive observability with metrics, logs, and tracing for microservices. It facilitates load balancing, service discovery, and failure recovery within a distributed system, enhancing reliability and scalability. By abstracting networking complexity, service mesh enables developers to focus on business logic while maintaining robust connectivity and security across microservices.
Key Capabilities of API Gateway
API Gateway provides critical capabilities such as request routing, traffic shaping, load balancing, and authentication, enabling secure and efficient API management. It handles rate limiting, request transformation, and analytics, facilitating developer access control and monitoring. These features optimize API exposure, improve performance, and enhance security for external and internal applications.
Architectural Differences
Service Mesh operates at the infrastructure level to manage service-to-service communication within microservices architectures, handling traffic routing, load balancing, and security through sidecar proxies deployed alongside each service instance. API Gateway functions at the application layer, providing a single entry point for external client requests, handling tasks such as request routing, authentication, rate limiting, and API composition. Architecturally, Service Mesh decentralizes communication control across services, while API Gateway centralizes external API management, making them complementary components in modern cloud-native environments.
Use Cases: When to Choose Service Mesh
Service Mesh is ideal for managing complex microservices architectures requiring fine-grained service-to-service communication, observability, and security features like mutual TLS. It excels in scenarios where developers need automated traffic management, policy enforcement, and consistent telemetry across distributed services without modifying application code. Organizations aiming for deep operational insights and service-level resilience within Kubernetes or multi-cloud environments should prioritize deploying a Service Mesh over an API Gateway.
Use Cases: When to Use API Gateway
API Gateway is ideal for managing external client requests, handling functions like request routing, authentication, rate limiting, and API composition, making it suitable for public-facing APIs and microservices exposed to outside consumers. Use cases include authenticating and authorizing user access, aggregating multiple backend services into a single API response, and enforcing security policies at the edge of the network. It excels in scenarios requiring centralized entry points, protocol translation, and API monetization strategies.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Service Mesh enhances microservices communication by managing service-to-service traffic with low latency and high throughput, optimizing performance through lightweight proxies like Envoy. API Gateway handles external client requests with features like rate limiting and authentication, which can add overhead and impact latency under high load. Scalability in Service Mesh is achieved by distributed data planes supporting dynamic scaling of services, whereas API Gateways may become bottlenecks without proper horizontal scaling strategies.
Security Features Comparison
Service Mesh enhances security by providing mTLS encryption for service-to-service communication, fine-grained access control, and automatic certificate rotation, ensuring strong identity verification within microservices architectures. API Gateway focuses on perimeter security with features like request authentication, rate limiting, IP whitelisting, and API key validation to protect external endpoints from unauthorized access and threats. Both solutions complement each other by securing different layers: Service Mesh secures internal traffic while API Gateway secures external API access.
Integration with Microservices
Service Mesh offers granular control over microservices communication by managing service-to-service interactions with features like traffic routing, load balancing, and security enforcement, enabling deep integration within microservices architectures. API Gateway centralizes external API management, handling request routing, authentication, and protocol translation between clients and microservices, streamlining entry points for external consumers. Combining Service Mesh and API Gateway provides a robust strategy for internal microservices communication and external API exposure, enhancing scalability and security in microservices ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Architecture
Service Mesh excels in managing service-to-service communication within microservices architectures by providing features like traffic management, security, and observability at the network level. API Gateway focuses on handling external client requests, offering functions such as authentication, rate limiting, and request routing for APIs. Selecting the right solution depends on your architecture's complexity: opt for a Service Mesh if internal service interactions dominate, or an API Gateway if managing external API traffic is the priority.
Service Mesh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com