Star symbolism carries profound meanings across cultures, often representing guidance, hope, and inspiration in the night sky. Their brilliance and constancy have been used to navigate journeys and symbolize dreams or spiritual enlightenment. Explore the full article to discover how stars can illuminate your understanding of both the cosmos and your inner aspirations.
Table of Comparison
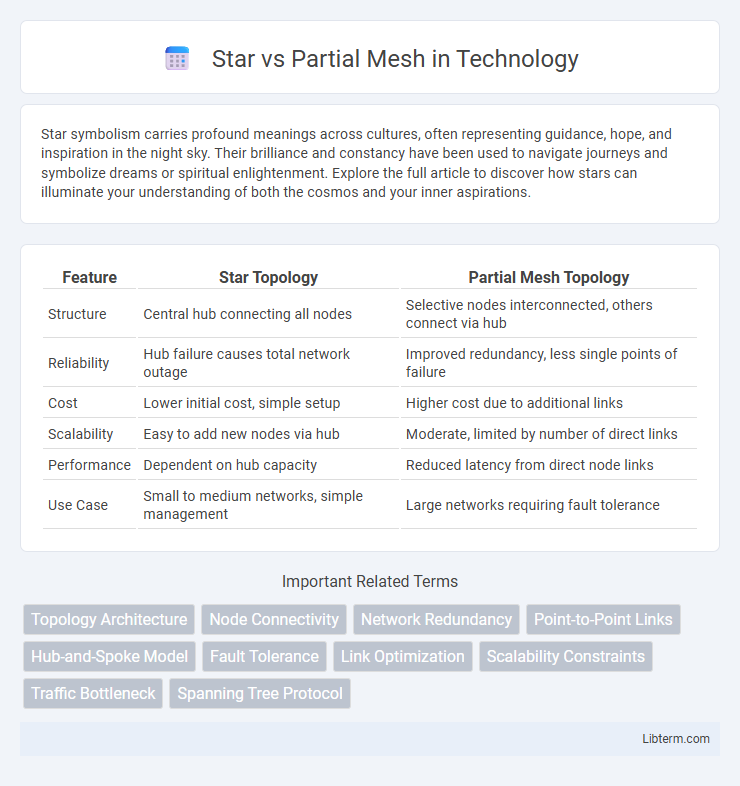
| Feature | Star Topology | Partial Mesh Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Central hub connecting all nodes | Selective nodes interconnected, others connect via hub |
| Reliability | Hub failure causes total network outage | Improved redundancy, less single points of failure |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, simple setup | Higher cost due to additional links |
| Scalability | Easy to add new nodes via hub | Moderate, limited by number of direct links |
| Performance | Dependent on hub capacity | Reduced latency from direct node links |
| Use Case | Small to medium networks, simple management | Large networks requiring fault tolerance |
Introduction to Star vs Partial Mesh Topologies
Star topology features a central hub connecting all nodes, ensuring straightforward management and easy fault isolation. Partial mesh topology links multiple nodes in a network with some nodes connected to many others, enhancing redundancy and fault tolerance without full mesh complexity. Both topologies balance network reliability and scalability but differ in design, cost, and connection density.
Core Differences Between Star and Partial Mesh
Star topology features a central node that manages all communication, resulting in simplified network management and easier fault isolation. Partial mesh topology connects some nodes directly to multiple other nodes, enhancing redundancy and reducing the risk of a single point of failure. The core difference lies in star's reliance on a central hub versus partial mesh's selective interconnections for optimized resilience and performance.
Network Architecture Overview: Star Topology
Star topology features a centralized network architecture where each device connects directly to a central hub or switch, facilitating straightforward data transmission and management. This setup enhances performance by minimizing data collisions and simplifies troubleshooting due to its point-to-point links between nodes and the central device. Ideal for environments requiring high reliability and easy scalability, the star topology provides clear advantages over partial mesh, especially in reducing network complexity and centralizing control.
Network Architecture Overview: Partial Mesh Topology
Partial mesh topology in network architecture involves connecting some devices directly, while others communicate through intermediate nodes, optimizing resource usage and redundancy. It balances the scalability and fault tolerance found in full mesh and star topologies by enabling critical nodes to maintain multiple direct links without the complexity of universal interconnections. This design supports efficient data routing and resilience by ensuring key paths remain operational even if some connections fail.
Advantages of Star Topology
Star topology offers centralized management, making network troubleshooting and maintenance more efficient by isolating individual device failures without affecting the entire network. It provides high performance through dedicated point-to-point connections between devices and the central hub, reducing data collisions and improving speed. Scalability is enhanced as new devices can be easily added without disrupting existing connections, making it ideal for growing networks.
Benefits of Partial Mesh Topology
Partial mesh topology enhances network reliability by providing multiple pathways for data transmission, reducing the risk of total network failure. It balances cost and redundancy effectively, offering improved fault tolerance without the high expense of a full mesh setup. Network performance benefits from optimized data routing, resulting in better bandwidth utilization and reduced latency.
Limitations of Star Topology
Star topology faces significant limitations in scalability due to its dependence on a central hub, which creates a single point of failure that can disrupt the entire network. Bandwidth bottlenecks frequently occur because all data traffic passes through this central node, reducing performance as network size increases. Maintenance costs and complexity rise with the need for robust central hardware and cabling infrastructure to support numerous connected devices.
Drawbacks of Partial Mesh Topology
Partial mesh topology can lead to increased complexity and higher costs compared to simpler network designs due to the multiple redundant connections required. Troubleshooting becomes more difficult as the network grows, since multiple paths complicate fault isolation and network management. Scalability issues arise because each new node may require multiple links, leading to possible congestion and maintenance challenges in larger networks.
Use Cases: When to Choose Star or Partial Mesh
Star topology suits small to medium-sized networks requiring centralized control and simple management, ideal for home networks and office environments with limited devices. Partial mesh topology is preferable in larger, mission-critical networks where redundancy and fault tolerance are essential, such as enterprise WANs connecting multiple branch offices. Businesses needing a balance between cost and reliability often select partial mesh to ensure key nodes maintain multiple communication paths without the complexity of full mesh.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Network Topology
Star topology offers simplicity and easy fault isolation with a central hub, ideal for small to medium-sized networks prioritizing straightforward management. Partial mesh provides enhanced redundancy and reliability by connecting critical nodes directly, suitable for larger, high-traffic networks requiring fault tolerance and load balancing. Choosing between star and partial mesh depends on balancing network size, budget, performance needs, and desired resilience against potential failures.
Star Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com