Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. They are ideal for teams, businesses, or anyone wanting to add an extra layer of protection beyond a single key. Explore how multi-signature wallets work and why they might be essential for your digital asset management in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
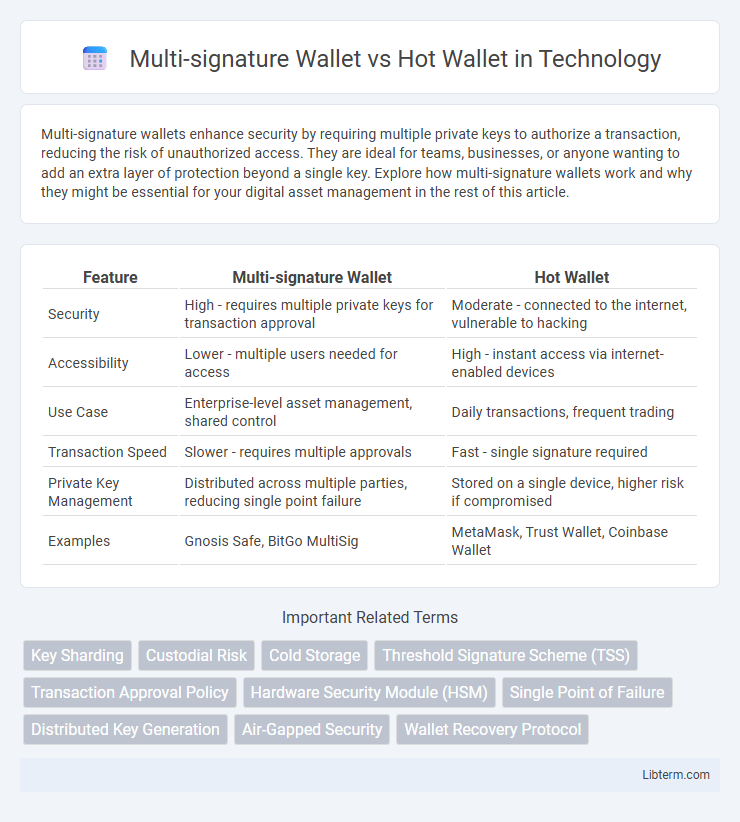
| Feature | Multi-signature Wallet | Hot Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High - requires multiple private keys for transaction approval | Moderate - connected to the internet, vulnerable to hacking |
| Accessibility | Lower - multiple users needed for access | High - instant access via internet-enabled devices |
| Use Case | Enterprise-level asset management, shared control | Daily transactions, frequent trading |
| Transaction Speed | Slower - requires multiple approvals | Fast - single signature required |
| Private Key Management | Distributed across multiple parties, reducing single point failure | Stored on a single device, higher risk if compromised |
| Examples | Gnosis Safe, BitGo MultiSig | MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet |
Understanding Multi-signature Wallets
Multi-signature wallets require multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, enhancing security by preventing single points of failure common in hot wallets that rely on one key. Unlike hot wallets, which are constantly connected to the internet and vulnerable to hacking, multi-signature wallets distribute transaction approval among several parties or devices. This added layer of security makes multi-signature wallets ideal for securing large amounts of cryptocurrency and institutional use cases.
What is a Hot Wallet?
A hot wallet is a cryptocurrency wallet connected to the internet, enabling quick and easy access to digital assets for frequent transactions. Unlike multi-signature wallets that require multiple approvals for security, hot wallets prioritize convenience but carry higher risks of hacking and unauthorized access. Common examples include mobile wallets, desktop wallets, and web wallets used by traders and everyday users.
Security Features Compared
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access and single-point failures. Hot wallets, while convenient for frequent transactions, store private keys online, exposing them to higher vulnerabilities such as hacking and phishing attacks. The multi-signature approach provides stronger defense mechanisms through distributed control, making it ideal for safeguarding larger crypto assets compared to the typically less secure hot wallets.
Ease of Use and Accessibility
Multi-signature wallets require multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, providing enhanced security but often at the cost of ease of use due to more complex setups and transaction processes. Hot wallets offer greater accessibility and user-friendliness by enabling quick, single-key transactions on connected devices, though they inherently carry higher security risks. Users prioritizing convenience and frequent access tend to prefer hot wallets, while those valuing security and shared control lean towards multi-signature wallets.
Transaction Approval Processes
Multi-signature wallets require multiple private keys to approve a transaction, enhancing security by distributing authorization authority among several parties. Hot wallets store private keys online, allowing faster transaction approvals with a single signature but increasing vulnerability to hacking. The multi-signature approval process reduces the risk of unauthorized transfers compared to the quicker but less secure confirmations typical of hot wallets.
Typical Use Cases
Multi-signature wallets excel in high-security environments such as corporate fund management and multi-party escrow services, requiring multiple approvals for transaction execution to prevent unauthorized access. Hot wallets are preferred for frequent, small-value transactions, offering convenience and quick access but with increased exposure to cybersecurity risks. Typical use cases for hot wallets include daily trading and online payments, while multi-signature wallets serve best in governance, shared control, and enhanced security scenarios.
Risk of Hacks and Theft
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple private keys for transaction authorization, significantly reducing the risk of hacks and theft compared to hot wallets, which rely on a single key often stored online. Hot wallets, being connected to the internet, are more vulnerable to phishing attacks, malware, and unauthorized access, leading to higher susceptibility to theft. Multi-signature wallets mitigate these risks by distributing control over the transaction process, making unauthorized transfers far more difficult.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Multi-signature wallets generally incur higher setup and maintenance costs due to the need for multiple private keys management and more complex security protocols, whereas hot wallets offer lower initial expenses but require ongoing vigilance against cyber threats. Hot wallets are cost-effective and user-friendly for frequent transactions but demand continuous updates and monitoring, increasing operational overhead. Multi-signature wallets reduce the risk of unauthorized access by distributing signing authority, which can lead to increased administrative efforts and potential delays in transaction approvals.
Best Practices for Storage
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions, making them ideal for storing large amounts of cryptocurrency or corporate funds. Hot wallets offer convenience and quick access but are vulnerable to hacking due to continuous internet connection, so they should be used for small, frequently accessed balances. Best practices include combining a multi-signature wallet for long-term storage with a hot wallet for daily transactions, regularly updating software, and using hardware devices for key management to minimize exposure.
Choosing the Right Wallet for Your Needs
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple approvals for transactions, making them ideal for businesses or groups needing shared control over funds, while hot wallets offer convenient, real-time access suitable for frequent trading or daily use but carry higher risks due to constant internet connectivity. Selecting the right wallet depends on balancing security and accessibility, considering factors like transaction frequency, risk tolerance, and collaborative management requirements. For long-term storage with robust protection, multi-signature wallets provide superior safeguards; hot wallets prioritize ease of use for active asset management.
Multi-signature Wallet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com