LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is a protocol used to access and maintain distributed directory information services over an IP network. It enables efficient management of user credentials, authentication, and organizational data within enterprise systems. Discover how LDAP can enhance your network security and streamline directory management by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
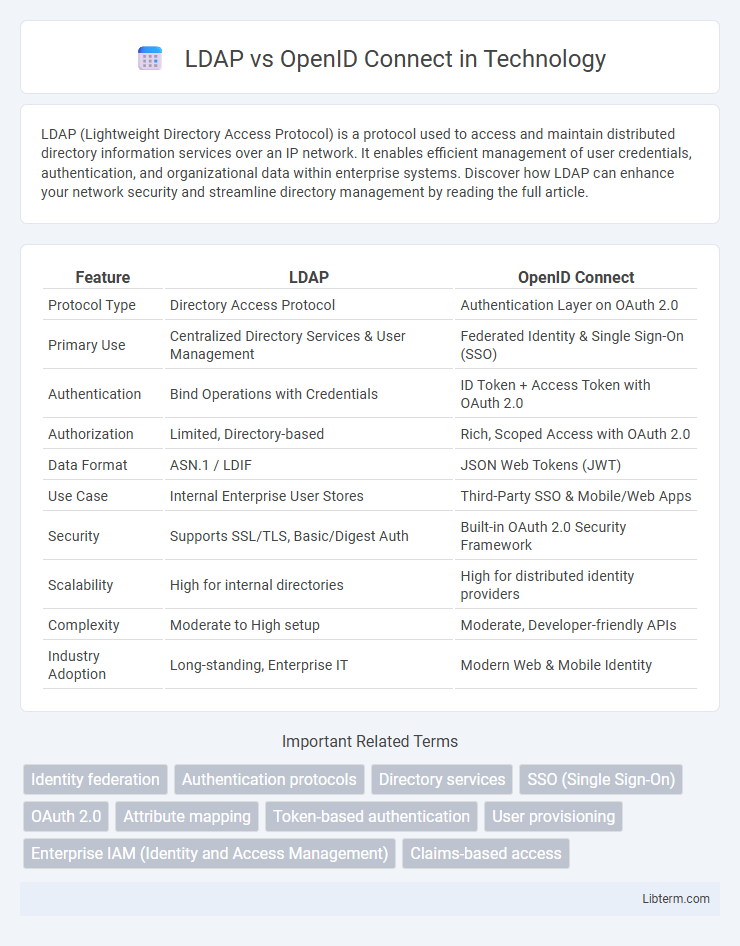
| Feature | LDAP | OpenID Connect |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Directory Access Protocol | Authentication Layer on OAuth 2.0 |
| Primary Use | Centralized Directory Services & User Management | Federated Identity & Single Sign-On (SSO) |
| Authentication | Bind Operations with Credentials | ID Token + Access Token with OAuth 2.0 |
| Authorization | Limited, Directory-based | Rich, Scoped Access with OAuth 2.0 |
| Data Format | ASN.1 / LDIF | JSON Web Tokens (JWT) |
| Use Case | Internal Enterprise User Stores | Third-Party SSO & Mobile/Web Apps |
| Security | Supports SSL/TLS, Basic/Digest Auth | Built-in OAuth 2.0 Security Framework |
| Scalability | High for internal directories | High for distributed identity providers |
| Complexity | Moderate to High setup | Moderate, Developer-friendly APIs |
| Industry Adoption | Long-standing, Enterprise IT | Modern Web & Mobile Identity |
Introduction to LDAP and OpenID Connect
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) serves as a protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network, primarily used for user authentication and authorization in enterprise environments. OpenID Connect is an identity layer built on top of OAuth 2.0, facilitating modern web-based single sign-on (SSO) and consumer identity authentication by providing verified user identity information. Both technologies address authentication but differ significantly in architecture, with LDAP relying on centralized directory services and OpenID Connect leveraging token-based, decentralized authentication federations.
