Firewall protection serves as a critical barrier between your internal network and external threats, effectively monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. It helps prevent unauthorized access, cyber attacks, and data breaches, ensuring the safety of sensitive information. Discover how implementing the right firewall protection can strengthen your digital security by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
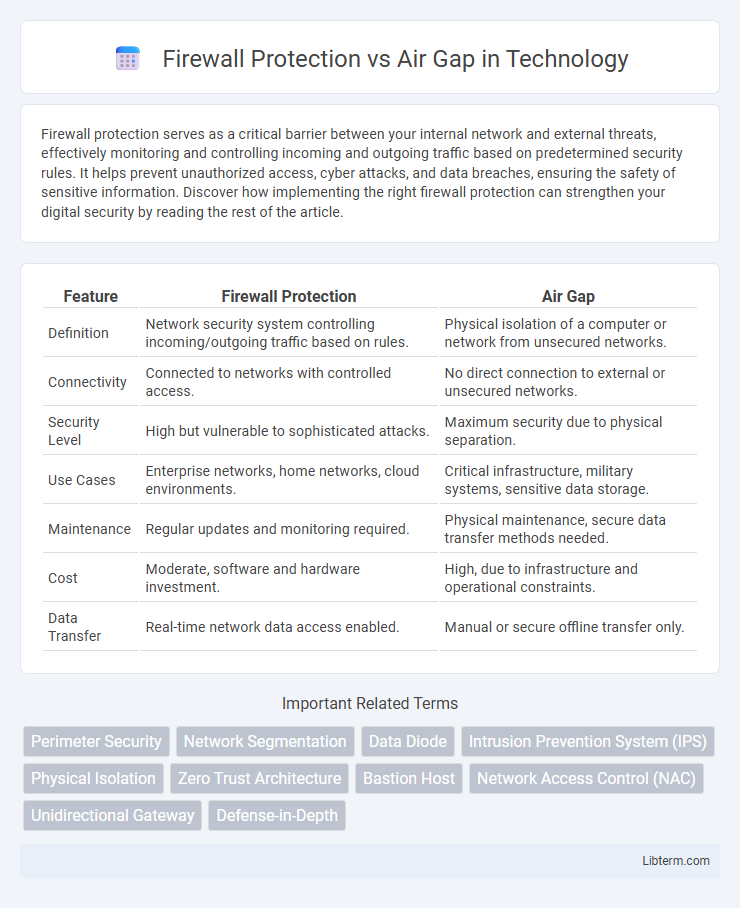
| Feature | Firewall Protection | Air Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network security system controlling incoming/outgoing traffic based on rules. | Physical isolation of a computer or network from unsecured networks. |
| Connectivity | Connected to networks with controlled access. | No direct connection to external or unsecured networks. |
| Security Level | High but vulnerable to sophisticated attacks. | Maximum security due to physical separation. |
| Use Cases | Enterprise networks, home networks, cloud environments. | Critical infrastructure, military systems, sensitive data storage. |
| Maintenance | Regular updates and monitoring required. | Physical maintenance, secure data transfer methods needed. |
| Cost | Moderate, software and hardware investment. | High, due to infrastructure and operational constraints. |
| Data Transfer | Real-time network data access enabled. | Manual or secure offline transfer only. |
Introduction to Firewall Protection and Air Gap
Firewall protection utilizes software or hardware systems to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, creating a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks. Air gap security involves physically isolating a computer or network from unsecured networks, including the internet, ensuring no direct or indirect connection exists to external systems. Both methods aim to protect sensitive data and systems, with firewalls providing real-time monitoring and filtering while air gaps offer absolute isolation against cyber threats.
Key Differences Between Firewall and Air Gap Security
Firewall protection uses software or hardware to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules, providing a barrier against unauthorized access while allowing authorized communication. Air gap security physically isolates a computer or network from any external connections, creating a complete disconnection from unsecured networks and eliminating remote hacking risks. The key difference lies in firewalls permitting filtered data flow to maintain connectivity, whereas air gaps maintain total physical separation to ensure maximum security against cyber threats.
How Firewalls Work: Features and Functionality
Firewalls protect networks by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules, employing techniques such as packet filtering, stateful inspection, and proxy service to prevent unauthorized access. They feature intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), application awareness, and VPN support to safeguard against cyber threats while allowing legitimate communication. Unlike air gaps, which physically isolate systems, firewalls provide flexible, manageable security layers that adapt dynamically to evolving network environments.
Understanding Air Gap: Concept and Applications
Air gap security isolates critical systems by physically separating them from unsecured networks, preventing digital access and minimizing cyberattack risks. Commonly implemented in highly sensitive environments such as military, industrial control systems, and financial networks, air gaps ensure data integrity by eliminating network connectivity. Unlike firewall protection, which monitors and filters traffic between networks, air gaps provide absolute isolation, making unauthorized remote access virtually impossible.
Advantages of Firewall-Based Security
Firewall-based security offers robust protection by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, enabling real-time threat detection and prevention. It allows for granular access control, ensuring only authorized connections are permitted while logging all activities for auditing and compliance purposes. Unlike air gap systems, firewalls provide flexible connectivity with external networks while maintaining strong defenses against malware, intrusion attempts, and unauthorized access.
Benefits of Air Gap Isolation
Air gap isolation provides superior security by physically separating critical systems from untrusted networks, eliminating any direct digital connections that could be exploited by cyber attackers. This complete network segregation prevents lateral movement of threats, ensuring that sensitive data and infrastructure remain immune to remote hacking, malware, and ransomware attacks. Unlike firewall protection, which relies on software rules that can be bypassed or misconfigured, air gap isolation offers a foolproof defense by creating an unbreachable physical barrier.
Limitations of Firewall Protection
Firewall protection limits network access by filtering traffic based on predefined rules, but it cannot fully prevent sophisticated cyber threats such as insider attacks, zero-day exploits, or advanced persistent threats (APTs). Firewalls struggle to detect encrypted malware or unauthorized lateral movement within a compromised network, leaving internal systems vulnerable. Unlike air gap security, firewalls do not physically isolate systems, which means they cannot guarantee complete network segregation or immunity from targeted breaches.
Drawbacks and Challenges of Air Gapping
Air gapping, which isolates a network physically from unsecured environments, presents significant challenges such as limited data transfer speed and cumbersome maintenance processes. Its reliance on manual updates increases the risk of human error and delays in deploying critical security patches. Additionally, air-gapped systems struggle to integrate with modern networked environments, leading to operational inefficiencies and higher costs.
Use Cases: When to Choose Firewalls vs. Air Gap
Firewalls are ideal for environments requiring controlled network traffic management, such as corporate networks, where real-time monitoring and access control prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Air gaps are best suited for high-security scenarios like critical infrastructure, military, or sensitive research facilities where completely isolating systems from any external network minimizes the risk of cyberattacks. Choosing firewalls supports operational connectivity with robust defense, while air gaps prioritize total network isolation for maximum security.
Firewall Protection vs Air Gap: Which is Right for Your Organization?
Firewall protection offers dynamic monitoring and filtering of network traffic, making it ideal for organizations requiring real-time threat detection and remote access control. In contrast, air gap security physically isolates critical systems from unsecured networks, providing superior defense against cyberattacks but limiting operational flexibility and data exchange. Choosing between firewall protection and air gap depends on the organization's risk tolerance, operational needs, and the sensitivity of the data involved.
Firewall Protection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com