Centralized computing involves consolidating processing power and data storage in a single location, enhancing control and security while simplifying maintenance. This approach reduces redundancy and streamlines resource management across an organization's network. Explore the article to understand how centralized computing can optimize your IT infrastructure and boost operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
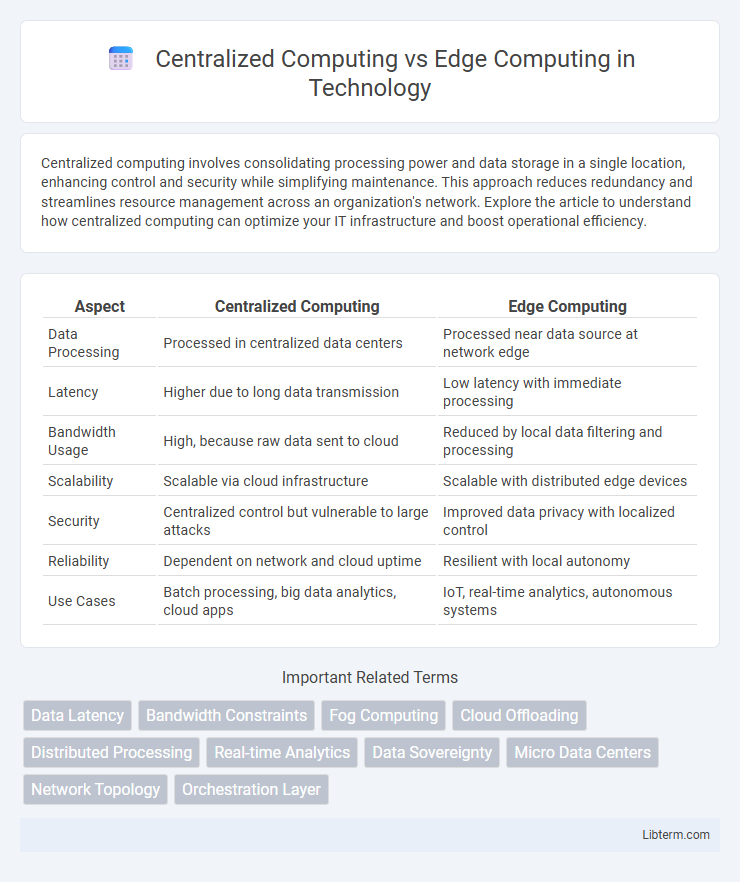
| Aspect | Centralized Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing | Processed in centralized data centers | Processed near data source at network edge |
| Latency | Higher due to long data transmission | Low latency with immediate processing |
| Bandwidth Usage | High, because raw data sent to cloud | Reduced by local data filtering and processing |
| Scalability | Scalable via cloud infrastructure | Scalable with distributed edge devices |
| Security | Centralized control but vulnerable to large attacks | Improved data privacy with localized control |
| Reliability | Dependent on network and cloud uptime | Resilient with local autonomy |
| Use Cases | Batch processing, big data analytics, cloud apps | IoT, real-time analytics, autonomous systems |
Introduction to Centralized and Edge Computing
Centralized computing relies on a single, powerful data center to process and store information, ensuring streamlined management and centralized control of applications and resources. Edge computing distributes data processing closer to the source of data generation, reducing latency and improving real-time responsiveness by leveraging local devices or edge servers. This shift addresses the growing demand for faster data handling in IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities by minimizing reliance on distant centralized servers.
Defining Centralized Computing
Centralized computing refers to the architectural model where all computational resources and data processing occur at a single, centralized data center or server. This approach enables streamlined management, enhanced security, and efficient resource allocation by consolidating processing power and storage in one location. Centralized computing often supports large-scale enterprise applications and cloud services, relying heavily on network connectivity to deliver data and services to end-users.
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby edge servers, minimizing latency and reducing dependency on centralized cloud infrastructures. This decentralized approach enhances real-time data handling for applications such as autonomous vehicles, IoT devices, and smart factories. By distributing computing resources closer to data sources, edge computing improves responsiveness, bandwidth efficiency, and privacy protection compared to traditional centralized computing models.
Core Differences Between Centralized and Edge Computing
Centralized computing relies on a single central server or data center to process and store data, ensuring streamlined management but often causing latency and bandwidth issues for distributed users. Edge computing decentralizes processing by handling data near its source at edge devices, enhancing real-time response and reducing network congestion. Key differences include data proximity, latency, scalability, and dependency on continuous connectivity to central servers.
Advantages of Centralized Computing
Centralized computing offers enhanced data security by consolidating sensitive information within a single, controlled environment, reducing the risk of breaches. It enables streamlined resource management and maintenance, as servers and software updates are handled centrally, improving efficiency and lowering operational costs. High computational power and robust infrastructure in centralized systems support complex processing tasks and large-scale data analytics more effectively than distributed edge devices.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, enhancing real-time decision-making and improving application performance. It decreases bandwidth usage and cloud dependency, resulting in cost savings and increased reliability during network outages. Enhanced security through localized data processing limits exposure to cyber threats and ensures compliance with data privacy regulations.
Key Use Cases for Centralized Computing
Centralized computing excels in large-scale data processing environments such as cloud data centers supporting enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and big data analytics platforms. It is ideal for tasks requiring significant computational power and centralized data storage, including financial transaction processing and centralized content delivery networks (CDNs). Organizations leverage centralized computing to ensure robust security, simplified management, and efficient resource allocation for applications with consistent connectivity and high latency tolerance.
Real-World Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing enables real-time data processing in autonomous vehicles, reducing latency and improving safety through instant decision-making at the source. In smart cities, edge devices manage traffic signals and environmental sensors locally, enhancing responsiveness and lowering bandwidth costs. Industrial IoT leverages edge computing for predictive maintenance, analyzing machine data on-site to prevent downtime and optimize production efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations
Centralized computing faces challenges such as latency issues, bandwidth limitations, and single points of failure that impact real-time data processing and scalability. Edge computing encounters limitations including constrained device resources, security vulnerabilities at distributed nodes, and complex management of heterogeneous edge environments. Both architectures require balancing trade-offs between processing power, network efficiency, and system resilience to optimize overall performance.
Future Trends: Centralized vs Edge Computing
Future trends in centralized computing emphasize enhanced data center scalability, integration of AI-driven resource management, and increased reliance on cloud infrastructures for massive data processing. Edge computing is evolving with advancements in 5G connectivity, real-time analytics, and decentralized processing to reduce latency and improve security in IoT and autonomous systems. The convergence of centralized and edge computing creates hybrid architectures that optimize performance, cost-efficiency, and data sovereignty for diverse applications across industries.
Centralized Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com