Microrepos enable developers to manage small, focused codebases independently within larger projects, enhancing modularity and simplifying maintenance. These lightweight repositories improve collaboration and accelerate deployment by isolating changes to specific components without affecting the entire system. Discover how adopting microrepos can transform your development workflow and boost productivity in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
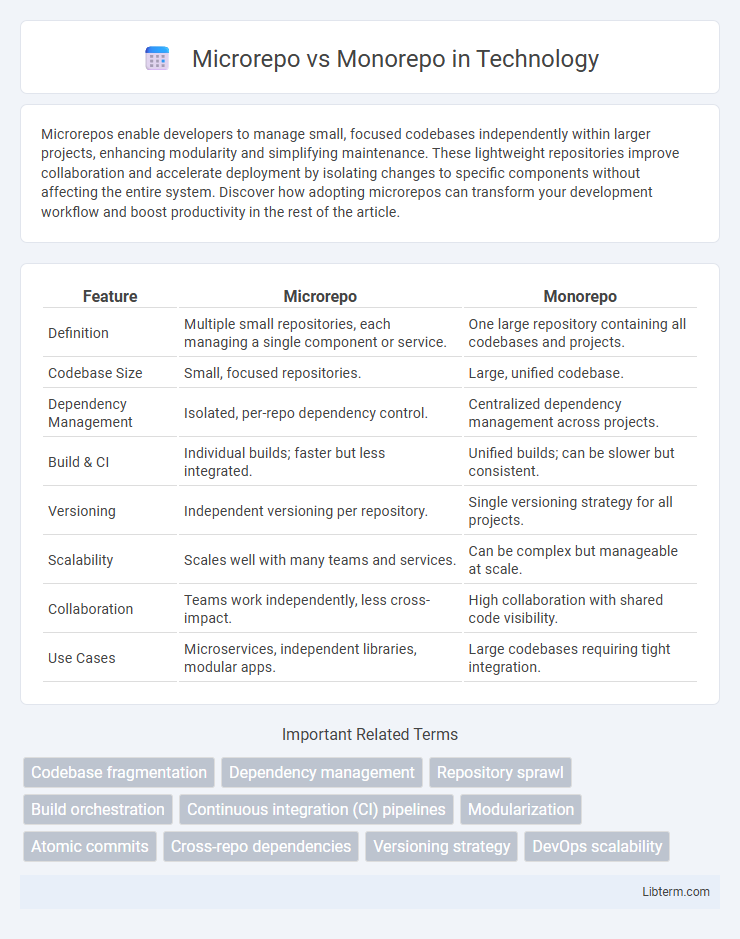
| Feature | Microrepo | Monorepo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple small repositories, each managing a single component or service. | One large repository containing all codebases and projects. |
| Codebase Size | Small, focused repositories. | Large, unified codebase. |
| Dependency Management | Isolated, per-repo dependency control. | Centralized dependency management across projects. |
| Build & CI | Individual builds; faster but less integrated. | Unified builds; can be slower but consistent. |
| Versioning | Independent versioning per repository. | Single versioning strategy for all projects. |
| Scalability | Scales well with many teams and services. | Can be complex but manageable at scale. |
| Collaboration | Teams work independently, less cross-impact. | High collaboration with shared code visibility. |
| Use Cases | Microservices, independent libraries, modular apps. | Large codebases requiring tight integration. |
Introduction to Microrepo and Monorepo
Monorepos consolidate multiple projects or components into a single repository, simplifying dependency management and enabling consistent versioning across the codebase. Microrepos, by contrast, maintain individual repositories for each component or service, promoting isolation, easier access control, and independent versioning. Choosing between Microrepo and Monorepo depends on factors such as team size, deployment frequency, and complexity of interdependencies.
Core Concepts: What is a Microrepo?
A microrepo is a version control strategy where each repository contains a single, focused project or component, enabling independent development and deployment. This approach emphasizes modularity, faster CI/CD pipelines, and reduced complexity by isolating codebases. Unlike monorepos, microrepos facilitate granular access control and minimize inter-project dependencies, enhancing scalability for large organizations.
Core Concepts: What is a Monorepo?
A monorepo is a single repository that stores the code for multiple projects or components, enabling unified version control and streamlined collaboration across teams. It centralizes dependencies and shared libraries, reducing duplication and easing refactoring efforts. This approach supports atomic commits and consistent code quality by applying uniform tooling and testing strategies across the entire codebase.
Key Differences Between Microrepos and Monorepos
Microrepos organize codebases into small, independent repositories promoting modularity and isolated version control, while monorepos centralize all projects in a single repository to simplify dependency management and unified build processes. Microrepos enable granular access control and reduced build times per repository, whereas monorepos facilitate cross-project refactoring, consistent tooling, and streamlined collaboration across teams. The choice hinges on factors like team size, project interdependencies, and deployment strategies, with microrepos favoring decoupled development and monorepos optimizing integration and coherence.
Advantages of Microrepo Architecture
Microrepo architecture offers enhanced modularity by isolating codebases into smaller, manageable repositories, improving team autonomy and reducing merge conflicts. It enables faster CI/CD pipelines through targeted builds and tests, lowering resource consumption and improving deployment speed. This approach simplifies dependency management and version control, allowing independent updates without impacting unrelated projects.
Advantages of Monorepo Architecture
Monorepo architecture centralizes all codebases into a single repository, enabling consistent dependency management and streamlined code sharing across projects. It simplifies complex refactoring processes and enhances collaboration by providing a unified view of the entire codebase. Large tech companies like Google and Facebook leverage monorepos to improve build efficiency and enforce coding standards across extensive teams.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Microrepos
Microrepos often face challenges in managing dependency consistency across multiple repositories, leading to potential version conflicts and integration difficulties. Scalability issues arise from increased overhead in coordinating builds, tests, and deployments for numerous small repositories compared to the centralized control in monorepos. Maintaining developer productivity can be hindered by fragmented codebases and complex repository management tools required for effective synchronization.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Monorepos
Monorepos present significant challenges such as scalability issues, where large codebases can lead to slow build times and increased complexity in dependency management. The risk of extensive merge conflicts and codebase bottlenecks often slows development velocity, especially in teams with numerous contributors. Additionally, maintaining a monolithic structure requires substantial tooling and infrastructure investment to handle continuous integration and deployment effectively.
Use Cases: When to Choose Microrepo vs Monorepo
Microrepos are ideal for organizations managing independent, small-scale projects or teams that require isolated codebases to avoid dependencies and reduce build times. Monorepos suit large enterprises with interconnected projects needing centralized version control, streamlined code sharing, and coherent dependency management across numerous teams. Choose microrepo for flexibility and scalability in decentralized workflows, while monorepo supports tight collaboration and consistency across extensive codebases.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Repository Strategy
Microrepo and monorepo strategies each offer distinct advantages in scalability and team collaboration. Microrepos enhance modularity and allow independent deployments, ideal for teams prioritizing isolated development and reduced build times. Monorepos streamline dependency management and enable easier code sharing, best suited for organizations aiming for unified version control and consistent tooling across projects.
Microrepo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com