Unmanaged systems offer simplicity and cost savings by allowing devices to operate without extensive configuration or oversight. These networks are ideal for small businesses or home environments where basic connectivity is sufficient and minimal troubleshooting is needed. Explore the rest of the article to understand how unmanaged solutions can fit your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
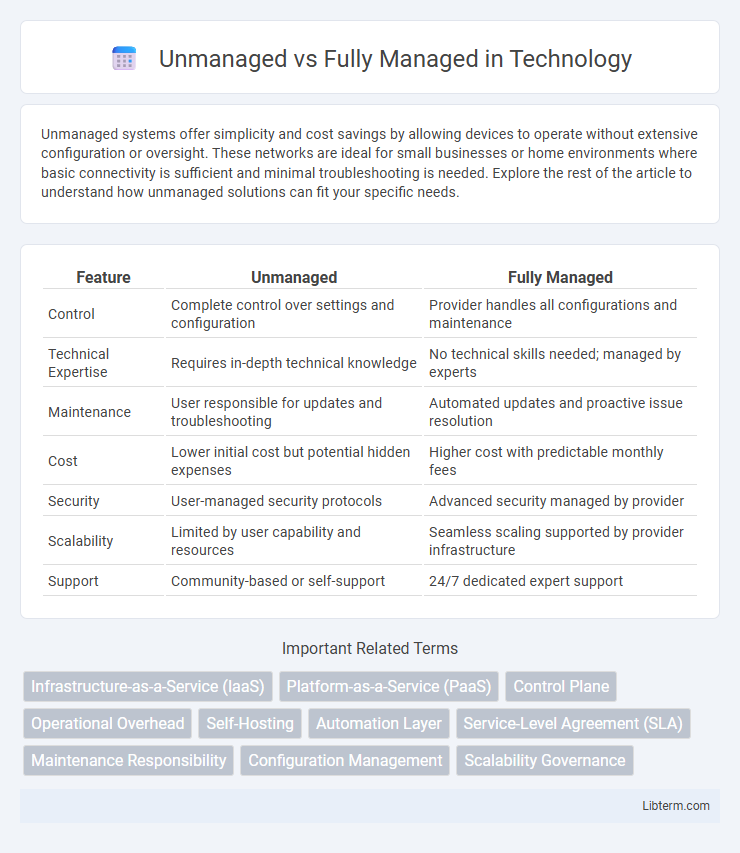
| Feature | Unmanaged | Fully Managed |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Complete control over settings and configuration | Provider handles all configurations and maintenance |
| Technical Expertise | Requires in-depth technical knowledge | No technical skills needed; managed by experts |
| Maintenance | User responsible for updates and troubleshooting | Automated updates and proactive issue resolution |
| Cost | Lower initial cost but potential hidden expenses | Higher cost with predictable monthly fees |
| Security | User-managed security protocols | Advanced security managed by provider |
| Scalability | Limited by user capability and resources | Seamless scaling supported by provider infrastructure |
| Support | Community-based or self-support | 24/7 dedicated expert support |
Introduction to Unmanaged vs Fully Managed Services
Unmanaged services provide basic infrastructure access without support, requiring users to handle setup, maintenance, and troubleshooting independently. Fully managed services include comprehensive management, monitoring, and support, allowing clients to focus on their core business while the provider handles technical complexities. Choosing between unmanaged and fully managed services depends on the client's technical expertise, budget, and desire for control over system administration.
Key Differences Between Unmanaged and Fully Managed
Unmanaged services require users to handle setup, maintenance, and troubleshooting independently, offering greater control but demanding technical expertise and time commitment. Fully managed services provide end-to-end support, including monitoring, updates, and security management, ensuring minimal user intervention and optimized performance. The key differences lie in responsibility allocation, where unmanaged places operational duties on the user, while fully managed transfers these tasks to the service provider for convenience and reliability.
Pros and Cons of Unmanaged Services
Unmanaged services offer greater control and flexibility, allowing businesses to customize their infrastructure and reduce costs by handling maintenance and troubleshooting internally. However, they require significant technical expertise and time investment, increasing the risk of downtime and security vulnerabilities due to lack of dedicated support. Organizations must weigh the cost savings against potential operational challenges and consider their in-house capabilities before opting for unmanaged solutions.
Advantages of Fully Managed Solutions
Fully managed solutions offer enhanced security by providing continuous monitoring, updates, and proactive threat mitigation, ensuring optimal system protection without requiring user intervention. They reduce operational complexity and save time by outsourcing infrastructure management, allowing businesses to focus on core activities rather than maintenance tasks. Access to expert support and scalable resources ensures reliable performance and seamless adaptability to changing workloads, improving overall operational efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Unmanaged vs Fully Managed
Unmanaged services typically incur lower upfront costs as users handle configuration and maintenance themselves, while fully managed services include higher fees reflecting comprehensive support, automated updates, and proactive monitoring. The total cost of ownership for fully managed solutions often offsets initial expenses by reducing downtime and IT personnel requirements. Businesses must evaluate budget constraints and long-term value when comparing unmanaged versus fully managed service pricing models.
Security Implications in Both Approaches
Unmanaged hosting requires users to handle all security configurations, updates, and threat monitoring, increasing the risk of vulnerabilities due to potential mismanagement or lack of expertise. Fully managed hosting includes comprehensive security measures such as automated updates, proactive threat detection, and dedicated support teams, significantly reducing exposure to cyberattacks. Companies prioritizing data protection and compliance often prefer fully managed solutions to ensure robust security protocols are consistently maintained.
Performance and Reliability Considerations
Unmanaged services require users to handle performance tuning and maintenance, which can lead to inconsistent reliability and potential downtime without expert oversight. Fully managed services offer optimized performance through proactive monitoring, automatic updates, and expert support, ensuring higher uptime and stability. Choosing fully managed solutions minimizes operational risks and enhances system responsiveness, particularly for mission-critical applications.
Use Cases: When to Choose Unmanaged or Fully Managed
Unmanaged services suit businesses with in-house IT expertise that require maximum control over infrastructure and customization, ideal for startups and developers focusing on specific application development. Fully managed services benefit enterprises seeking to offload routine maintenance, security, and updates to experienced providers, ensuring high reliability and scalability for mission-critical workloads. Choose unmanaged for cost efficiency and flexibility in technical environments, while fully managed supports organizations prioritizing operational simplicity and continuous performance optimization.
Migration from Unmanaged to Fully Managed
Migrating from unmanaged to fully managed cloud services involves transferring data, applications, and infrastructure to a provider that handles maintenance, security, and updates, reducing operational overhead. This transition enhances scalability and reliability by leveraging automated monitoring, disaster recovery, and expert support. Careful planning, including data integrity checks and minimal downtime strategies, ensures a seamless migration without disrupting business continuity.
Conclusion: Which Option Is Right for You?
Choosing between unmanaged and fully managed services depends on your technical expertise, budget, and desired level of control. Unmanaged services suit businesses with in-house IT teams seeking maximum customization and cost efficiency, while fully managed services benefit organizations prioritizing convenience, expert support, and reduced downtime. Assessing your operational needs and resource availability will help determine the best fit for your infrastructure management.
Unmanaged Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com