Circuit breaking is a crucial pattern in software architecture designed to prevent system failures by stopping the flow of requests to a failing service. It helps maintain system stability and improves fault tolerance by monitoring error rates and temporarily halting interactions when thresholds are exceeded. Discover how implementing circuit breaking can safeguard Your applications and enhance overall performance in the following article.
Table of Comparison
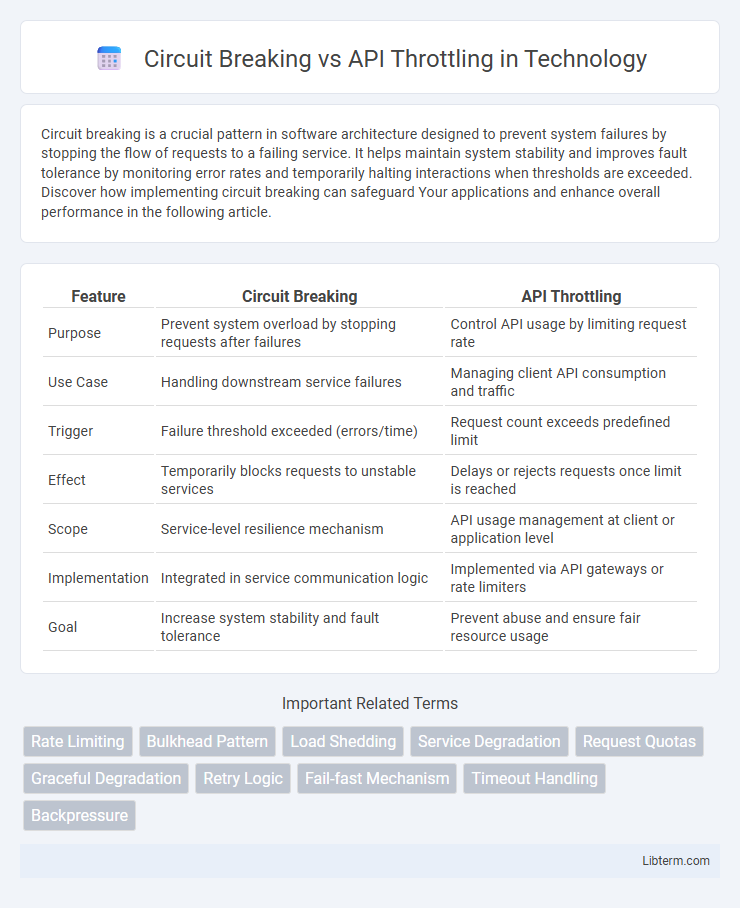
| Feature | Circuit Breaking | API Throttling |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevent system overload by stopping requests after failures | Control API usage by limiting request rate |
| Use Case | Handling downstream service failures | Managing client API consumption and traffic |
| Trigger | Failure threshold exceeded (errors/time) | Request count exceeds predefined limit |
| Effect | Temporarily blocks requests to unstable services | Delays or rejects requests once limit is reached |
| Scope | Service-level resilience mechanism | API usage management at client or application level |
| Implementation | Integrated in service communication logic | Implemented via API gateways or rate limiters |
| Goal | Increase system stability and fault tolerance | Prevent abuse and ensure fair resource usage |
Introduction to Circuit Breaking and API Throttling
Circuit breaking and API throttling are essential mechanisms for managing system reliability and performance in distributed applications. Circuit breaking prevents cascading failures by temporarily halting requests to a failing service, allowing it to recover before resuming traffic. API throttling controls the rate of incoming requests to an API, protecting backend services from overload and ensuring fair resource usage among clients.
Definition of Circuit Breaking
Circuit breaking is a design pattern used in microservices to detect failures and prevent cascading system crashes by temporarily halting requests to a failing service. It monitors service health and automatically switches to a fallback mode when error thresholds are exceeded, improving system resilience. Unlike API throttling, which limits the rate of requests to manage traffic, circuit breaking focuses on fault tolerance and failure isolation.
Definition of API Throttling
API throttling is a mechanism that controls the rate at which clients can send requests to an API, ensuring system stability by preventing traffic overload. It limits the number of API calls within a specified time window, protecting backend services from excessive use and maintaining performance. Circuit breaking, in contrast, temporarily halts requests to a failing service to prevent cascading failures, while throttling focuses on controlling request frequency regardless of service health.
Key Differences Between Circuit Breaking and API Throttling
Circuit breaking and API throttling serve distinct purposes in system resilience and traffic management. Circuit breaking prevents system overload by stopping requests when a service is failing, allowing recovery and avoiding cascading failures, whereas API throttling controls the rate of incoming requests to maintain performance and resource limits. Key differences include circuit breaking's focus on fault tolerance and service health, contrasted with throttling's emphasis on limiting request rates to prevent abuse and ensure fair usage.
Use Cases for Circuit Breaking
Circuit breaking prevents cascading failures in distributed systems by stopping requests to a failing service, essential in microservices architectures to maintain system stability during outages or degraded performance. It is particularly useful in scenarios with unreliable third-party APIs or resource-intensive operations that risk overwhelming services, enabling graceful degradation and faster recovery. By contrast, API throttling controls traffic volume to manage resource consumption, while circuit breaking dynamically responds to failure conditions to ensure resilience.
Use Cases for API Throttling
API throttling controls the number of requests a client can make within a specified time frame, preventing system overloads during peak usage and ensuring fair resource distribution among users. Use cases for API throttling include protecting backend services from excessive traffic spikes, managing costs by limiting access to premium features, and maintaining consistent Quality of Service (QoS) in multi-tenant environments. This mechanism is essential for APIs exposed to public or high-volume consumers, such as social media platforms, payment gateways, and cloud service providers.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Circuit Breaking
Circuit breaking improves system resilience by preventing cascading failures and reducing downtime during service outages, ensuring better fault isolation in microservices architectures. However, it may cause temporary service disruptions for users when the circuit is open and requires careful threshold tuning to avoid premature or delayed triggering. Unlike API throttling, which limits request rates to manage load and prevent abuse, circuit breaking focuses on gracefully handling failing dependencies to maintain overall system stability.
Benefits and Drawbacks of API Throttling
API throttling helps control the rate of incoming requests to maintain system stability and prevent server overload, ensuring fair resource allocation among users. It enhances overall performance and protects backend services from traffic spikes, but excessive throttling may frustrate users by limiting access to APIs and causing request failures. Balancing throughput limits with user experience is critical to maximize benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Best Practices for Implementation
Implement circuit breaking by setting failure thresholds and fallback mechanisms to prevent cascading system failures and maintain service stability under high error rates. Implement API throttling with rate limits based on user tiers or IP addresses to control traffic, ensuring equitable resource distribution and protecting backend systems from overload. Combine both techniques to enhance resilience, using circuit breakers to handle fault isolation and throttling for traffic shaping, monitored continuously with real-time metrics to optimize system performance.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your API
Circuit breaking prevents system overload by temporarily halting API requests when failure thresholds are met, enhancing resilience during outages. API throttling controls the rate of incoming requests to maintain optimal performance and fair resource usage among clients. Selecting the right strategy depends on your API's tolerance for failure versus traffic spikes, with circuit breaking ideal for safeguarding against cascading failures and throttling suited for managing usage limits and preventing abuse.
Circuit Breaking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com