API Gateway serves as a critical intermediary that manages, secures, and routes requests between clients and backend services, ensuring efficient communication and traffic control. It offers features such as authentication, rate limiting, and load balancing to protect and optimize your application's API performance. Explore the article to discover how implementing an API Gateway can enhance your system's scalability and security.
Table of Comparison
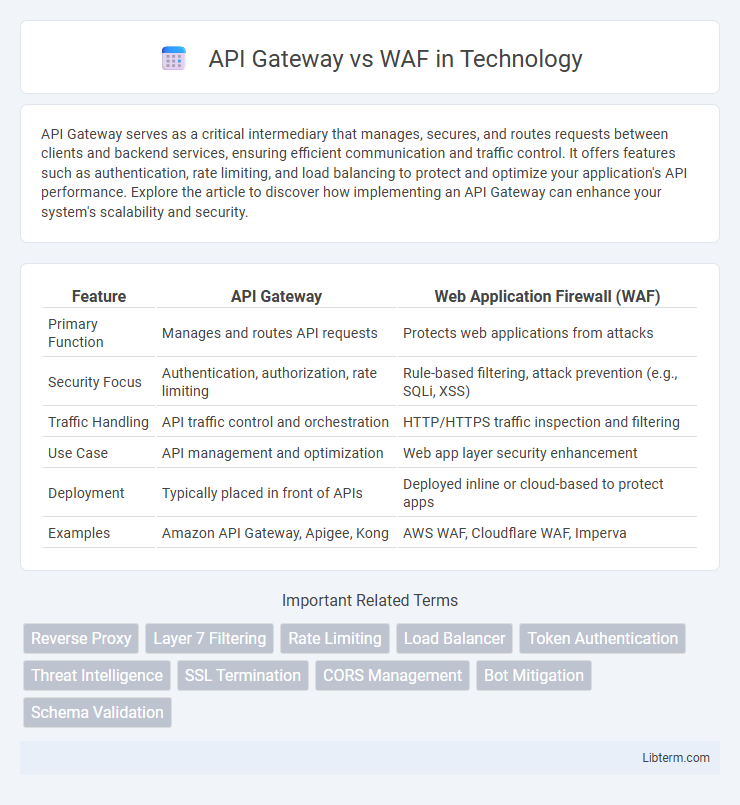
| Feature | API Gateway | Web Application Firewall (WAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages and routes API requests | Protects web applications from attacks |
| Security Focus | Authentication, authorization, rate limiting | Rule-based filtering, attack prevention (e.g., SQLi, XSS) |
| Traffic Handling | API traffic control and orchestration | HTTP/HTTPS traffic inspection and filtering |
| Use Case | API management and optimization | Web app layer security enhancement |
| Deployment | Typically placed in front of APIs | Deployed inline or cloud-based to protect apps |
| Examples | Amazon API Gateway, Apigee, Kong | AWS WAF, Cloudflare WAF, Imperva |
Introduction to API Gateway and WAF
API Gateway acts as a centralized entry point that manages, secures, and routes API traffic between clients and backend services, supporting authentication, traffic control, and protocol translation. Web Application Firewall (WAF) protects web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic, preventing attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and other vulnerabilities. Both API Gateway and WAF enhance security but serve distinct roles: API Gateway focuses on API traffic management, while WAF specializes in defending web application layers.
Core Functions of API Gateways
API Gateways primarily manage and orchestrate API traffic by handling request routing, API composition, and protocol translation, ensuring seamless communication between clients and backend services. They enforce security through authentication, authorization, rate limiting, and request validation, optimizing API performance and reliability. Unlike Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), which focus on protecting applications from common web exploits and attacks, API Gateways provide comprehensive API lifecycle management and traffic control essential for modern microservices architectures.
Key Features of Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
Web Application Firewalls (WAF) provide critical security by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between web applications and the internet, protecting against common threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and DDoS attacks. Key features include customizable rule sets, real-time threat intelligence, and bot mitigation capabilities, ensuring adaptive protection tailored to specific application vulnerabilities. Unlike API Gateways that primarily manage API traffic and integration, WAFs specialize in comprehensive threat detection and prevention for web applications.
Security Capabilities: API Gateway vs WAF
API Gateway secures APIs by managing authentication, rate limiting, and request validation to prevent unauthorized access and abuse, directly protecting API endpoints. WAF (Web Application Firewall) defends web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic for common threats like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and DDoS attacks. While API Gateway focuses on API-specific security policies and traffic management, WAF provides broad application-layer protection against various web vulnerabilities.
Traffic Management: How Each Solution Operates
API Gateway manages traffic by routing API requests efficiently, load balancing, and throttling to ensure optimal performance and uptime. Web Application Firewall (WAF) focuses on inspecting incoming traffic for malicious patterns, blocking attacks, and filtering harmful requests before they reach the server. While API Gateway optimizes traffic flow for legitimate API calls, WAF safeguards the infrastructure by preventing security threats within the traffic.
Use Cases: When to Use API Gateway or WAF
API Gateway is ideal for managing and securing API traffic, enabling features like request routing, authentication, rate limiting, and analytics for microservices and mobile applications. Web Application Firewall (WAF) is best used for protecting web applications from common cyber threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and DDoS attacks by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic. Use an API Gateway when controlling API access and enforcing policies at the API level, and deploy a WAF to safeguard web applications by inspecting incoming traffic for malicious patterns.
Integration with Cloud Services and DevOps
API Gateway seamlessly integrates with cloud services such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Run, enabling streamlined deployment and management of APIs within DevOps pipelines using tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and Terraform. In contrast, WAF (Web Application Firewall) focuses on security, often integrating with cloud security offerings like AWS Shield, Azure Security Center, and Google Cloud Armor to protect web applications while supporting CI/CD workflows through automated rule deployment and monitoring. Both tools enhance DevOps efficiency; API Gateway facilitates API lifecycle management and scalability, whereas WAF ensures application security compliance within cloud-based development environments.
Performance Impact and Scalability Comparison
API Gateway offers efficient request routing and load balancing, enhancing scalability by distributing traffic across multiple services while minimizing latency. Web Application Firewall (WAF) focuses on security filtering, which can introduce additional processing overhead and impact performance under high traffic conditions. Scalability in API Gateway is typically more dynamic due to built-in support for auto-scaling and API throttling, whereas WAF scalability depends on its underlying infrastructure and may require more resources to maintain low latency.
Cost Considerations: Pricing Models Explained
API Gateway pricing typically relies on request volume, data transfer, and the number of APIs managed, while WAF costs are primarily influenced by traffic volume, rule sets applied, and protection features enabled. API Gateways often use pay-as-you-go or tiered pricing models based on API calls, whereas WAFs may charge based on the number of rules, requests filtered, and additional security services. Evaluating total cost includes examining both fixed and variable expenses, potential scaling costs, and integration with existing infrastructure to optimize budget efficiency.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Web Applications
API Gateway focuses on managing, securing, and monitoring API traffic with features like request routing, rate limiting, and authentication, making it ideal for complex microservices architectures. WAF (Web Application Firewall) prioritizes protecting web applications from common exploits such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and DDoS attacks by analyzing HTTP/HTTPS traffic. Selecting the right solution depends on whether your primary need is API traffic management and developer experience (API Gateway) or comprehensive security against web threats (WAF) for your web applications.
API Gateway Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com