Effective certificate management ensures the secure issuance, renewal, and revocation of digital certificates critical for protecting sensitive data and authenticating users and devices. Implementing automated tools and strict policies helps minimize security risks and operational disruptions caused by expired or compromised certificates. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to optimize your certificate management strategy for enhanced cybersecurity.
Table of Comparison
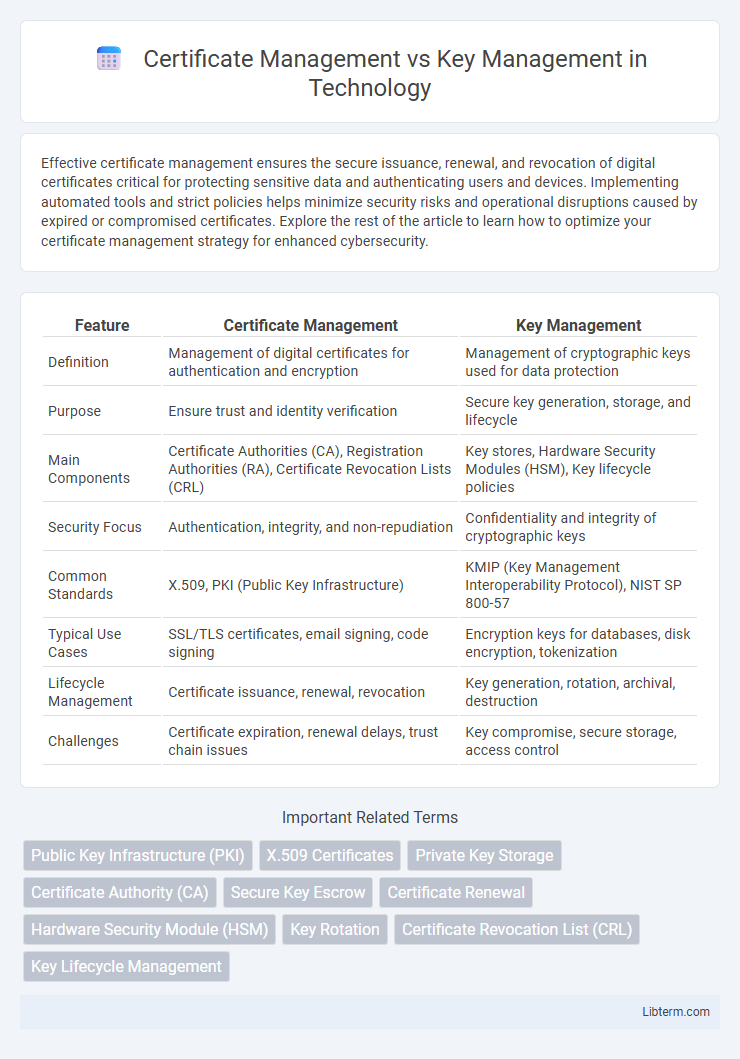
| Feature | Certificate Management | Key Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of digital certificates for authentication and encryption | Management of cryptographic keys used for data protection |
| Purpose | Ensure trust and identity verification | Secure key generation, storage, and lifecycle |
| Main Components | Certificate Authorities (CA), Registration Authorities (RA), Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL) | Key stores, Hardware Security Modules (HSM), Key lifecycle policies |
| Security Focus | Authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation | Confidentiality and integrity of cryptographic keys |
| Common Standards | X.509, PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) | KMIP (Key Management Interoperability Protocol), NIST SP 800-57 |
| Typical Use Cases | SSL/TLS certificates, email signing, code signing | Encryption keys for databases, disk encryption, tokenization |
| Lifecycle Management | Certificate issuance, renewal, revocation | Key generation, rotation, archival, destruction |
| Challenges | Certificate expiration, renewal delays, trust chain issues | Key compromise, secure storage, access control |
Understanding Certificate Management
Certificate management involves the processes of issuing, renewing, revoking, and validating digital certificates to establish trust and secure communications in a network. It ensures identity verification by managing Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) components such as Certificate Authorities (CAs) and Registration Authorities (RAs). Effective certificate management reduces security risks like expired certificates or misconfigurations that could lead to unauthorized access or data breaches.
