Smart cards enhance security by embedding microprocessors that store and process data for authentication and secure transactions. They are widely used in banking, access control, and healthcare to protect sensitive information and prevent fraud. Discover how smart cards can safeguard Your digital identity and streamline secure interactions by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
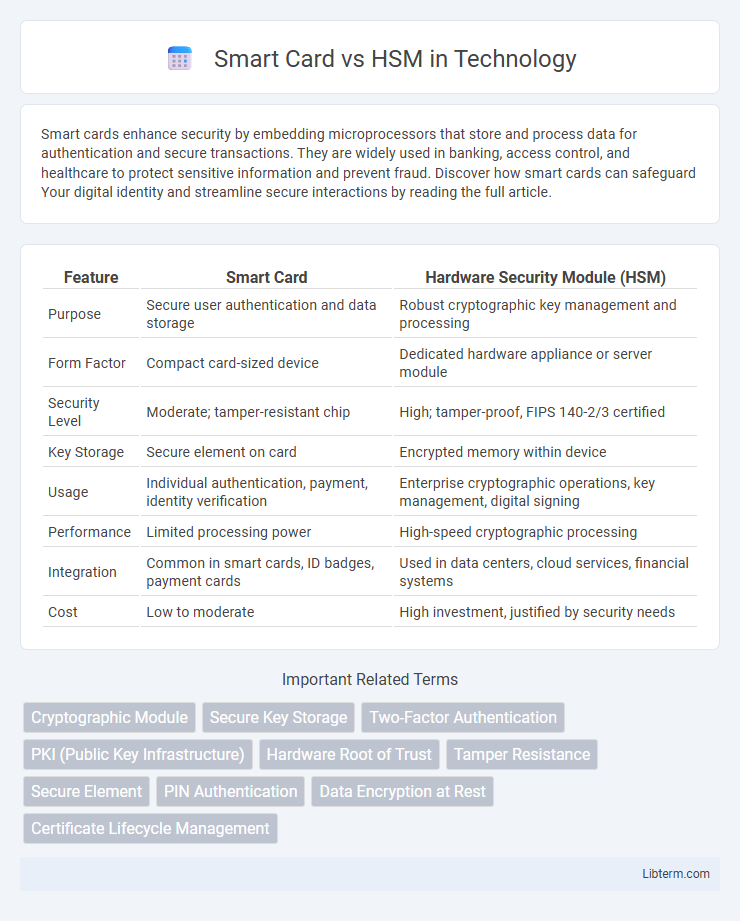
| Feature | Smart Card | Hardware Security Module (HSM) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Secure user authentication and data storage | Robust cryptographic key management and processing |
| Form Factor | Compact card-sized device | Dedicated hardware appliance or server module |
| Security Level | Moderate; tamper-resistant chip | High; tamper-proof, FIPS 140-2/3 certified |
| Key Storage | Secure element on card | Encrypted memory within device |
| Usage | Individual authentication, payment, identity verification | Enterprise cryptographic operations, key management, digital signing |
| Performance | Limited processing power | High-speed cryptographic processing |
| Integration | Common in smart cards, ID badges, payment cards | Used in data centers, cloud services, financial systems |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High investment, justified by security needs |
Introduction to Smart Cards and HSMs
Smart cards are portable, tamper-resistant devices embedded with integrated circuits used for secure authentication, data storage, and cryptographic processing. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) are specialized physical devices designed to generate, store, and manage digital keys, providing a high level of cryptographic security in enterprise environments. While smart cards offer individual user-level security, HSMs deliver scalable, centralized key management solutions for large-scale cryptographic operations.
What is a Smart Card?
A Smart Card is a physical card embedded with an integrated circuit chip that securely stores and processes data, often used for authentication, secure access, and digital transactions. Unlike a Hardware Security Module (HSM), which is a dedicated hardware device designed to manage and safeguard cryptographic keys within larger infrastructures, a Smart Card provides portable, user-specific security solutions. Smart Cards support cryptographic functions like encryption, digital signatures, and secure key storage directly on the card, making them ideal for identity verification and secure payment systems.
What is a Hardware Security Module (HSM)?
A Hardware Security Module (HSM) is a dedicated physical device designed to manage digital keys securely and perform cryptographic operations such as encryption, decryption, and authentication. Unlike smart cards, HSMs offer high-throughput processing capabilities and robust tamper-resistant features to ensure data protection at enterprise and cloud scale. HSMs comply with strict security standards like FIPS 140-2 and Common Criteria, making them essential for safeguarding cryptographic assets in financial services, government, and large enterprises.
Key Differences Between Smart Card and HSM
Smart Cards provide secure storage for cryptographic keys and perform limited cryptographic functions within a portable card format, mainly used for user authentication and digital signatures. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) offer advanced cryptographic processing power, support multi-user environments, and handle high-volume key management tasks with robust physical and logical protections. Key differences include Smart Cards' focus on individual user security and portability, versus HSMs' enterprise-grade key management capabilities and scalability for large-scale cryptographic operations.
Security Features Comparison
Smart cards use embedded microchips to provide secure storage for cryptographic keys and support two-factor authentication, ensuring data confidentiality and user identity verification. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) offer robust protection through tamper-resistant hardware designed to safeguard large-scale cryptographic operations and manage keys with stringent access controls. While smart cards excel in portable, user-centric security, HSMs deliver high-performance, enterprise-grade encryption and key management for critical infrastructure.
Performance and Scalability
Smart cards offer limited cryptographic performance due to constrained processing power and memory, making them suitable for individual user authentication but less effective for high-throughput environments. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) deliver superior performance by leveraging dedicated cryptographic processors capable of handling thousands of transactions per second, which supports large-scale enterprise security needs. Scalability is enhanced with HSMs through modular architectures and cluster configurations, allowing seamless expansion to accommodate growing transaction volumes and complex cryptographic operations.
Use Cases: When to Use Smart Card vs HSM
Smart Cards excel in scenarios requiring portable, user-specific authentication such as secure access to facilities, mobile authentication, and digital signatures. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) are ideal for high-volume cryptographic processing, key management, and enterprise-level data encryption, especially in banking, cloud security, and certificate authority operations. For individual secure identity verification and transaction signing, Smart Cards are preferred, whereas HSMs handle scalable, centralized cryptographic tasks demanding robust physical and logical protections.
Integration and Deployment Considerations
Smart cards offer seamless integration with existing access control systems through standardized interfaces like PKCS#11 and ISO/IEC 7816, enabling straightforward deployment in user authentication and secure storage environments. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) require dedicated network connectivity and specialized APIs for integration, often involving complex configuration to support cryptographic operations in data centers or cloud infrastructures. Deployment of smart cards is typically user-centric with minimal infrastructure changes, while HSMs demand robust physical security, scalability planning, and compliance with stringent regulatory standards for high-assurance cryptographic key management.
Cost Implications of Smart Cards vs HSMs
Smart cards typically entail lower upfront costs due to affordable manufacturing and mass production, making them suitable for large-scale deployments with minimal initial investment. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) involve significant capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance expenses, reflecting their advanced cryptographic capabilities and enterprise-grade security features. Total cost of ownership for HSMs can be higher, but justifiable by enhanced performance, compliance requirements, and secure key management in high-risk environments.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Security Needs
Selecting between a Smart Card and a Hardware Security Module (HSM) depends on the required security level and use case. Smart Cards offer portable, user-level authentication and encryption, ideal for individual access control and secure identification. HSMs provide robust, high-performance cryptographic processing and key management, making them suitable for enterprise environments demanding centralized, scalable protection of sensitive data.
Smart Card Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com