COPE methods help individuals effectively manage stress and challenges by promoting emotional regulation, problem-solving skills, and social support. These strategies enable you to build resilience and maintain mental well-being during difficult times. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical COPE techniques tailored for your needs.
Table of Comparison
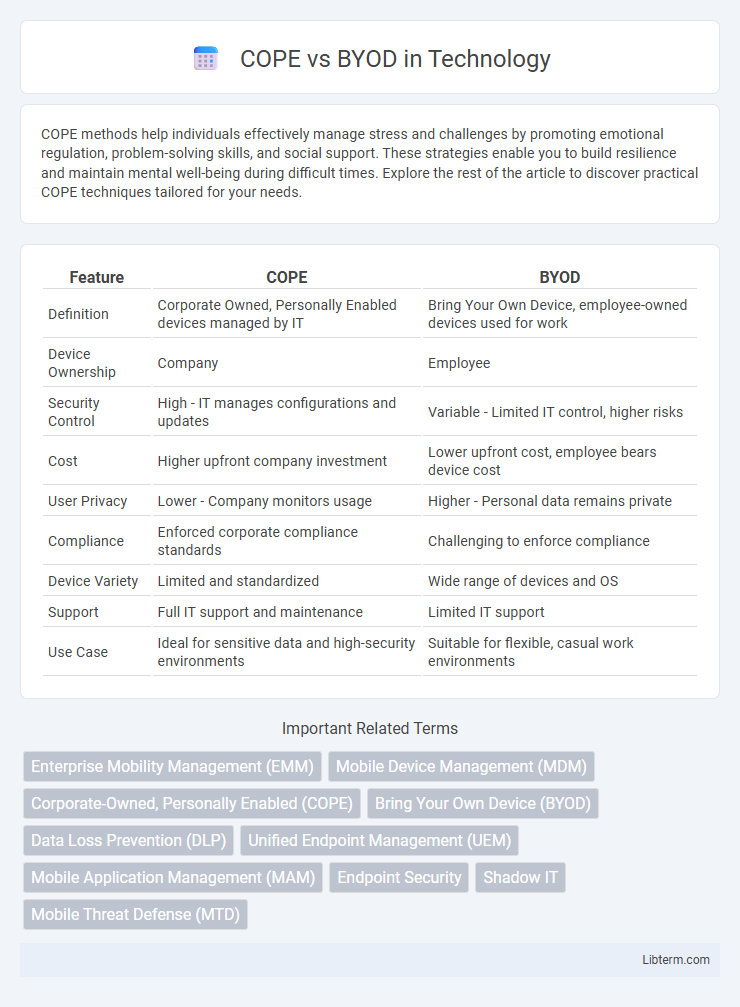
| Feature | COPE | BYOD |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Corporate Owned, Personally Enabled devices managed by IT | Bring Your Own Device, employee-owned devices used for work |
| Device Ownership | Company | Employee |
| Security Control | High - IT manages configurations and updates | Variable - Limited IT control, higher risks |
| Cost | Higher upfront company investment | Lower upfront cost, employee bears device cost |
| User Privacy | Lower - Company monitors usage | Higher - Personal data remains private |
| Compliance | Enforced corporate compliance standards | Challenging to enforce compliance |
| Device Variety | Limited and standardized | Wide range of devices and OS |
| Support | Full IT support and maintenance | Limited IT support |
| Use Case | Ideal for sensitive data and high-security environments | Suitable for flexible, casual work environments |
Introduction to COPE and BYOD
COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled) and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) represent distinct mobile device management strategies in the workplace. COPE involves company-owned devices provided to employees, ensuring enhanced security, standardized software, and easier IT control, while BYOD allows employees to use their personal devices for work, offering flexibility but increasing security risks and management complexity. Understanding these models is crucial for organizations aiming to balance productivity, security, and cost-effectiveness in their device deployment policies.
