On-premises solutions provide organizations with complete control over their hardware and software infrastructure, enhancing security and customization options. This approach allows for direct management of data, reducing dependency on third-party services and potential connectivity issues. Explore the rest of the article to understand if on-premises deployment aligns with your business needs and how it compares to cloud alternatives.
Table of Comparison
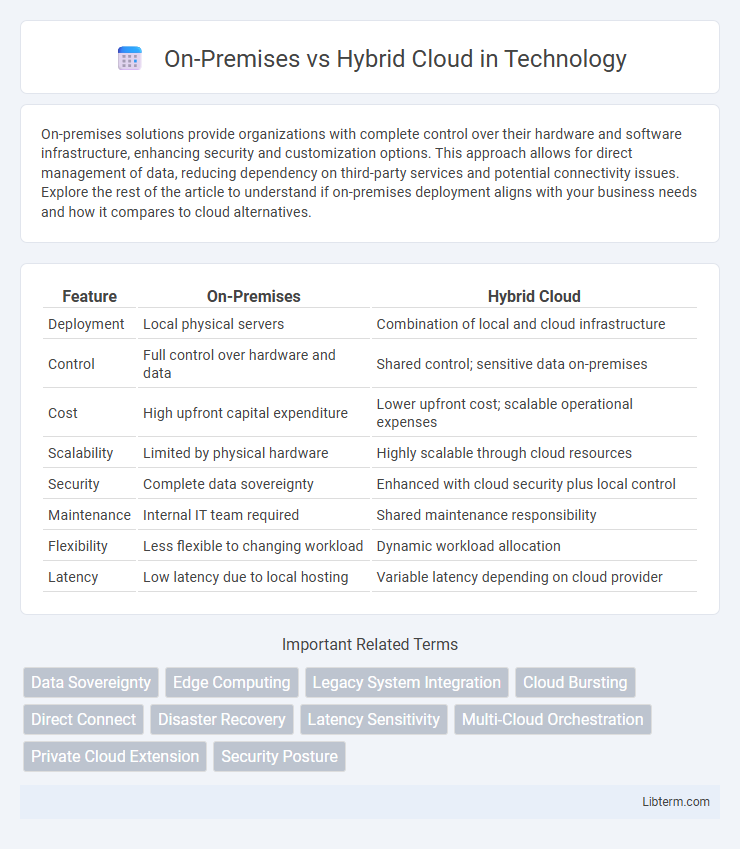
| Feature | On-Premises | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Local physical servers | Combination of local and cloud infrastructure |
| Control | Full control over hardware and data | Shared control; sensitive data on-premises |
| Cost | High upfront capital expenditure | Lower upfront cost; scalable operational expenses |
| Scalability | Limited by physical hardware | Highly scalable through cloud resources |
| Security | Complete data sovereignty | Enhanced with cloud security plus local control |
| Maintenance | Internal IT team required | Shared maintenance responsibility |
| Flexibility | Less flexible to changing workload | Dynamic workload allocation |
| Latency | Low latency due to local hosting | Variable latency depending on cloud provider |
Introduction to On-Premises and Hybrid Cloud
On-premises infrastructure involves housing servers and data storage within a company's physical location, offering full control over security, data, and hardware management. Hybrid cloud combines on-premises systems with public and private cloud services, enabling flexible workload distribution and enhanced scalability. Organizations leverage hybrid cloud models to optimize resource usage while maintaining critical data onsite for compliance and performance.
Key Differences Between On-Premises and Hybrid Cloud
On-premises environments provide full control over infrastructure, data security, and compliance management within a localized data center, ensuring complete data sovereignty. Hybrid cloud integrates on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, enabling flexible scalability, optimized workload distribution, and cost-efficiency by leveraging both private and public cloud resources. Key differences include resource elasticity, capital expenditure versus operational expenditure models, and complexity in management due to hybrid orchestration tools and cloud service integration.
Cost Comparison: On-Premises vs Hybrid Cloud
On-premises infrastructure requires significant upfront capital expenditure for hardware, software, and maintenance, leading to higher fixed costs compared to hybrid cloud models. Hybrid cloud solutions offer flexible operating expenses by combining on-premises resources with scalable cloud services, optimizing cost efficiency through pay-as-you-go pricing and reduced physical infrastructure investments. Total cost of ownership for hybrid cloud often results in lower long-term expenses due to improved resource utilization and minimized downtime.
Security Considerations in Both Models
On-premises environments offer direct control over physical security and data access, reducing external vulnerabilities but requiring significant investment in infrastructure and cybersecurity expertise. Hybrid cloud models combine on-premises control with cloud flexibility, necessitating robust encryption, identity management, and compliance protocols to mitigate risks associated with data transfer and multi-environment integration. Effective security in both setups relies on continuous monitoring, threat detection, and adherence to regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Scalability and Flexibility Analysis
On-premises infrastructure offers limited scalability due to fixed hardware resources, restricting rapid adaptation to fluctuating workloads. Hybrid cloud solutions combine on-premises systems with public cloud services, providing enhanced flexibility to dynamically scale resources based on demand. This hybrid model enables organizations to optimize performance and cost efficiency by leveraging the elasticity of cloud platforms while maintaining control over critical data on-premises.
Performance and Reliability Factors
On-premises infrastructure offers high performance and low latency due to localized control over hardware and network resources, ensuring consistent reliability in environments with predictable workloads. Hybrid cloud solutions provide flexibility by combining on-premises performance for critical applications with cloud scalability, optimizing resource allocation and fault tolerance. Performance in hybrid models depends on seamless integration and robust network connectivity to maintain reliability across distributed systems.
Compliance and Regulatory Implications
On-premises environments offer greater control over data residency, making them ideal for organizations facing strict regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Hybrid cloud solutions provide flexibility by enabling sensitive data to remain on-premises while leveraging cloud resources for non-critical workloads, balancing compliance with scalability. Effective governance and security policies are essential to navigate complex compliance landscapes when integrating hybrid cloud infrastructures.
Use Cases Best Suited for On-Premises
On-premises environments excel in use cases demanding high data security, strict regulatory compliance, and low-latency access, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies. Enterprises managing sensitive workloads benefit from complete control over infrastructure, ensuring enhanced customization and direct hardware management. Critical applications requiring predictable performance, disaster recovery, and legacy system integration are optimally supported by on-premises deployments.
Ideal Scenarios for Hybrid Cloud Adoption
Hybrid cloud adoption is ideal for organizations seeking scalability and flexibility by combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources. Businesses with fluctuating workloads or seasonal demand benefit from hybrid models to optimize costs and performance. Enterprises requiring enhanced data security while leveraging cloud innovation often adopt hybrid cloud to maintain sensitive operations on-premises alongside cloud-based applications.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Evaluating On-Premises versus Hybrid Cloud requires analyzing data security needs, workload flexibility, and cost efficiency. Organizations handling sensitive data often favor On-Premises for complete control, while Hybrid Cloud appeals to those needing scalable resources and disaster recovery options. Assessing IT infrastructure capabilities and compliance requirements ensures alignment with business goals and operational agility.
On-Premises Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com