Bandit testing is a dynamic strategy used to optimize decision-making by continuously allocating more resources to higher-performing options based on real-time feedback. This method enhances conversion rates and user engagement by balancing exploration of new variations with exploitation of proven winners. Discover how bandit testing can transform Your optimization efforts in the full article.
Table of Comparison
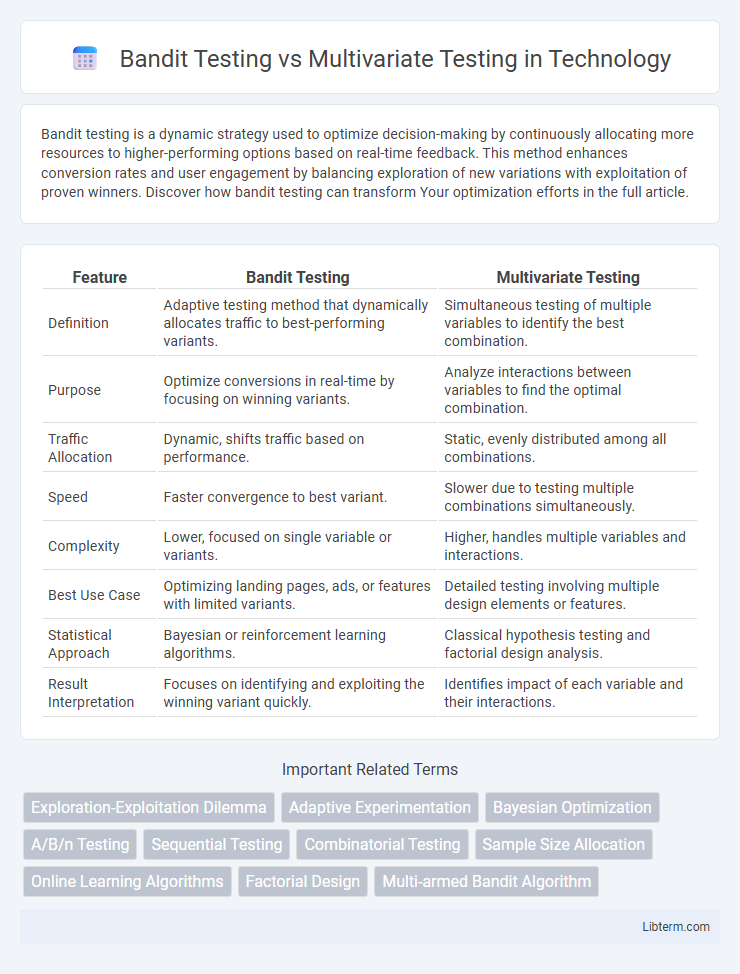
| Feature | Bandit Testing | Multivariate Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adaptive testing method that dynamically allocates traffic to best-performing variants. | Simultaneous testing of multiple variables to identify the best combination. |
| Purpose | Optimize conversions in real-time by focusing on winning variants. | Analyze interactions between variables to find the optimal combination. |
| Traffic Allocation | Dynamic, shifts traffic based on performance. | Static, evenly distributed among all combinations. |
| Speed | Faster convergence to best variant. | Slower due to testing multiple combinations simultaneously. |
| Complexity | Lower, focused on single variable or variants. | Higher, handles multiple variables and interactions. |
| Best Use Case | Optimizing landing pages, ads, or features with limited variants. | Detailed testing involving multiple design elements or features. |
| Statistical Approach | Bayesian or reinforcement learning algorithms. | Classical hypothesis testing and factorial design analysis. |
| Result Interpretation | Focuses on identifying and exploiting the winning variant quickly. | Identifies impact of each variable and their interactions. |
Introduction to Bandit Testing and Multivariate Testing
Bandit Testing leverages adaptive algorithms to dynamically allocate traffic to various options, optimizing for the best-performing variant in real time, which reduces exposure to suboptimal choices. Multivariate Testing simultaneously evaluates multiple variables and their combinations to identify the most effective elements and interactions within a website or campaign. Both methodologies aim to improve conversion rates but differ in approach: Bandit Testing focuses on continuous learning and real-time optimization, while Multivariate Testing seeks comprehensive insights through controlled experimentation.
