Puppet is an open-source configuration management tool that automates the provisioning, configuration, and management of infrastructure across your entire IT environment. It uses declarative language to define system configurations, ensuring consistency and reducing manual errors. Discover how Puppet can streamline your IT operations and simplify infrastructure management in the rest of this article.
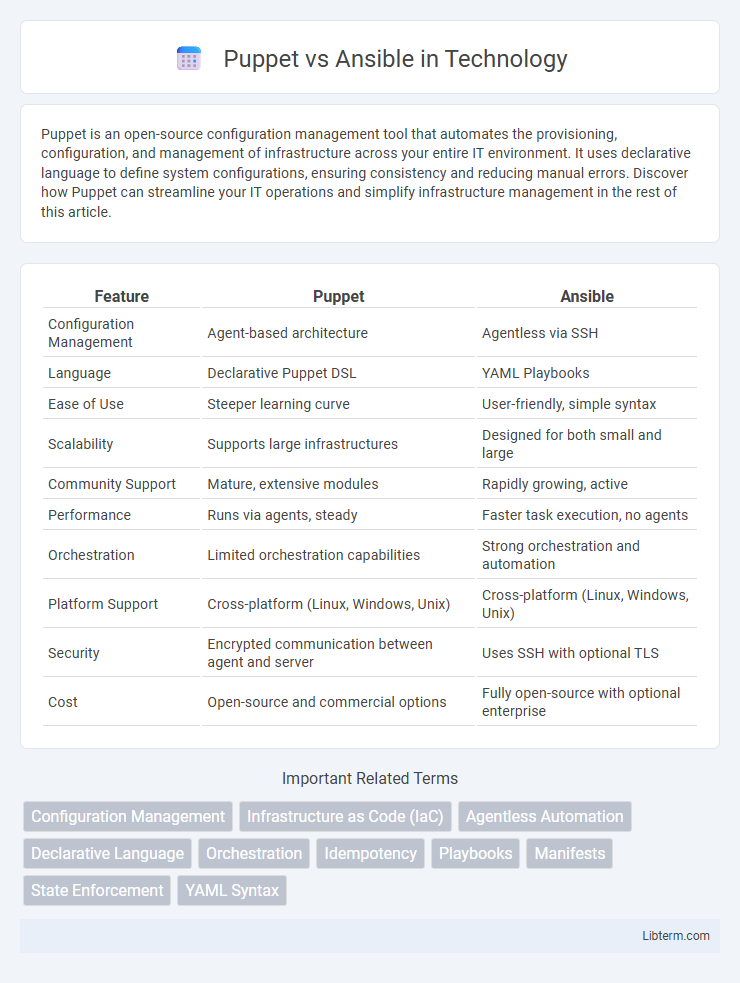
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Puppet | Ansible |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration Management | Agent-based architecture | Agentless via SSH |
| Language | Declarative Puppet DSL | YAML Playbooks |
| Ease of Use | Steeper learning curve | User-friendly, simple syntax |
| Scalability | Supports large infrastructures | Designed for both small and large |
| Community Support | Mature, extensive modules | Rapidly growing, active |
| Performance | Runs via agents, steady | Faster task execution, no agents |
| Orchestration | Limited orchestration capabilities | Strong orchestration and automation |
| Platform Support | Cross-platform (Linux, Windows, Unix) | Cross-platform (Linux, Windows, Unix) |
| Security | Encrypted communication between agent and server | Uses SSH with optional TLS |
| Cost | Open-source and commercial options | Fully open-source with optional enterprise |
Introduction to Puppet and Ansible
Puppet is a configuration management tool that automates the deployment and management of infrastructure using a declarative language to define system states. Ansible employs agentless architecture and uses YAML-based playbooks to simplify automation tasks across multi-tier IT environments. Both tools enhance IT orchestration by streamlining application deployment, configuration, and continuous delivery processes.
