Hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud environments to deliver scalable, flexible, and secure IT solutions tailored to your business needs. This approach optimizes workload distribution, enhances data security, and enables seamless integration across platforms. Explore the full article to discover how hybrid cloud can transform your organization's technology strategy.
Table of Comparison
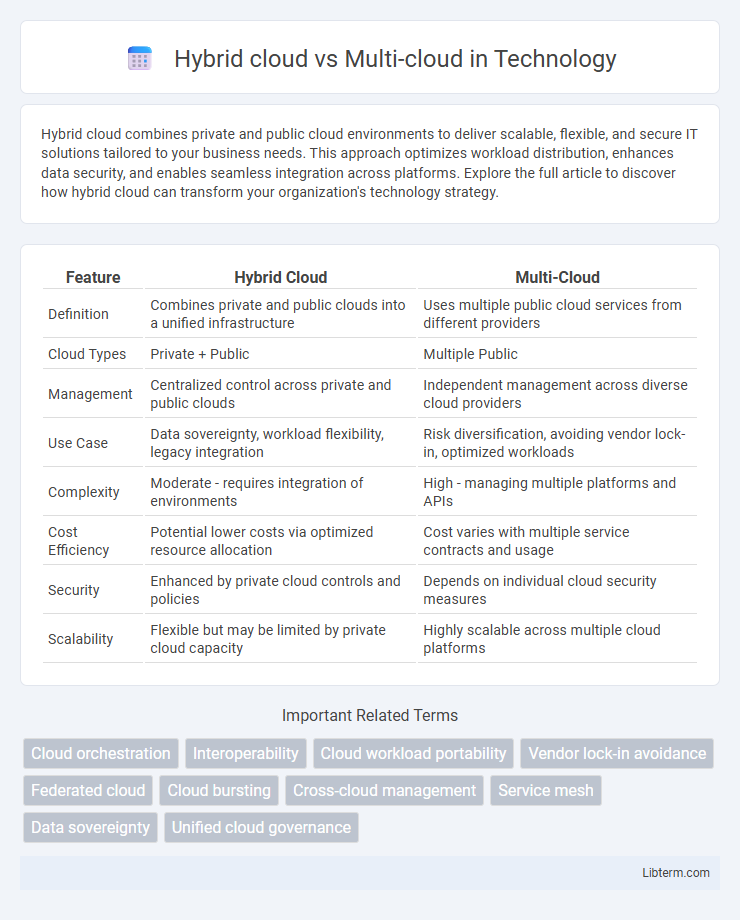
| Feature | Hybrid Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines private and public clouds into a unified infrastructure | Uses multiple public cloud services from different providers |
| Cloud Types | Private + Public | Multiple Public |
| Management | Centralized control across private and public clouds | Independent management across diverse cloud providers |
| Use Case | Data sovereignty, workload flexibility, legacy integration | Risk diversification, avoiding vendor lock-in, optimized workloads |
| Complexity | Moderate - requires integration of environments | High - managing multiple platforms and APIs |
| Cost Efficiency | Potential lower costs via optimized resource allocation | Cost varies with multiple service contracts and usage |
| Security | Enhanced by private cloud controls and policies | Depends on individual cloud security measures |
| Scalability | Flexible but may be limited by private cloud capacity | Highly scalable across multiple cloud platforms |
Understanding Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud: Key Definitions
Hybrid cloud integrates private and public cloud environments, enabling seamless data and application portability for optimized workload management. Multi-cloud involves using multiple cloud services from different providers simultaneously to enhance redundancy, minimize vendor lock-in, and improve performance. Understanding these definitions clarifies strategic cloud adoption tailored to business agility and scalability needs.
Architecture Differences: Hybrid Cloud vs Multi-Cloud
Hybrid cloud architecture integrates private and public cloud environments, enabling seamless data and application portability between on-premises infrastructure and external cloud services. Multi-cloud architecture involves deploying workloads across multiple public cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in, optimize performance, and leverage specific cloud service strengths. The key difference lies in hybrid cloud's combination of private and public clouds versus multi-cloud's use of multiple public clouds without on-premises integration.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Hybrid cloud solutions offer enhanced flexibility by integrating private and public cloud environments, allowing businesses to optimize workload distribution based on performance, security, and cost considerations. They provide improved data security and compliance by keeping sensitive data on private clouds while leveraging public clouds for scalability and disaster recovery. Hybrid clouds also facilitate seamless application portability and scalability, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to changing business demands with minimal disruption.
Advantages of Multi-Cloud Strategies
Multi-cloud strategies provide enhanced flexibility by allowing organizations to leverage the best services from multiple cloud providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, optimizing performance and cost efficiency. They reduce dependency on a single vendor, increasing resilience and minimizing risks of downtime or vendor lock-in. Furthermore, multi-cloud environments improve compliance by enabling data residency and governance tailored to regional regulations.
Use Cases: When to Choose Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud is ideal for organizations needing to balance on-premises infrastructure with public cloud flexibility, especially in regulated industries requiring strict data compliance and security. Use cases include disaster recovery solutions, where sensitive data remains on-site while leveraging public clouds for backup, and workloads demanding low latency or legacy system integration. This approach supports gradual cloud adoption, enabling businesses to optimize costs and performance by dynamically allocating resources across private and public environments.
Use Cases: When to Adopt Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud adoption is ideal for organizations seeking to minimize vendor lock-in by distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Enterprises with diverse geographic operations benefit from multi-cloud to optimize latency and meet regional compliance requirements like GDPR or HIPAA. Also, multi-cloud supports high availability and disaster recovery strategies by leveraging different providers' unique capabilities and infrastructure resilience.
Security Considerations in Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Hybrid cloud environments combine private and public clouds, requiring robust security measures like encryption, identity management, and unified policy enforcement to protect data across different infrastructures. Multi-cloud strategies involve using multiple public cloud providers, increasing complexity in securing data due to varying security protocols, necessitating advanced solutions like cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and consistent compliance monitoring. Both environments demand vigilant threat detection, risk assessment, and continuous security updates to mitigate vulnerabilities inherent in disparate cloud services.
Cost Comparison: Hybrid Cloud vs Multi-Cloud
Hybrid cloud typically reduces costs by combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources, optimizing workload placement for cost-efficiency. Multi-cloud can increase expenses due to managing multiple providers, data transfer fees, and complex integration requirements. Understanding workload patterns and vendor pricing models is essential to minimize total cost of ownership in both hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.
Management and Integration Challenges
Hybrid cloud environments often face complex management challenges due to the need to seamlessly integrate on-premises infrastructure with multiple public cloud services, requiring unified monitoring tools and consistent security policies. Multi-cloud strategies exacerbate integration difficulties by involving multiple public cloud providers, each with distinct APIs and management consoles, complicating automation and governance. Effective management demands robust cloud management platforms that support interoperability, comprehensive visibility, and streamlined orchestration across diverse cloud environments.
Future Trends in Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Computing
Hybrid cloud and multi-cloud environments are evolving rapidly, driven by increasing demands for flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency in enterprise IT strategies. Future trends emphasize enhanced AI-driven workload management, improved interoperability standards, and advanced security frameworks to streamline operations across diverse cloud platforms. Emerging technologies such as edge computing integration and serverless architectures will further optimize performance and resource allocation in both hybrid and multi-cloud deployments.
Hybrid cloud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com