Object storage offers scalable and durable data management by storing information as discrete units called objects, each tagged with unique identifiers and metadata. It enables efficient handling of unstructured data, making it ideal for cloud services, backups, and big data analytics. Explore the full article to understand how object storage can enhance your data strategy and streamline access.
Table of Comparison
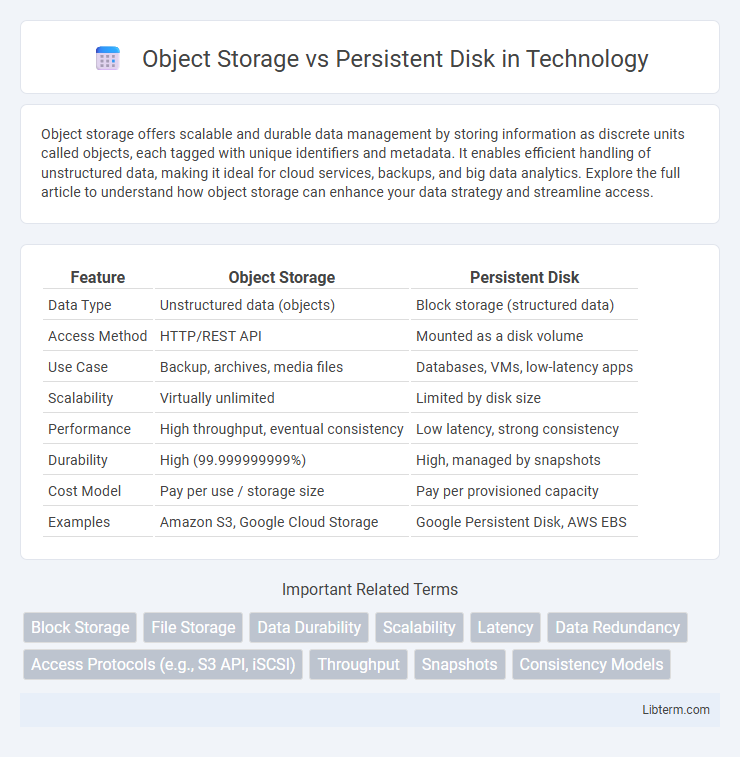
| Feature | Object Storage | Persistent Disk |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Unstructured data (objects) | Block storage (structured data) |
| Access Method | HTTP/REST API | Mounted as a disk volume |
| Use Case | Backup, archives, media files | Databases, VMs, low-latency apps |
| Scalability | Virtually unlimited | Limited by disk size |
| Performance | High throughput, eventual consistency | Low latency, strong consistency |
| Durability | High (99.999999999%) | High, managed by snapshots |
| Cost Model | Pay per use / storage size | Pay per provisioned capacity |
| Examples | Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage | Google Persistent Disk, AWS EBS |
Introduction to Object Storage and Persistent Disk
Object Storage is a scalable, high-availability data storage architecture that manages data as objects, ideal for unstructured data like multimedia files, backups, and big data analytics. Persistent Disk provides block storage volumes that can be attached to virtual machines, offering consistent performance and durability for applications requiring low-latency access to file systems or databases. Both storage types support cloud environments, but Object Storage excels in massive scalability and metadata-rich files, while Persistent Disk prioritizes high IOPS and seamless integration with compute instances.
Key Features of Object Storage
Object Storage provides scalable, durable, and cost-effective data storage optimized for unstructured data, supporting metadata-rich objects accessible via RESTful APIs. It excels in high availability with built-in redundancy across multiple geographic locations, enabling seamless data replication and versioning. Unlike Persistent Disk, Object Storage offers virtually unlimited capacity and is ideal for backup, archiving, and big data analytics workloads requiring massive amounts of data accessibility.
Core Benefits of Persistent Disks
Persistent disks provide high-performance block storage with low latency and consistent throughput, making them ideal for databases and mission-critical applications. They offer seamless integration with virtual machines, enabling easy data durability, backup, and snapshot capabilities. Persistent disks also support encryption at rest and automatically scale storage without impacting application availability.
Architecture Comparison: Object Storage vs Persistent Disk
Object Storage architecture utilizes a flat namespace with metadata-rich objects stored across distributed nodes, enhancing scalability and fault tolerance, whereas Persistent Disk employs block storage with fixed-size blocks managed by a centralized volume manager for efficient random access. Object Storage supports massive unstructured data with eventual consistency models, compared to Persistent Disk's structured data and strong consistency ideal for database workloads. The design of Object Storage enables high durability through data replication or erasure coding, while Persistent Disk ensures low latency and high IOPS through dedicated physical resources attached to virtual machines.
Performance and Scalability Differences
Object Storage offers massive scalability by distributing data across multiple nodes with metadata-rich objects, enabling efficient handling of unstructured data at petabyte scale. Persistent Disk provides high-performance, low-latency block storage optimized for transactional workloads and virtual machine instances, delivering consistent IOPS and throughput. While Object Storage excels in horizontal scalability and durability for large-scale archival and backup, Persistent Disk is designed for vertical scaling with predictable performance for active data access.
Data Durability and Availability
Object Storage offers high data durability with multiple redundant copies distributed across geographically separate locations, ensuring continuous availability even in case of regional failures. Persistent Disk provides strong durability through replication within a single zone or region, delivering low-latency access ideal for virtual machines but with less cross-region redundancy than Object Storage. Cloud providers typically guarantee Object Storage durability up to 99.999999999% (11 nines), while Persistent Disk durability ranges around 99.999% (5 nines), reflecting their respective architectures and use cases.
Cost Considerations and Pricing Models
Object storage typically offers lower cost per gigabyte and scales more efficiently, making it ideal for massive unstructured data with infrequent access, while persistent disks are priced higher due to consistent performance and low latency requirements suitable for active workloads. Pricing models for object storage often include pay-as-you-go with additional fees for data retrieval or API requests, whereas persistent disks usually charge based on allocated capacity and provisioned IOPS, leading to predictable monthly expenses. Cost optimization depends on workload patterns, with object storage favoring archival and backup scenarios and persistent disks optimized for transactional databases and operational consistency.
Use Cases for Object Storage
Object Storage excels in handling unstructured data such as multimedia files, backups, and archival content due to its scalability and cost-effectiveness. It is ideal for cloud-native applications, big data analytics, and disaster recovery scenarios that require high durability and easy global access. Use cases include storing user-generated content, hosting static websites, and managing large datasets in machine learning workflows.
When to Choose Persistent Disks
Persistent Disks are ideal for applications requiring low-latency, high-throughput block storage such as databases, virtual machines, and transactional workloads. They provide consistent and durable storage with strong data integrity guarantees, making them suitable for scenarios demanding frequent read/write operations. Choose Persistent Disks when your workload necessitates fast, reliable access to data with strict performance and consistency requirements.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Storage Solution
Choosing between Object Storage and Persistent Disk depends on workload requirements: Object Storage excels in scalability and unstructured data management, offering cost-effective, durable storage ideal for backups and archives. Persistent Disk provides high-performance, low-latency block storage suited for database applications and virtual machines requiring consistent IOPS. Evaluate factors such as access patterns, data consistency, and performance needs to select the optimal storage solution for your cloud environment.
Object Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com