A Load Balancer efficiently distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability and optimal resource use. It prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck, improving your application's responsiveness and uptime. Discover how implementing a Load Balancer can enhance your system's performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
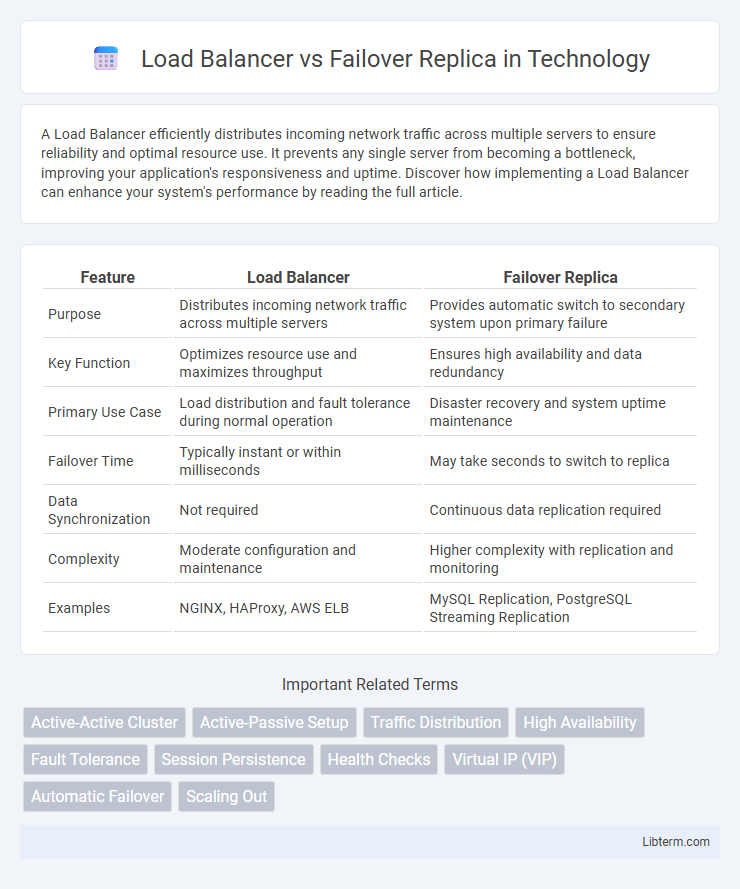
| Feature | Load Balancer | Failover Replica |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers | Provides automatic switch to secondary system upon primary failure |
| Key Function | Optimizes resource use and maximizes throughput | Ensures high availability and data redundancy |
| Primary Use Case | Load distribution and fault tolerance during normal operation | Disaster recovery and system uptime maintenance |
| Failover Time | Typically instant or within milliseconds | May take seconds to switch to replica |
| Data Synchronization | Not required | Continuous data replication required |
| Complexity | Moderate configuration and maintenance | Higher complexity with replication and monitoring |
| Examples | NGINX, HAProxy, AWS ELB | MySQL Replication, PostgreSQL Streaming Replication |
Understanding Load Balancer and Failover Replica
A Load Balancer distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use, maximize throughput, and minimize response time, ensuring high availability. A Failover Replica is a standby server that automatically takes over when the primary server fails, providing disaster recovery and maintaining system continuity. Understanding Load Balancer and Failover Replica highlights their roles in scalability versus reliability within distributed systems.
Key Differences: Load Balancer vs Failover Replica
Load balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use, maximize throughput, and ensure high availability, while failover replicas serve as standby systems that automatically take over when the primary server fails, ensuring data consistency and minimal downtime. Load balancers operate at the network or transport layer, managing load distribution in real-time, whereas failover replicas involve data synchronization and state replication to maintain seamless continuity. The key difference lies in load balancers enhancing performance and scalability, whereas failover replicas focus on reliability and disaster recovery.
How Load Balancers Work
Load balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed, optimizing resource use and maximizing throughput. They use algorithms such as round-robin, least connections, and IP hash to determine the best server for each request, improving application availability and responsiveness. By continuously monitoring server health and performance, load balancers reroute traffic away from failing or overloaded servers, maintaining seamless service delivery.
The Role of Failover Replicas
Failover replicas serve as standby systems that automatically take over workload processing in the event of primary system failure, ensuring high availability and minimizing downtime. Unlike load balancers that distribute traffic across multiple active servers to optimize performance, failover replicas remain passive until triggered by a failure event. Their critical role lies in disaster recovery and maintaining data integrity by replicating the primary server's state for seamless transition during outages.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Load balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers, enhancing performance by maximizing resource utilization and reducing latency under high load. Failover replicas primarily ensure high availability by replicating data to standby servers, which automatically take over during failures but do not actively improve performance under normal conditions. Scalability is greater with load balancers since they enable horizontal scaling by adding more active nodes, whereas failover replicas maintain a passive standby system focused on disaster recovery rather than handling increased traffic.
High Availability: Load Balancer vs Failover Replica
Load balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability by preventing any single server from becoming a bottleneck or point of failure. Failover replicas maintain synchronized copies of data on secondary servers, enabling automatic switchover in case the primary server fails, thus ensuring continuous service availability. Combining load balancers with failover replicas enhances system resilience by balancing load while providing seamless recovery during server outages.
Use Cases for Load Balancers
Load balancers efficiently distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers, enhancing application availability and scalability for high-demand environments like web services and e-commerce platforms. They optimize resource utilization and prevent server overload by ensuring no single server bears excessive traffic. Ideal use cases include managing session persistence for user requests and balancing workloads in cloud infrastructures to maintain seamless user experiences.
Use Cases for Failover Replicas
Failover replicas are essential for disaster recovery and high availability in database systems, automatically switching to a standby replica during primary server failures to prevent downtime. They are ideal for mission-critical applications requiring uninterrupted service, such as financial transactions, e-commerce platforms, and healthcare systems. Load balancers distribute traffic to multiple servers for performance optimization, but failover replicas specifically ensure data integrity and service continuity under system failures.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Infrastructure
Selecting between a load balancer and a failover replica depends on your infrastructure's scalability and availability needs. Load balancers distribute network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use and improve response times, making them ideal for handling high volumes of concurrent requests. Failover replicas provide redundancy by automatically switching to a standby database or server during failures, ensuring business continuity and data integrity in critical systems.
Conclusion: Load Balancer or Failover Replica?
Load Balancers optimize traffic distribution across multiple servers to enhance performance and scalability, making them ideal for environments with high user demand and variable workloads. Failover Replicas provide automatic redundancy and data protection by switching to a standby server during failures, ensuring high availability and disaster recovery. Choosing between a Load Balancer or Failover Replica depends on prioritizing either load distribution for improved responsiveness or failover capabilities for system reliability.
Load Balancer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com