Tape storage remains a reliable and cost-effective solution for archiving large volumes of data with long retention periods. Its high capacity and energy efficiency make it ideal for backup and disaster recovery in both enterprise and personal environments. Discover how tape storage can safeguard your valuable information by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
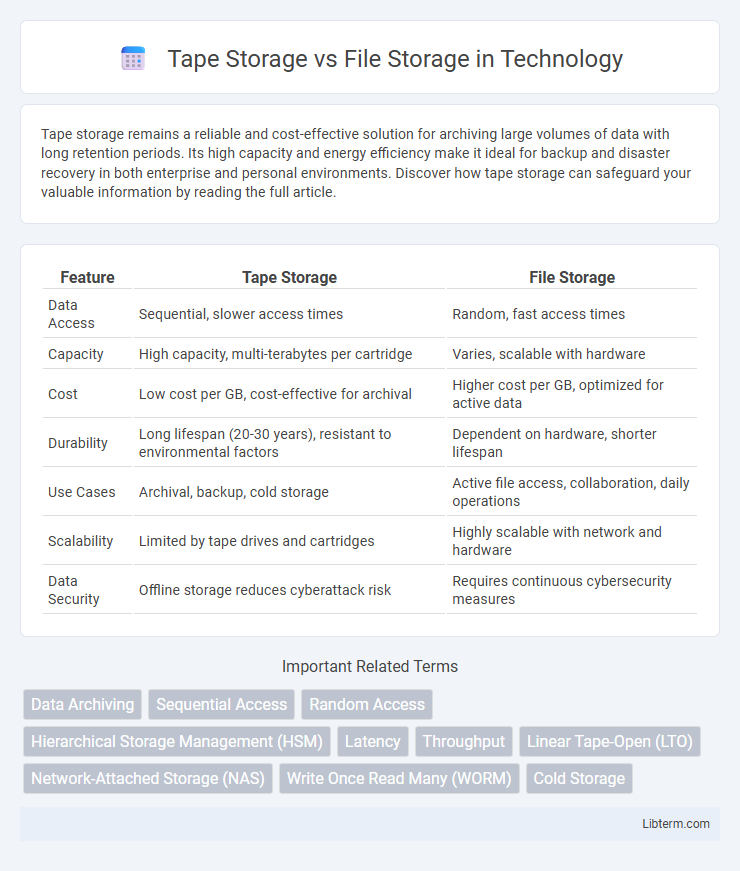
| Feature | Tape Storage | File Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Data Access | Sequential, slower access times | Random, fast access times |
| Capacity | High capacity, multi-terabytes per cartridge | Varies, scalable with hardware |
| Cost | Low cost per GB, cost-effective for archival | Higher cost per GB, optimized for active data |
| Durability | Long lifespan (20-30 years), resistant to environmental factors | Dependent on hardware, shorter lifespan |
| Use Cases | Archival, backup, cold storage | Active file access, collaboration, daily operations |
| Scalability | Limited by tape drives and cartridges | Highly scalable with network and hardware |
| Data Security | Offline storage reduces cyberattack risk | Requires continuous cybersecurity measures |
Introduction to Data Storage Solutions
Tape storage offers a cost-effective and durable solution for long-term data archiving, providing high capacity and offline protection against cyber threats. File storage organizes data in a hierarchical structure, enabling fast access and easy management for frequently used files and applications. Choosing between tape and file storage depends on factors like data access speed, budget constraints, and retention requirements.
Overview of Tape Storage
Tape storage uses magnetic tape cartridges to store large volumes of data, offering a cost-effective solution for long-term archival and backup purposes. It provides high durability and offline storage capabilities, reducing risks of data loss due to cyber threats or hardware failures. Modern tape systems support fast data transfer rates and extensive scalability, making them ideal for enterprise-level data preservation.
Overview of File Storage
File storage manages data by organizing it into a hierarchical structure of files and folders, allowing easy access, modification, and sharing across networks or local systems. It supports various file types and is optimized for quick retrieval and frequent updates, making it ideal for collaborative environments and real-time data processing. Unlike tape storage, file storage systems offer faster access speeds and better integration with modern applications and operating systems.
How Tape Storage Works
Tape storage operates by sequentially writing data onto magnetic tape, where information is encoded in tracks along the tape's length. Data retrieval requires the tape drive to physically wind the tape to the desired position, making access slower compared to random-access file storage systems. This method excels in high-capacity, long-term archival storage due to its cost efficiency and durability.
How File Storage Works
File storage organizes data in a hierarchical structure using files and folders, allowing users to access and manage information through operating systems with familiar interfaces. It employs metadata to index and retrieve files efficiently, supporting real-time data access and collaboration across networks. File storage systems are ideal for unstructured data, offering scalability and ease of integration with applications in business environments.
Key Differences Between Tape and File Storage
Tape storage offers sequential data access, making it ideal for archival and backup purposes due to its high capacity and low cost per gigabyte. File storage provides random access to files, supporting faster data retrieval and real-time access for everyday use in network-attached storage (NAS) systems. Tape is more durable for long-term retention, whereas file storage emphasizes accessibility and ease of data management.
Performance Comparison: Tape vs File Storage
Tape storage offers high capacity and low cost per terabyte but exhibits slower data access speeds compared to file storage systems. File storage provides rapid random access and low latency, making it ideal for frequently accessed data and real-time applications. Performance benchmarks show tape excels in sequential read/write throughput, while file storage outperforms in response time and data retrieval efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Tape vs File Storage
Tape storage offers significantly lower cost-per-gigabyte compared to file storage, making it a cost-effective solution for long-term data archiving and backup. File storage incurs higher expenses due to the need for continuous power, cooling, and maintenance of active storage devices. Enterprises with large volumes of infrequently accessed data benefit from tape storage's lower total cost of ownership and reduced energy consumption.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Tape storage offers cost-effective, long-term archival solutions ideal for industries with massive data retention needs like media and entertainment, healthcare, and finance, where compliance and backup are critical. File storage excels in environments requiring fast, frequent access and collaboration, such as software development, engineering, and content creation, supporting real-time data sharing and version control. Enterprises leverage tape storage for disaster recovery and regulatory archiving, while file storage underpins operational workflows with scalable, high-performance network attached storage (NAS) systems.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution
Tape storage offers high-capacity, cost-effective archival solutions ideal for long-term data retention with low access frequency, while file storage provides faster, more flexible access suitable for active data and collaboration environments. Selecting the right storage solution depends on factors such as data access speed requirements, budget constraints, and intended use cases like backup, disaster recovery, or daily operations. Organizations benefit from combining tape storage for archival and file storage for real-time data management to optimize cost efficiency and performance.
Tape Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com