Core Differences between Puppet and Ansible
Puppet operates on a declarative model using a master-agent architecture, managing configurations through a compiled catalog system, while Ansible employs an agentless, push-based approach leveraging SSH for task execution. Puppet's domain-specific language (DSL) allows for complex state definitions and long-term node management, whereas Ansible uses YAML-based playbooks focusing on simplicity and ad-hoc automation. Ansible excels in ease of use and quick deployment with less infrastructure overhead, contrasting with Puppet's strength in large-scale, continuous infrastructure management and compliance enforcement.
Architecture Overview: Puppet vs Ansible
Puppet uses a master-agent architecture where the Puppet master controls configuration data and agents run on nodes to pull configurations, enabling scalable and consistent management across large infrastructures. Ansible operates with an agentless architecture relying on SSH or WinRM for direct, push-based communication from a control node to managed systems, simplifying deployment and reducing overhead. Puppet's declarative model contrasts with Ansible's procedural playbooks, influencing their respective architectures and use cases in infrastructure automation.
Language and Syntax Comparison
Puppet uses a declarative language called Puppet DSL, designed specifically for configuration management, making it straightforward to describe system states but with a steeper learning curve for beginners. Ansible leverages YAML for its playbooks, which offers a simple, human-readable syntax that accelerates adoption and reduces complexity. The choice between Puppet's domain-specific language and Ansible's YAML often depends on the team's familiarity with programming concepts and the need for expressiveness versus simplicity in automation tasks.
Configuration Management Features
Puppet offers a model-driven approach with a robust declarative language for defining system configurations, enabling automated enforcement and detailed reporting across large infrastructures. Ansible utilizes YAML-based playbooks and a push-based architecture that simplifies configuration management and supports agentless operation for seamless integration and real-time orchestration. Both tools provide idempotency and extensive module libraries, but Puppet excels in state enforcement while Ansible prioritizes ease of use and flexibility in configuration deployment.
Scalability and Performance
Puppet excels in managing large-scale infrastructure with a model-driven approach that ensures consistent configuration enforcement across thousands of nodes, making it ideal for complex, enterprise environments. Ansible offers agentless architecture and efficient SSH-based execution, enabling faster deployment times and better performance in dynamic or smaller-scale setups where rapid scalability is required. Both tools scale effectively, but Puppet's declarative language suits stable, long-term configurations while Ansible's procedural playbooks optimize for agile, performance-centric automation.
Ease of Setup and Use
Puppet requires a more complex setup involving a master-agent architecture, making initial configuration time-consuming and requiring deeper knowledge of Ruby and Puppet DSL. Ansible uses an agentless architecture relying on SSH, which simplifies installation and makes it accessible for users with basic Linux command-line skills. Ansible's YAML-based playbooks promote readability and faster learning curves compared to Puppet's declarative manifests.
Community Support and Ecosystem
Puppet boasts a mature community with extensive modules available in the Puppet Forge, supporting diverse automation needs and seamless integration with major cloud platforms. Ansible features a vibrant community and a rapidly growing ecosystem, with Ansible Galaxy providing thousands of reusable roles and collections that enhance configuration management and orchestration. Both tools benefit from active forums, regular updates, and strong vendor backing, ensuring continuous improvement and robust support for enterprise automation.
Security and Compliance
Puppet enforces security and compliance through its robust role-based access control (RBAC) and detailed audit logging, enabling precise user permissions and comprehensive tracking of configuration changes. Ansible emphasizes security with agentless architecture, minimizing attack surfaces, and integrates seamlessly with secrets management tools like HashiCorp Vault for secure credential handling. Both tools support policy as code frameworks, facilitating automated compliance checks and consistent enforcement of security baselines across infrastructures.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Puppet excels in managing complex infrastructure with its model-driven approach and strong support for immutable infrastructure, making it ideal for large-scale, enterprise environments requiring detailed compliance and reporting. Ansible offers simplicity and agentless architecture, favoring smaller teams or those needing quick automation with an easier learning curve and rapid deployment. Evaluating infrastructure size, existing skill sets, and specific use cases like configuration management or orchestration helps determine whether Puppet's robust capabilities or Ansible's flexibility aligns better with organizational requirements.
Puppet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com