Automatic scaling adjusts your system's resources dynamically to match workload demands, ensuring optimal performance without manual intervention. This technology helps prevent over-provisioning, reducing costs, while maintaining efficiency during peak usage times. Discover how automatic scaling can transform your infrastructure by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
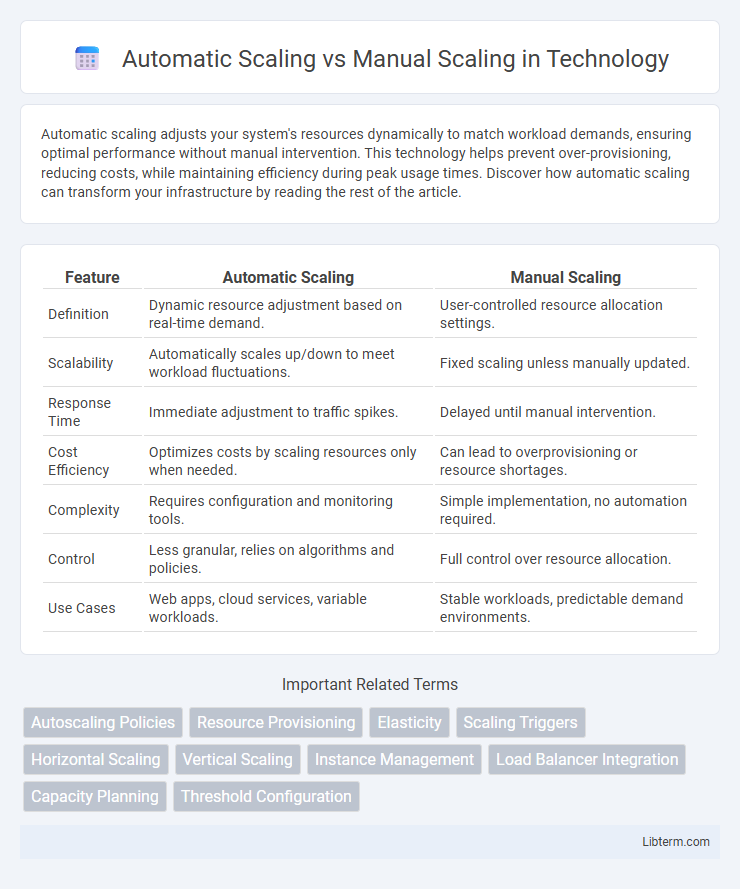
| Feature | Automatic Scaling | Manual Scaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dynamic resource adjustment based on real-time demand. | User-controlled resource allocation settings. |
| Scalability | Automatically scales up/down to meet workload fluctuations. | Fixed scaling unless manually updated. |
| Response Time | Immediate adjustment to traffic spikes. | Delayed until manual intervention. |
| Cost Efficiency | Optimizes costs by scaling resources only when needed. | Can lead to overprovisioning or resource shortages. |
| Complexity | Requires configuration and monitoring tools. | Simple implementation, no automation required. |
| Control | Less granular, relies on algorithms and policies. | Full control over resource allocation. |
| Use Cases | Web apps, cloud services, variable workloads. | Stable workloads, predictable demand environments. |
Introduction to Scaling in Cloud Computing
Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts cloud resources based on real-time demand, optimizing performance and cost efficiency by allocating or deallocating instances without human intervention. Manual scaling requires administrators to predict workload changes and adjust resources accordingly, which can lead to inefficiencies during unexpected traffic spikes or drops. Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provide built-in automatic scaling tools such as AWS Auto Scaling, Azure Scale Sets, and Google Cloud Autoscaler to manage resource scalability effectively.
What is Automatic Scaling?
Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts computing resources based on real-time demand, optimizing performance and cost efficiency in cloud environments. It uses predefined metrics such as CPU utilization, network traffic, or application load to trigger the addition or removal of instances without human intervention. This contrasts with manual scaling, where administrators allocate resources manually, potentially leading to underutilization or resource shortages.
What is Manual Scaling?
Manual scaling involves adjusting computing resources by human intervention, allowing administrators to increase or decrease server capacity based on anticipated demand. This method provides precise control over resource allocation but requires ongoing monitoring and timely decision-making to handle traffic fluctuations effectively. Manual scaling is commonly used in environments where predictable workloads or specific operational constraints dictate fixed resource adjustments.
Key Features of Automatic Scaling
Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts computing resources based on real-time demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency without manual intervention. Key features include predictive analytics for workload forecasting, seamless integration with cloud platforms, and rapid response to traffic spikes to prevent downtime. This proactive resource management contrasts with manual scaling's fixed schedules and human dependency, enabling businesses to efficiently handle variable workloads.
Key Features of Manual Scaling
Manual scaling allows precise control over resource allocation by enabling administrators to adjust the number of active servers or instances based on specific demand forecasts or operational preferences. Key features include the ability to set fixed capacity limits, schedule scaling actions at predetermined times, and tailor resource management to unique workload patterns without relying on automated algorithms. This approach benefits environments where predictable workloads and consistent performance requirements take precedence over real-time adaptability.
Pros and Cons of Automatic Scaling
Automatic scaling offers significant advantages such as real-time resource adjustment based on demand, which improves cost efficiency and ensures optimal performance during traffic fluctuations. However, it may lead to unexpected costs if not properly configured and can introduce complexity in monitoring and debugging due to its dynamic nature. This approach is ideal for applications with variable workloads but may require predefined rules and thresholds to avoid scaling inefficiencies or resource shortages.
Pros and Cons of Manual Scaling
Manual scaling offers precise control over resource allocation, allowing tailored adjustments based on specific workload requirements, which can optimize cost efficiency in predictable environments. However, it requires constant monitoring and timely intervention, increasing the risk of human error and potential service downtime during unexpected traffic spikes. Reliance on manual scaling can lead to slower response times compared to automatic scaling, making it less suitable for highly dynamic or rapidly growing applications.
Performance Comparison: Automatic vs Manual Scaling
Automatic scaling optimizes resource allocation by dynamically adjusting compute power based on real-time demand, resulting in minimized latency and enhanced performance under fluctuating workloads. Manual scaling relies on predefined thresholds and human intervention, often leading to delayed resource adjustments and potential performance bottlenecks during sudden traffic spikes. Performance metrics indicate that automatic scaling consistently delivers higher availability and response times compared to manual scaling in cloud and containerized environments.
Cost Implications of Scaling Methods
Automatic scaling optimizes costs by dynamically adjusting resource allocation based on real-time demand, minimizing over-provisioning and reducing unnecessary expenses. Manual scaling often leads to higher costs due to fixed resource allocation, potentially causing overuse during low traffic or performance issues during unexpected spikes. Cloud providers like AWS and Azure offer cost management tools integrated with automatic scaling to enhance budget control and efficiency.
Choosing the Right Scaling Strategy for Your Business
Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts resources in response to real-time demand, optimizing cost-efficiency and ensuring system reliability during traffic spikes. Manual scaling requires predefined resource allocation, offering precise control but risking under-provisioning or over-provisioning. Businesses with fluctuating workloads benefit from automatic scaling for agility, while stable, predictable workloads may suit manual scaling to maintain consistent performance and budget control.
Automatic Scaling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com