Managed services streamline your IT operations by outsourcing routine management to experts, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. This proactive approach ensures continuous monitoring, quick issue resolution, and optimized system performance tailored to your business needs. Discover how managed services can transform your IT strategy by reading the full article.
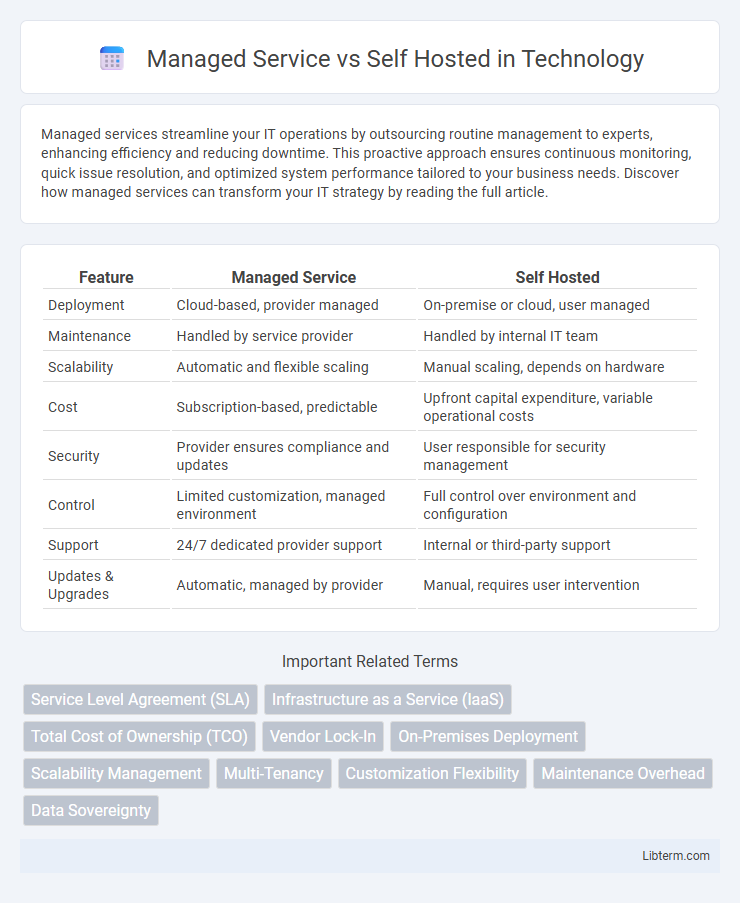
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Managed Service | Self Hosted |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Cloud-based, provider managed | On-premise or cloud, user managed |
| Maintenance | Handled by service provider | Handled by internal IT team |
| Scalability | Automatic and flexible scaling | Manual scaling, depends on hardware |
| Cost | Subscription-based, predictable | Upfront capital expenditure, variable operational costs |
| Security | Provider ensures compliance and updates | User responsible for security management |
| Control | Limited customization, managed environment | Full control over environment and configuration |
| Support | 24/7 dedicated provider support | Internal or third-party support |
| Updates & Upgrades | Automatic, managed by provider | Manual, requires user intervention |
Introduction to Managed Service vs Self Hosted
Managed services provide businesses with outsourced IT solutions that include continuous monitoring, maintenance, and support, reducing the need for in-house technical expertise. Self-hosted environments require organizations to deploy and manage their own infrastructure, offering full control over hardware, software, and security configurations. The choice between managed service and self-hosted solutions depends on factors such as budget, scalability needs, internal IT capabilities, and compliance requirements.
Core Differences Between Managed and Self Hosted Solutions
Managed services offer outsourced IT infrastructure and support, providing automatic updates, scalability, and expert monitoring, minimizing downtime and internal resource allocation. Self-hosted solutions require organizations to own, configure, and maintain hardware and software onsite, offering greater control but demanding significant technical expertise and ongoing maintenance. Core differences include cost structure, control level, security responsibility, and scalability flexibility, with managed services typically reducing operational complexity while self-hosting emphasizes customization and autonomy.
Cost Comparison: Managed Service vs Self Hosted
Managed Service solutions often have predictable monthly fees that cover infrastructure, maintenance, and support, reducing upfront capital expenditure compared to Self Hosted environments, which require significant initial investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT staffing. Self Hosted setups can incur hidden costs like system upgrades, security patches, and disaster recovery, which increase total cost of ownership over time, whereas Managed Services usually include these in subscription pricing. Companies must evaluate long-term operational expenses and scalability needs, as Managed Services provide flexible cost models while Self Hosted solutions may offer cost advantages at scale but involve higher ongoing management overhead.
Scalability and Flexibility Considerations
Managed service platforms offer superior scalability by automatically adjusting resources based on demand, eliminating the need for manual intervention and allowing businesses to handle traffic spikes efficiently. Self-hosted solutions provide greater flexibility in customization and control but require significant technical expertise to scale infrastructure, leading to potential delays and higher costs during expansion. Evaluating workload variability and available IT resources is critical for choosing between the managed service's ease of scaling and the self-hosted model's adaptability.
Security Implications: Managed vs Self Hosted
Managed services offer enhanced security through continuous monitoring, automated updates, and expert threat management, reducing the risk of breaches. Self-hosted environments require dedicated in-house security teams to handle patching, firewall management, and compliance adherence, which can increase vulnerability if not properly maintained. Choosing between managed and self-hosted solutions depends on an organization's capacity to implement robust security protocols and its tolerance for risk exposure.
Maintenance and Support Requirements
Managed service solutions provide comprehensive maintenance and support, including automatic updates, security patches, and 24/7 monitoring, reducing the need for in-house technical resources. Self-hosted environments demand dedicated IT staff to handle server maintenance, software upgrades, and troubleshooting, increasing operational overhead. Organizations must evaluate their technical expertise and resource availability when choosing between managed services and self-hosting to ensure consistent system performance and support.
Customization and Control Factors
Managed services offer limited customization due to standardized platforms but provide enhanced control through vendor-managed security and updates. Self-hosted solutions deliver extensive customization options, allowing businesses to tailor software, infrastructure, and configurations to specific needs while maintaining full control over system administration and data privacy. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing turnkey convenience with restricted flexibility or deep customization with increased management responsibility.
Performance and Reliability Overview
Managed services offer enhanced performance and reliability through expert infrastructure management, automated updates, and proactive monitoring, reducing downtime and latency. Self-hosted solutions provide greater control over hardware and software configurations but often require dedicated IT resources to maintain optimal performance and ensure system availability. Organizations seeking scalable, resilient environments tend to favor managed services for consistent uptime and rapid incident response.
Compliance and Regulatory Concerns
Managed services offer built-in compliance frameworks aligned with industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, reducing the risk of regulatory penalties. Self-hosted solutions require dedicated internal resources to continuously monitor, update, and document compliance efforts, often leading to increased operational overhead. Organizations subject to stringent regulatory environments benefit from managed services' automated audit trails and expert security management.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Choosing between managed service and self-hosted solutions depends on factors such as budget, technical expertise, and control requirements. Managed services offer streamlined maintenance, scalability, and vendor support, ideal for organizations lacking in-house IT resources. Self-hosted options provide greater customization and data control but demand significant technical skills and ongoing management efforts.
Managed Service Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com