APIs enable your applications to communicate and exchange data seamlessly, while webhooks provide real-time notifications by sending automated messages when specific events occur. Integrating both technologies can enhance system efficiency and responsiveness significantly. Explore the rest of the article to discover how APIs and webhooks can optimize your digital workflows.
Table of Comparison
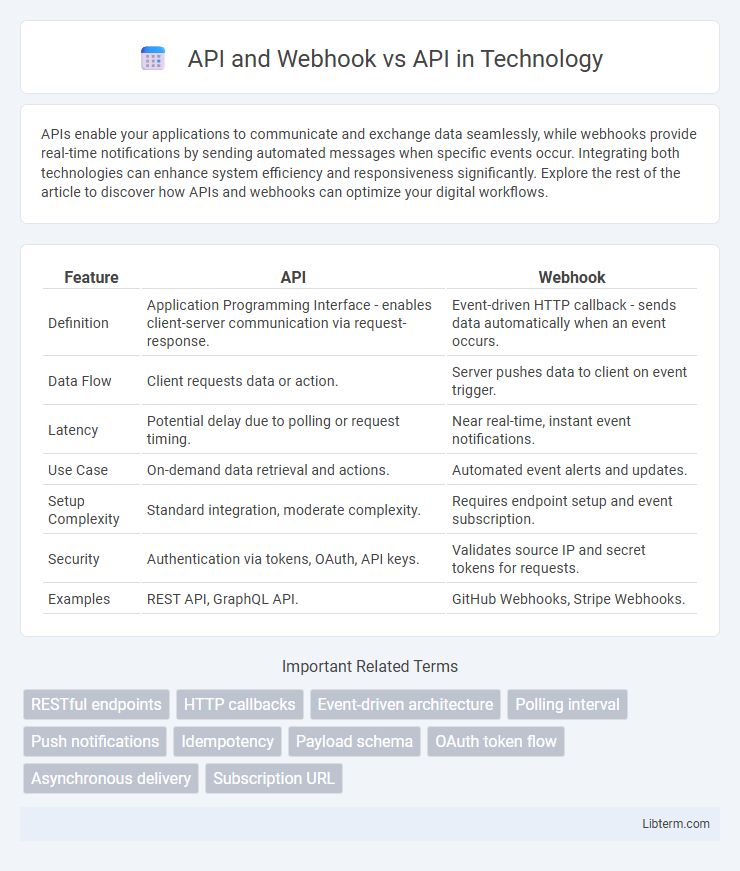
| Feature | API | Webhook |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Application Programming Interface - enables client-server communication via request-response. | Event-driven HTTP callback - sends data automatically when an event occurs. |
| Data Flow | Client requests data or action. | Server pushes data to client on event trigger. |
| Latency | Potential delay due to polling or request timing. | Near real-time, instant event notifications. |
| Use Case | On-demand data retrieval and actions. | Automated event alerts and updates. |
| Setup Complexity | Standard integration, moderate complexity. | Requires endpoint setup and event subscription. |
| Security | Authentication via tokens, OAuth, API keys. | Validates source IP and secret tokens for requests. |
| Examples | REST API, GraphQL API. | GitHub Webhooks, Stripe Webhooks. |
Understanding APIs: Definition and Core Functions
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are sets of protocols and tools enabling different software applications to communicate and exchange data efficiently. Webhooks function as automated messages sent from one app to another when specific events occur, facilitating real-time data updates without continuous polling. Understanding these distinctions clarifies that APIs provide a broad communication framework, while webhooks offer event-driven data transfer for improved responsiveness and efficiency.
What is a Webhook? Key Concepts Explained
A webhook is a user-defined HTTP callback that triggers an event or sends real-time data to a specified URL when a particular action occurs, eliminating the need for continuous polling in APIs. Unlike traditional APIs that require requests to fetch data, webhooks push information automatically, enhancing efficiency and immediacy in data transmission. Key concepts include event-driven architecture, payload delivery, and security measures like authentication tokens to ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
API vs Webhook: Fundamental Differences
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) require clients to request data or services actively, functioning on a pull-based model where the client initiates communication. Webhooks operate on a push-based model, sending real-time data automatically to a specified URL when an event occurs, eliminating the need for continuous polling. This fundamental difference highlights APIs' request-response nature versus webhooks' event-driven notifications for efficient, asynchronous data transfer.
How APIs Work: Request-Response Model
APIs operate on a request-response model where a client sends a request to a server, which processes it and returns a response, enabling seamless data exchange between applications. Unlike webhooks that push real-time updates from server to client without explicit requests, APIs require an active call to retrieve information. This model ensures controlled interactions, supports multiple request types such as GET, POST, and DELETE, and facilitates synchronous communication crucial for reliable data access.
How Webhooks Work: Event-Driven Communication
Webhooks operate through event-driven communication by automatically sending real-time data from one system to another when specific events occur, eliminating the need for continuous polling. While APIs require clients to request data actively, webhooks push updates instantaneously via HTTP POST requests to predefined URLs, enhancing responsiveness and reducing server load. This event-triggered mechanism enables seamless integration across applications for time-sensitive workflows, such as notifications, synchronization, and automation tasks.
Use Cases: When to Choose API or Webhook
APIs are ideal for real-time data retrieval and on-demand requests, such as fetching user information or processing payments. Webhooks excel in event-driven scenarios, automatically pushing notifications or updates when specific actions occur, like receiving alerts for new form submissions or payment statuses. Choose APIs for interactive, pull-based communication and webhooks for automated, push-based event updates to optimize integration efficiency.
Security Considerations: API and Webhook
API security involves authentication mechanisms such as OAuth, API keys, and rate limiting to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity. Webhook security requires validating incoming requests using signatures, secret tokens, and IP whitelisting to protect against spoofing and replay attacks. Both API and webhook implementations must enforce encryption through HTTPS and regularly update security protocols to mitigate vulnerabilities and maintain secure data transmission.
Performance and Efficiency: Comparing API and Webhook
Webhooks offer superior performance and efficiency compared to traditional APIs by enabling real-time, event-driven data delivery, eliminating the need for continuous polling and reducing server load. APIs rely on frequent client requests to check for updates, which can increase latency and waste bandwidth, especially under high traffic conditions. Webhooks optimize resource usage by pushing data only when specific events occur, leading to faster response times and lower operational costs.
Real-World Examples: API vs Webhook in Action
APIs enable applications like Twitter to fetch real-time tweets through endpoint requests, while webhooks automatically push event-driven updates, such as GitHub notifying a continuous integration service when code is committed. In e-commerce, Amazon's API allows developers to retrieve product data on demand, whereas Shopify uses webhooks to instantly alert merchants about orders placed. These examples highlight APIs' role in pull-based interactions and webhooks' efficiency in real-time push notifications within modern software ecosystems.
Best Practices for Integrating APIs and Webhooks
Best practices for integrating APIs and webhooks include using secure authentication methods like OAuth 2.0 to protect data integrity and privacy. Implementing retry mechanisms and proper error handling ensures reliability in API responses and webhook event deliveries. Prioritize data validation and timely logging to monitor interactions and troubleshoot integration issues effectively.
API and Webhook Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com