Key Management: An Overview
Key management involves the generation, distribution, storage, and destruction of cryptographic keys, ensuring secure communication and data protection across digital systems. Effective key management minimizes the risk of unauthorized access by enforcing strict policies for key lifecycle management, including periodic rotation and secure backup. Unlike certificate management, which focuses on the issuance and validation of digital certificates, key management is critical for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of cryptographic operations.
Core Differences Between Certificates and Keys
Certificates serve as digital documents that authenticate the identity of entities by binding public keys with organizational information through a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Keys, specifically cryptographic keys, are the fundamental elements used to encrypt and decrypt data, with private keys requiring stringent protection to maintain security. The core difference lies in certificates providing verified identity and trust frameworks, while keys enable secure encryption and decryption processes within cryptographic systems.
Key Functions of Certificate Management
Certificate Management involves the lifecycle handling of digital certificates, including issuance, renewal, revocation, and storage to ensure trust in PKI (Public Key Infrastructure). Key functions focus on validating identities, enabling secure communications, and maintaining certificate repositories to prevent unauthorized access. Effective Certificate Management supports compliance by automating expiration tracking and integrating with directory services for scalable certificate deployment.
Essential Tasks in Key Management
Key management involves crucial tasks such as generating, storing, distributing, and revoking cryptographic keys to ensure secure data encryption and authentication processes. It requires implementing policies for key lifecycle management, including periodic key rotation and backup to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Effective key management integrates access control mechanisms and auditing to maintain compliance with security standards and protect sensitive information.
Security Challenges in Certificate Management
Certificate management faces significant security challenges such as the risk of certificate expiration leading to service disruptions and increased vulnerability to cyberattacks. Mismanagement of public key infrastructure (PKI) can result in unauthorized certificate issuance, undermining trust and enabling man-in-the-middle attacks. Effective certificate revocation and timely updates are critical to maintaining robust security and preventing compromised certificates from being exploited.
Key Management: Common Risks and Solutions
Key management involves securing cryptographic keys throughout their lifecycle, encompassing generation, storage, distribution, rotation, and destruction. Common risks include key compromise, unauthorized access, poor key storage practices, and insufficient key rotation, leading to data breaches and cryptographic failures. Effective solutions involve implementing Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), enforcing strict access controls, automating key rotation, and employing robust key backup and recovery procedures to ensure integrity and confidentiality.
Tools and Best Practices for Certificate Management
Effective certificate management relies on specialized tools such as Venafi, DigiCert CertCentral, and Let's Encrypt ACME clients that automate the issuance, renewal, and revocation of digital certificates to ensure secure communications. Best practices emphasize continuous monitoring for certificate expiration, deployment of automated alerts, and integration with identity and access management (IAM) systems to prevent service disruptions and enhance security posture. Centralized certificate repositories and role-based access controls (RBAC) further streamline management and minimize risks associated with unauthorized access or certificate misuse.
Best Practices for Effective Key Management
Effective key management involves implementing strict access controls, regular key rotation, and secure storage mechanisms such as hardware security modules (HSMs) to protect cryptographic keys from unauthorized access or compromise. Unlike certificate management, which focuses on the lifecycle of digital certificates including issuance, renewal, and revocation, key management emphasizes the generation, distribution, usage, and destruction of cryptographic keys to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. Adopting automated key management solutions and maintaining comprehensive audit trails are best practices that enhance security and compliance in protecting sensitive cryptographic material.
Certificate Management vs Key Management: Which Do You Need?
Certificate management involves the lifecycle administration of digital certificates, ensuring authentication, encryption, and secure communication, whereas key management focuses on generating, distributing, storing, and revoking cryptographic keys essential for data protection. Organizations require certificate management to maintain trust and validate identities in networks, while key management is critical for safeguarding the encryption keys that protect sensitive information. The choice depends on whether the priority is managing digital identities and certificates or securing cryptographic keys to enforce data confidentiality and integrity.
Certificate Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com