Defining COPE: Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled
COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled) is a device management strategy where the organization provides employees with company-owned devices that are configured for both professional and personal use. This approach ensures enhanced security and compliance by maintaining corporate control over the hardware and software environment while enabling employees to use their devices for personal tasks. COPE strikes a balance between organizational oversight and user flexibility, differentiating it from BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), where employees use their personal devices for work without corporate ownership.
Understanding BYOD: Bring Your Own Device
BYOD, or Bring Your Own Device, allows employees to use their personal smartphones, tablets, and laptops for work purposes, offering flexibility and cost savings to organizations by reducing the need for company-owned hardware. This approach enhances employee satisfaction and productivity but introduces challenges in managing security risks, data privacy, and device compatibility across multiple platforms. Effective BYOD policies involve implementing Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions, clear security protocols, and user training to protect corporate data while maintaining user convenience.
Key Differences Between COPE and BYOD
COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally-Enabled) provides employees with company-owned devices allowing both personal and business use, ensuring enhanced security and IT control. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) enables employees to use their personal devices for work, offering flexibility but increasing challenges in managing data privacy and security risks. Key differences include ownership, with COPE devices managed and secured by the company, whereas BYOD involves personal devices with variable security and compliance measures.
Security Implications: COPE vs BYOD
COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled) devices offer enhanced security control through centralized management, allowing IT teams to deploy uniform security policies, enforce encryption, and promptly apply patches. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) introduces greater security risks due to varied device types and user-controlled updates, increasing vulnerability to data breaches, malware, and unauthorized access. Enterprises adopting COPE benefit from reduced attack surfaces and better compliance with data protection regulations compared to the decentralized nature of BYOD environments.
Cost Considerations for Businesses
COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled) devices often incur higher upfront costs due to bulk purchasing and standardized hardware, but they offer long-term savings through streamlined management and enhanced security, reducing risks and potential expenses from data breaches. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) presents lower initial investment as employees use personal devices, but businesses may face increased costs from diverse device support, potential security vulnerabilities, and compliance challenges requiring robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions. Evaluating total cost of ownership (TCO) between COPE and BYOD models involves balancing hardware expenditures, IT support complexity, security investments, and employee productivity impacts.
Employee Privacy and Productivity
COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled) devices offer greater control over security and monitoring, which can enhance productivity by minimizing distractions and unauthorized app usage. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) prioritizes employee privacy by allowing use of personal devices, but this can lead to inconsistent security measures and potential productivity challenges due to mixed-use environments. Balancing privacy concerns with productivity outcomes requires careful policy design and clear agreements on data access and monitoring levels.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
COPE (Corporate Owned, Personally Enabled) and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) each present distinct implementation challenges; COPE demands substantial upfront investment in device procurement and management, while BYOD struggles with security risks due to diverse device types and user behavior. Solutions for COPE include deploying Mobile Device Management (MDM) platforms to enforce consistent security policies and streamline device updates, whereas BYOD benefits from robust endpoint security, clear user guidelines, and network segmentation to mitigate vulnerabilities. Balancing user privacy with corporate control remains critical, making unified endpoint management and employee training essential for both approaches' success.
Industry Trends and Adoption Rates
COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled) devices are gaining traction in industries requiring tight security, such as finance and healthcare, with adoption rates increasing by over 30% year-over-year due to enhanced control and compliance capabilities. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) remains popular in sectors prioritizing flexibility and cost savings, maintaining steady adoption rates at approximately 60% across small to medium enterprises. Industry trends indicate a growing hybrid approach, blending COPE's managed security benefits with BYOD's user convenience to address diverse workforce needs.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Selecting the right mobile device management strategy requires analyzing your organization's security needs, budget constraints, and employee flexibility demands. COPE (Corporate Owned, Personally Enabled) offers enhanced security and centralized control, ideal for industries with strict compliance requirements, while BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) promotes cost savings and employee satisfaction by leveraging personal devices. Evaluating factors like data sensitivity, IT resources, and user experience helps determine whether a COPE or BYOD approach aligns best with your organization's operational goals.
COPE Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com