A load balancer efficiently distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed, enhancing system reliability and performance. It optimizes resource use, maximizes throughput, reduces latency, and prevents downtime by balancing the load dynamically. Explore the rest of this article to understand how implementing a load balancer can improve your network's efficiency and scalability.
Table of Comparison
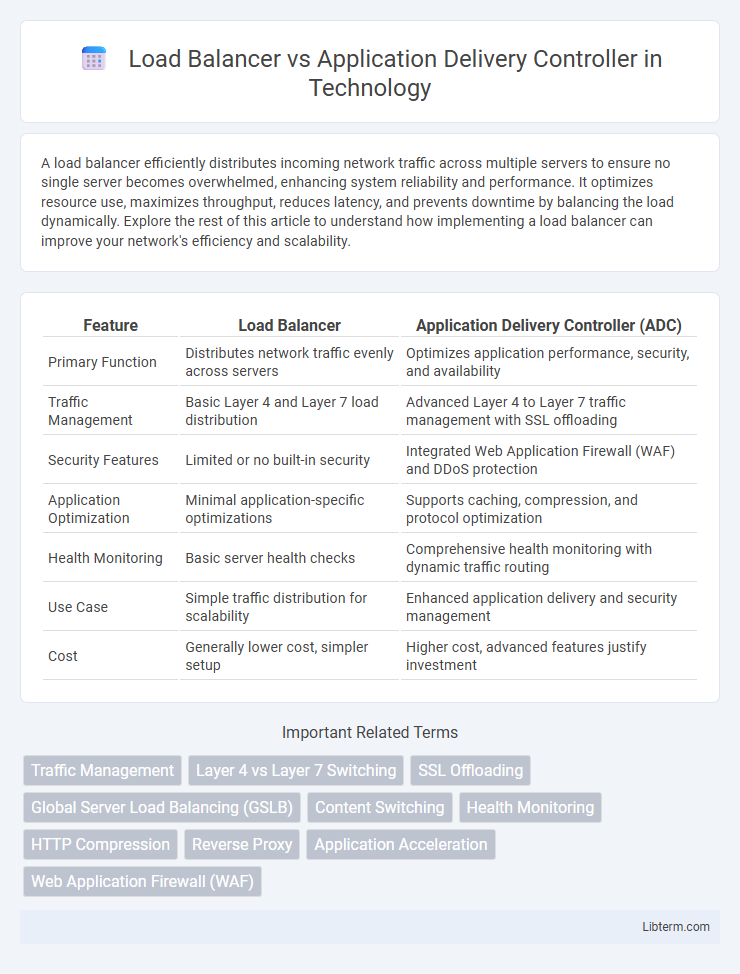
| Feature | Load Balancer | Application Delivery Controller (ADC) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distributes network traffic evenly across servers | Optimizes application performance, security, and availability |
| Traffic Management | Basic Layer 4 and Layer 7 load distribution | Advanced Layer 4 to Layer 7 traffic management with SSL offloading |
| Security Features | Limited or no built-in security | Integrated Web Application Firewall (WAF) and DDoS protection |
| Application Optimization | Minimal application-specific optimizations | Supports caching, compression, and protocol optimization |
| Health Monitoring | Basic server health checks | Comprehensive health monitoring with dynamic traffic routing |
| Use Case | Simple traffic distribution for scalability | Enhanced application delivery and security management |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, simpler setup | Higher cost, advanced features justify investment |
Introduction to Load Balancers and Application Delivery Controllers
Load balancers distribute network traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability and optimize resource use, improving application availability and performance. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) extend load balancing capabilities by incorporating advanced features such as SSL offloading, web application firewall, and application acceleration for enhanced security and efficiency. Both technologies play critical roles in modern IT infrastructure by managing traffic flow and enhancing the user experience.
Definitions: What is a Load Balancer?
A Load Balancer is a network device that distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability and optimize resource use. It operates at layers 4 and 7 of the OSI model, balancing TCP and HTTP/HTTPS requests to prevent server overload and enhance application availability. Load Balancers improve fault tolerance by automatically detecting server health and rerouting traffic to healthy nodes.
Definitions: What is an Application Delivery Controller?
An Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is a network device that optimizes the delivery of applications by managing and directing traffic between users and servers. It provides advanced functionalities such as load balancing, application acceleration, security features, and traffic management to ensure high availability and performance. Unlike traditional load balancers, ADCs offer deeper application-layer inspection and control, enhancing overall user experience and reliability.
Core Functions of a Load Balancer
A Load Balancer primarily distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability and optimal resource use, enhancing application availability and scalability. It performs health checks, session persistence, and traffic management to maintain seamless service delivery and avoid server overload. Unlike an Application Delivery Controller, which includes advanced features like application acceleration and security, a Load Balancer focuses on load distribution and traffic optimization at the network level.
Key Capabilities of an Application Delivery Controller
An Application Delivery Controller (ADC) extends beyond basic load balancing by offering advanced traffic management, application acceleration, and enhanced security features such as SSL offloading, web application firewall integration, and application-layer monitoring. Key capabilities include intelligent routing based on application health and user context, support for Layer 7 (application layer) traffic inspection, and optimization techniques like caching and compression to improve application performance. ADCs also provide detailed analytics and centralized control for application delivery, enabling seamless scalability and high availability across distributed environments.
Feature Comparison: Load Balancer vs ADC
Load balancers primarily distribute network traffic to ensure server availability and optimize resource use, focusing on Layer 4 TCP/UDP load distribution. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) provide advanced features including Layer 7 traffic management, SSL offloading, web application firewall (WAF) integration, and application acceleration for enhanced security and performance. While load balancers efficiently manage basic traffic routing, ADCs deliver comprehensive application optimization and security capabilities essential for modern, complex web environments.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Load balancers optimize network traffic by distributing incoming requests across multiple servers, enhancing overall system performance and ensuring high availability during peak loads. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) provide advanced features such as SSL offloading, web acceleration, and application-layer security, which improve application responsiveness and security while maintaining scalability. Both solutions support horizontal scaling, but ADCs offer greater flexibility in handling complex traffic management and performance optimization for enterprise-level applications.
Security Enhancements: How ADCs Differ
Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) offer advanced security enhancements beyond traditional Load Balancers by integrating features such as Web Application Firewalls (WAF), SSL offloading, and DDoS protection. These capabilities allow ADCs to inspect, filter, and encrypt traffic while mitigating threats at the application layer, providing comprehensive defense mechanisms. Load Balancers primarily distribute traffic for availability and performance but typically lack the deep security functionalities embedded in ADCs.
Use Cases: When to Choose Load Balancer or ADC
Load balancers are ideal for distributing network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability and improved response times in web applications and basic server environments. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) provide advanced features such as SSL offloading, application acceleration, and security policies, making them suitable for complex enterprise environments requiring enhanced application performance and security. Choose a load balancer for straightforward traffic distribution and an ADC when application-layer control, optimization, and integrated security are critical.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Application Architecture
A Load Balancer efficiently distributes network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability and reliability, making it ideal for basic traffic management in scalable application architectures. An Application Delivery Controller (ADC) goes beyond load balancing by integrating advanced features like SSL offloading, web application firewall, and application acceleration, providing enhanced security and optimized performance for complex and mission-critical applications. Choosing the right solution depends on your application's specific requirements for scalability, security, and performance optimization, with Load Balancers suited for straightforward distribution and ADCs for comprehensive application delivery and control.
Load Balancer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com