Core Concepts: LDAP Explained
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) functions as a centralized directory service enabling users and applications to access and manage distributed directory information efficiently. It organizes data into a hierarchical structure of entries, each containing attributes, facilitating authentication, authorization, and user information retrieval within local or enterprise networks. LDAP's design emphasizes simplicity and speed, making it ideal for querying and modifying directory data, unlike OpenID Connect, which focuses on federated identity and single sign-on across web applications.
Core Concepts: OpenID Connect Simplified
OpenID Connect is an identity layer built on the OAuth 2.0 protocol that simplifies authentication by using JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for secure user identity verification across web and mobile applications. Unlike LDAP, which is a directory service protocol focused on centralized user data management and querying within enterprise networks, OpenID Connect provides a standardized federated authentication process for single sign-on (SSO) and token-based access. This core distinction highlights OpenID Connect's streamlined approach to user authentication with RESTful APIs and modern cryptographic methods designed for internet-scale identity management.
Authentication vs Authorization: Key Differences
LDAP primarily focuses on authentication by verifying user credentials against a centralized directory, ensuring secure access to network resources. OpenID Connect extends authentication with robust authorization capabilities, allowing applications to obtain user identity and consented access tokens for resource access. The key difference lies in LDAP's strength in credential validation versus OpenID Connect's support for delegated authorization and federated identity management.
Use Cases: When to Choose LDAP
LDAP is ideal for organizations requiring centralized access control for on-premises applications and legacy systems, enabling efficient management of user credentials within corporate networks. It excels in environments where robust directory services are needed for authentication, authorization, and user attribute storage. Choose LDAP when strict control over internal resources, granular permission settings, and integration with traditional IT infrastructure are primary concerns.
Use Cases: When to Choose OpenID Connect
OpenID Connect is ideal for modern web and mobile applications requiring seamless single sign-on (SSO) and federated identity management across multiple platforms and services. It provides robust support for OAuth 2.0 frameworks, enabling secure authorization and delegated access in cloud environments and API-driven ecosystems. Enterprises choosing OpenID Connect prioritize scalable authentication with enhanced user experience, especially when integrating third-party identity providers or supporting social logins.
Security Features Comparison
LDAP provides robust authentication through centralized directory services with support for secure protocols like LDAPS and StartTLS to encrypt data in transit. OpenID Connect enhances security by leveraging OAuth 2.0 frameworks, enabling token-based authentication with scopes and claims for granular access control and protection against token replay attacks. While LDAP excels in internal network environments with strict access controls, OpenID Connect offers superior capabilities for modern web and mobile applications requiring federated identity and multi-factor authentication integration.
Integration and Compatibility
LDAP offers robust integration capabilities with legacy enterprise systems through standardized protocols like LDAP v3, supporting directory-based authentication and access management. OpenID Connect is designed for modern web and mobile applications, providing seamless Single Sign-On (SSO) integration and compatibility with OAuth 2.0 frameworks, enhancing user authentication across diverse platforms. Compatibility with LDAP relies on direct directory access, whereas OpenID Connect leverages token-based authentication for interoperability with cloud services and APIs.
Performance and Scalability
LDAP offers high performance for on-premises directory lookups with low latency due to its lightweight protocol and efficient caching mechanisms, making it suitable for enterprise environments with tightly controlled access. OpenID Connect, built on OAuth 2.0, excels in scalability by leveraging stateless tokens and decentralized identity providers, which enable better handling of large volumes of authentication requests in cloud-native and distributed systems. While LDAP may face challenges scaling beyond single data centers, OpenID Connect's token-based approach supports horizontal scaling and federation across multiple domains, enhancing its flexibility in dynamic, large-scale applications.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Organization
Choosing the right protocol for your organization depends on your authentication and identity management needs. LDAP excels in centralized directory services for internal networks, supporting structured data and access control in enterprise environments. OpenID Connect offers modern, scalable authentication for web and mobile applications with seamless single sign-on (SSO) across multiple platforms and federated identity management.
LDAP Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com