What is Bandit Testing?
Bandit Testing is an adaptive experimentation technique that dynamically allocates traffic to different variants based on their real-time performance, optimizing for maximum conversion or engagement rates. Unlike traditional A/B or multivariate testing, which divides traffic equally and waits for fixed results, Bandit Testing continuously learns and shifts traffic towards better-performing options, reducing opportunity cost and improving overall test efficiency. This method leverages algorithms such as the Multi-Armed Bandit to balance exploration and exploitation in decision-making under uncertainty.
What is Multivariate Testing?
Multivariate testing evaluates multiple variables simultaneously to determine the best combination of elements that improves user experience and conversion rates. It involves testing different versions of headlines, images, and call-to-action buttons on a webpage to analyze their interaction effects. This method provides detailed insights into which elements work together most effectively, unlike Bandit Testing, which dynamically allocates traffic based on performance to maximize immediate results.
Key Differences Between Bandit and Multivariate Testing
Bandit testing dynamically allocates traffic to variations based on real-time performance, optimizing for maximum conversion rates during the experiment. Multivariate testing simultaneously evaluates multiple variables and their combinations to identify the best performing variant but allocates traffic evenly until the test concludes. Bandit testing adapts quickly to changing user behavior, while multivariate testing provides detailed insights into interaction effects between variables but requires larger sample sizes and longer durations.
Use Cases for Bandit Testing
Bandit testing excels in optimizing real-time decision-making scenarios where rapid adaptation to user behavior is crucial, such as in personalized content recommendations or dynamic pricing models. It effectively balances exploration and exploitation, making it ideal for situations with fluctuating traffic patterns or evolving user preferences. Companies leveraging bandit algorithms benefit from increased conversion rates by continuously allocating traffic toward the best-performing variations without extensive manual intervention.
Use Cases for Multivariate Testing
Multivariate testing is ideal for optimizing complex web pages with multiple variables, such as headlines, images, and call-to-action buttons, allowing marketers to identify the most effective combination. This testing method excels in e-commerce environments where increasing conversion rates through detailed element interplay analysis is critical. Unlike bandit testing, multivariate testing provides granular insights into the impact of individual variations within a single experiment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bandit Testing
Bandit testing dynamically allocates traffic to better-performing variations in real time, significantly reducing the loss from underperforming options compared to traditional multivariate testing. This method excels in rapidly adapting to user behavior changes but may sacrifice the statistical rigor and detailed insight provided by multivariate testing's simultaneous variable analysis. While bandit testing efficiently maximizes conversions during the experiment, it can struggle with complex interactions between multiple variables that multivariate testing is designed to explore comprehensively.
Pros and Cons of Multivariate Testing
Multivariate testing allows marketers to evaluate multiple variables simultaneously, enabling the identification of the most effective combination of elements on a webpage, which can lead to optimized user experience and increased conversion rates. However, it requires a substantial amount of traffic to generate statistically significant results, making it less practical for low-traffic sites. The complexity of analyzing multiple variable interactions can also increase the duration and cost of testing compared to more straightforward methods like bandit testing.
How to Choose Between Bandit and Multivariate Testing
Choosing between Bandit Testing and Multivariate Testing depends on your primary goal and resource availability. Bandit Testing excels in optimizing real-time performance by dynamically allocating traffic to the best-performing variants, ideal for fast decision-making with fewer variants. Multivariate Testing suits scenarios requiring in-depth analysis of multiple variables simultaneously to understand interaction effects, demanding larger sample sizes and longer test durations.
Conclusion: Which Method Suits Your Business Goals?
Bandit testing excels in optimizing real-time decision-making by dynamically allocating traffic based on performance, making it ideal for businesses seeking rapid adaptation and maximized conversions with limited data. Multivariate testing provides comprehensive insights into interactions between multiple variables, suitable for organizations aiming for detailed analysis and long-term strategic improvements. Choosing between the two depends on whether your priority lies in immediate optimization and agility or in-depth understanding of complex variable combinations to drive incremental growth.
Bandit Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com