Centralized identity systems store all user information in a single database, simplifying management but introducing risks such as single points of failure and privacy concerns. This approach enables easier access control and streamlined authentication but may expose Your data to higher security vulnerabilities. Discover more about centralized identity benefits and challenges in the full article.
Table of Comparison
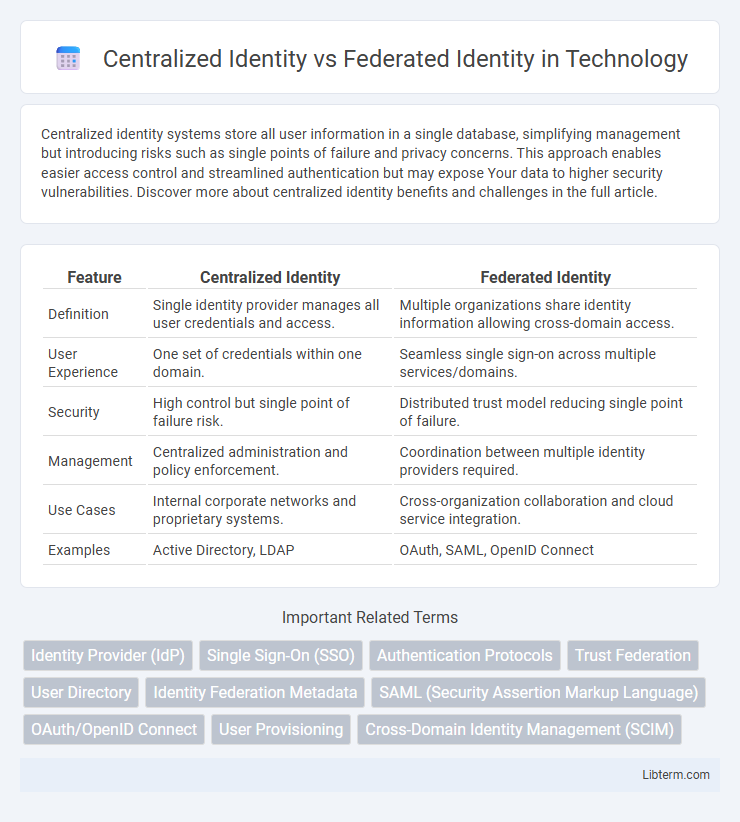
| Feature | Centralized Identity | Federated Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single identity provider manages all user credentials and access. | Multiple organizations share identity information allowing cross-domain access. |
| User Experience | One set of credentials within one domain. | Seamless single sign-on across multiple services/domains. |
| Security | High control but single point of failure risk. | Distributed trust model reducing single point of failure. |
| Management | Centralized administration and policy enforcement. | Coordination between multiple identity providers required. |
| Use Cases | Internal corporate networks and proprietary systems. | Cross-organization collaboration and cloud service integration. |
| Examples | Active Directory, LDAP | OAuth, SAML, OpenID Connect |
Understanding Centralized Identity
Centralized Identity management consolidates user authentication and authorization into a single system, streamlining access control and simplifying administrative tasks. This approach enhances security by maintaining a unified user database, reducing the risk of inconsistent identity data across multiple platforms. Centralized Identity frameworks are commonly implemented in enterprise environments to provide seamless access to internal resources through a single set of credentials.
What is Federated Identity?
Federated Identity enables users to access multiple systems or applications across different organizations using a single set of credentials managed by an identity provider. This approach relies on trust agreements between organizations, utilizing standards like SAML, OAuth, or OpenID Connect to facilitate secure authentication and authorization. Federated Identity enhances user experience by reducing password fatigue and improves security through centralized identity management while allowing seamless cross-domain access.
Key Differences Between Centralized and Federated Identity
Centralized Identity systems store user credentials and manage authentication within a single, unified domain, offering streamlined control and consistency across applications. Federated Identity enables users to access multiple independent systems using a single authentication session, leveraging trust relationships and standards like SAML or OAuth for cross-domain identity management. The core difference lies in data ownership and access scope: Centralized Identity centralizes user information in one repository, while Federated Identity distributes authentication across separate domains without consolidating identity data.
Pros and Cons of Centralized Identity
Centralized Identity systems offer simplified user management and streamlined access control by storing all user credentials in a single repository, enhancing security through consistent policies and easier monitoring. However, they pose risks such as single points of failure, making them vulnerable to breaches or downtime that can affect all connected services. Scalability challenges and limited interoperability with external systems also restrict flexibility compared to federated identity models.
Pros and Cons of Federated Identity
Federated Identity enables users to access multiple systems using a single set of credentials managed by a trusted identity provider, reducing password fatigue and improving user convenience. It enhances security by leveraging established identity providers that implement robust authentication protocols, yet it introduces reliance on third-party providers, which can pose risks if the provider experiences downtime or breaches. Challenges include potential privacy concerns due to data sharing across domains and complexities in establishing trust relationships among diverse organizations.
Security Implications of Each Approach
Centralized identity systems concentrate user credentials in a single repository, increasing the risk of a single point of failure and making the system an attractive target for cyberattacks such as data breaches and credential stuffing. Federated identity allows multiple trusted domains to share authentication, reducing dependency on one source and enhancing resilience by leveraging protocols like SAML, OAuth, and OpenID Connect to facilitate secure, token-based access across platforms. While federated identity improves user convenience and reduces password fatigue, it requires robust trust frameworks and vigilant monitoring to prevent unauthorized access and identity federation attacks.
User Experience: Centralized vs Federated Identity
Centralized identity systems offer users a streamlined experience by managing authentication through a single, controlled platform, simplifying password management and reducing sign-in friction. Federated identity enhances user experience by enabling seamless access across multiple applications and services without repeated logins, leveraging trust relationships between identity providers. Both models impact user convenience, with centralized identity prioritizing unified control and federated identity emphasizing interoperability and user mobility across digital ecosystems.
Popular Use Cases and Real-World Examples
Centralized identity systems, prevalent in enterprise environments like Microsoft Active Directory, provide streamlined user management and secure access control within a single organization. Federated identity solutions such as Single Sign-On (SSO) via OAuth and SAML are widely used by companies like Google and Facebook to enable seamless access across multiple independent online services. Popular use cases include centralized identity for internal corporate networks and federated identity for cross-platform authentication in cloud applications and partner ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Identity Solution for Your Organization
Centralized identity systems offer streamlined control and simplified administration by maintaining all user credentials within a single repository, ideal for organizations prioritizing security and uniform policy enforcement. Federated identity solutions enable seamless access across multiple organizations or platforms through shared authentication standards like SAML or OAuth, enhancing user convenience and collaboration in distributed environments. Selecting the right identity solution requires assessing factors such as organizational size, regulatory compliance needs, user experience goals, and integration complexity to balance security, scalability, and operational efficiency.
Future Trends in Digital Identity Management
Future trends in digital identity management emphasize a shift towards decentralized identity models that enhance user control and privacy, reducing reliance on centralized authorities. Federated identity systems are evolving to integrate blockchain technology and self-sovereign identity frameworks, enabling secure, interoperable, and user-centric authentication across multiple platforms. Artificial intelligence and biometric advancements will further strengthen identity verification processes, supporting seamless access while mitigating fraud in both centralized and federated environments.
Centralized Identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com