Automated testing enhances software quality by executing predefined test cases swiftly and consistently, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency. By integrating automated testing into your development process, you quickly identify defects and ensure reliable performance across various environments. Explore the rest of the article to discover how automated testing can transform your software development lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
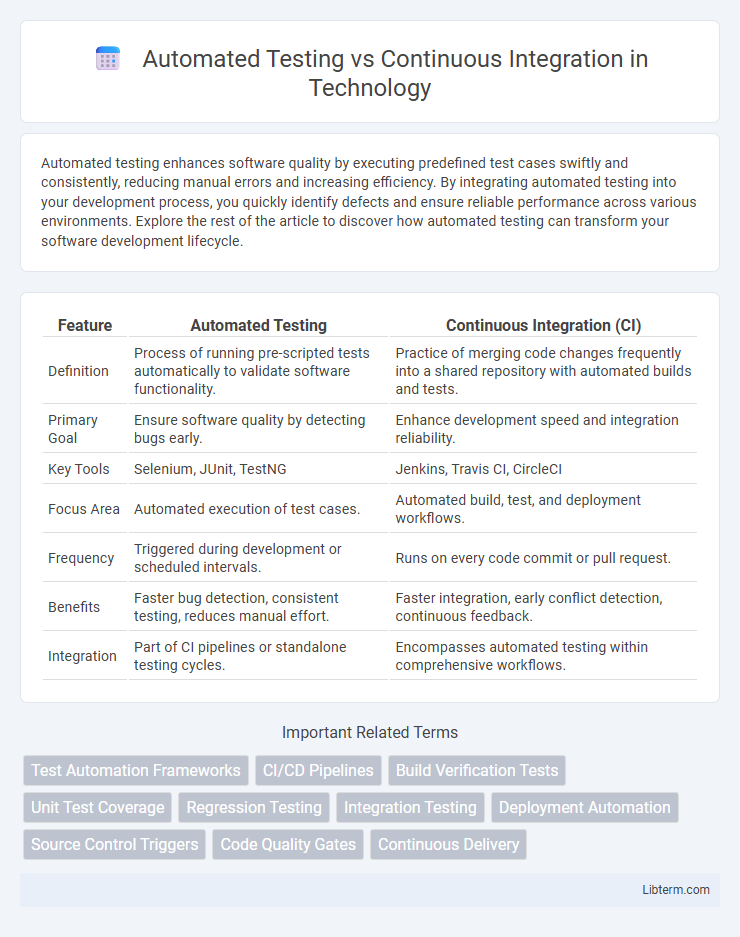
| Feature | Automated Testing | Continuous Integration (CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of running pre-scripted tests automatically to validate software functionality. | Practice of merging code changes frequently into a shared repository with automated builds and tests. |
| Primary Goal | Ensure software quality by detecting bugs early. | Enhance development speed and integration reliability. |
| Key Tools | Selenium, JUnit, TestNG | Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI |
| Focus Area | Automated execution of test cases. | Automated build, test, and deployment workflows. |
| Frequency | Triggered during development or scheduled intervals. | Runs on every code commit or pull request. |
| Benefits | Faster bug detection, consistent testing, reduces manual effort. | Faster integration, early conflict detection, continuous feedback. |
| Integration | Part of CI pipelines or standalone testing cycles. | Encompasses automated testing within comprehensive workflows. |
Introduction to Automated Testing and Continuous Integration
Automated testing involves using specialized software tools to execute pre-scripted tests on a software application to verify its functionality and identify defects efficiently. Continuous Integration (CI) is a development practice where code changes are automatically built, tested, and merged into a shared repository multiple times a day to ensure early detection of integration issues. Integrating automated testing within CI pipelines enhances software quality by providing rapid feedback on code changes and reducing manual testing effort.
Key Differences Between Automated Testing and Continuous Integration
Automated testing focuses on the systematic execution of predefined test cases using software tools to verify code functionality, improving accuracy and speed in bug detection. Continuous Integration (CI) is a development practice where code changes are automatically integrated into a shared repository, triggering builds and tests to ensure consistent software quality and immediate feedback on integration issues. Key differences include automated testing being a component within CI pipelines, while CI encompasses a broader workflow that includes code merging, build automation, and deployment readiness.
How Automated Testing Works in Modern Development
Automated testing in modern development involves executing pre-scripted tests on software applications automatically to validate functionality, performance, and security, thereby accelerating the feedback loop. Tools like Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG integrate with continuous integration platforms such as Jenkins and GitLab CI to run test suites with every code commit, ensuring early detection of defects. This process enhances code quality by enabling consistent, repeatable tests that support rapid development cycles and continuous delivery pipelines.
The Role of Continuous Integration in DevOps
Continuous Integration (CI) plays a critical role in DevOps by enabling automated testing to be seamlessly integrated into the development pipeline, ensuring code changes are frequently validated for functionality and quality. CI systems like Jenkins, CircleCI, and Travis CI execute automated tests on every code commit, facilitating early detection of bugs and reducing integration issues. This process enhances collaboration between development and operations teams, accelerates release cycles, and improves software reliability.
Benefits of Automated Testing for Software Quality
Automated testing significantly enhances software quality by enabling faster detection of defects, reducing human error, and ensuring consistent test coverage across development cycles. It facilitates frequent and reliable feedback, allowing developers to address issues early and improve code stability. Integration with continuous integration pipelines accelerates release cycles while maintaining high-quality standards.
Advantages of Continuous Integration for Faster Deployment
Continuous Integration (CI) accelerates deployment by automating code integration and testing, ensuring immediate detection of errors and reducing integration issues. It streamlines collaboration among development teams, enabling faster feedback loops and more frequent software releases. By continuously merging code changes, CI minimizes build failures and deployment risks, leading to higher software quality and quicker time-to-market.
Common Tools for Automated Testing and Continuous Integration
Common tools for automated testing include Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, and Cypress, which facilitate efficient test automation across various platforms and languages. Continuous integration platforms like Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, and GitLab CI/CD integrate automated tests into development workflows, ensuring early detection of code issues. Leveraging these tools together accelerates software delivery by continuously validating code changes through automated testing pipelines.
Integrating Automated Testing into a CI Pipeline
Integrating automated testing into a continuous integration (CI) pipeline significantly enhances software quality by enabling rapid feedback on code changes through automated test execution. Automated tests, including unit, integration, and end-to-end tests, are triggered automatically with each code commit, ensuring early detection of bugs and regression issues. This integration streamlines development workflows, reduces manual testing efforts, and supports faster, more reliable software delivery.
Challenges and Best Practices in Automation and CI Adoption
Automated Testing faces challenges such as maintaining test scripts amid frequent code changes, ensuring test coverage, and handling flaky tests that cause false positives or negatives. Continuous Integration adoption struggles with integrating diverse tools, managing build failures promptly, and balancing fast feedback loops with thorough testing. Best practices include adopting modular test design, utilizing version control for test scripts, implementing incremental builds, and fostering collaboration between development and QA teams to streamline automation and CI processes.
Choosing Between Automated Testing and Continuous Integration
Choosing between automated testing and continuous integration depends on project goals and development workflows. Automated testing ensures consistent validation of code quality through pre-scripted test cases, reducing manual errors and speeding up feedback. Continuous integration facilitates early detection of integration issues by automatically merging and building code changes frequently, promoting collaboration and maintaining stable codebases.
Automated Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com