GraphQL is a powerful query language for APIs that allows you to request exactly the data you need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of information. Its flexible structure enhances performance and efficiency by enabling clients to specify the shape of the responses, streamlining the interaction between front-end and back-end systems. Explore this article to understand how GraphQL can transform your data management strategies and boost your application's capabilities.
Table of Comparison
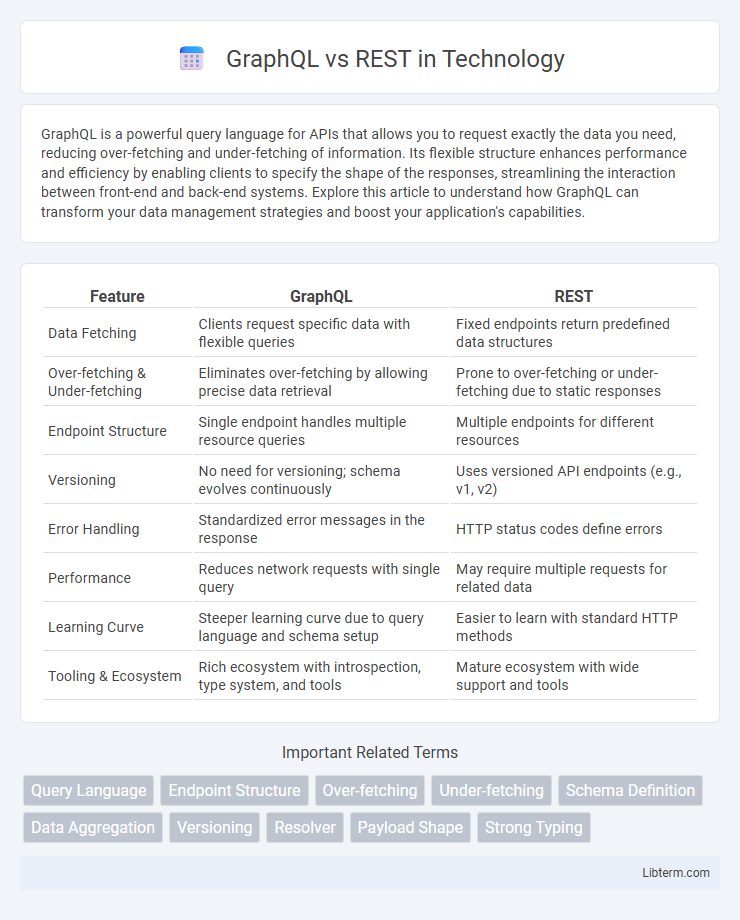
| Feature | GraphQL | REST |
|---|---|---|
| Data Fetching | Clients request specific data with flexible queries | Fixed endpoints return predefined data structures |
| Over-fetching & Under-fetching | Eliminates over-fetching by allowing precise data retrieval | Prone to over-fetching or under-fetching due to static responses |
| Endpoint Structure | Single endpoint handles multiple resource queries | Multiple endpoints for different resources |
| Versioning | No need for versioning; schema evolves continuously | Uses versioned API endpoints (e.g., v1, v2) |
| Error Handling | Standardized error messages in the response | HTTP status codes define errors |
| Performance | Reduces network requests with single query | May require multiple requests for related data |
| Learning Curve | Steeper learning curve due to query language and schema setup | Easier to learn with standard HTTP methods |
| Tooling & Ecosystem | Rich ecosystem with introspection, type system, and tools | Mature ecosystem with wide support and tools |
Introduction to GraphQL and REST
GraphQL is a query language for APIs developed by Facebook, enabling clients to request exactly the data they need, improving efficiency and reducing over-fetching. REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style that uses predefined endpoints and HTTP methods to interact with server resources, often resulting in multiple requests for related data. GraphQL provides a single endpoint with flexible queries, whereas REST relies on multiple endpoints serving fixed data structures.
Core Concepts and Architecture
GraphQL enables clients to request exactly the data they need through a single endpoint, using a strong, type-based schema that allows flexible queries and real-time updates via subscriptions. REST architecture relies on multiple endpoints representing distinct resources, with fixed request-response patterns typically using standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. GraphQL's schema-driven approach improves efficiency by reducing over-fetching and under-fetching, while REST emphasizes statelessness and resource manipulation through resource-specific URLs.
Data Fetching and Flexibility
GraphQL enables precise data fetching by allowing clients to request only the specific fields needed, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching common in REST APIs. REST relies on fixed endpoints returning predefined data structures, which can lead to multiple requests or excessive data transfer. GraphQL's flexible query structure supports complex data retrieval in a single call, enhancing efficiency and adaptability in dynamic applications.
Performance and Efficiency
GraphQL improves performance by allowing clients to request only the specific data fields needed, reducing over-fetching and minimizing response sizes compared to REST's fixed endpoints. REST APIs often result in multiple round trips to different endpoints to gather related data, while GraphQL consolidates queries into a single request, enhancing network efficiency. Furthermore, GraphQL's ability to batch and cache requests further optimizes data retrieval, reducing server load and improving overall application responsiveness.
API Versioning Strategies
GraphQL offers a flexible API versioning strategy by avoiding traditional versioning through a single evolving schema that supports deprecation and addition of fields without breaking changes. REST APIs often require explicit versioning via URL paths or headers (e.g., /v1/, /v2/) to manage backward compatibility and introduce new features. Using GraphQL's type system and introspection, developers can iterate rapidly while maintaining API stability, whereas REST's versioning can lead to multiple coexisting API versions and increased maintenance overhead.
Error Handling Approaches
GraphQL employs a unified error response format that combines data and errors in a single JSON object, allowing clients to receive partial data alongside detailed error messages, improving fault tolerance and debugging efficiency. REST typically relies on HTTP status codes to indicate errors, with separate response bodies containing error details, which can make handling partial successes or multiple errors more complex. GraphQL's structured error objects facilitate granular, client-specific error handling, while REST's approach emphasizes standardized status codes for signaling error types across diverse endpoints.
Security Considerations
GraphQL's single endpoint architecture reduces the attack surface compared to REST's multiple endpoints but requires robust query validation to prevent injection attacks and excessive data exposure. REST relies on standard HTTP methods, making it compatible with existing security tools and easier to implement rate limiting and authentication mechanisms. Implementing strong authorization rules at the resolver level in GraphQL is essential to control data access and maintain API security on par with REST APIs.
Tooling and Ecosystem Support
GraphQL offers advanced tooling such as GraphiQL and Apollo Studio for real-time query testing and schema exploration, enhancing developer productivity. REST benefits from a mature ecosystem with widespread support in frameworks like Express and Django, alongside comprehensive API documentation tools like Swagger. Both paradigms integrate well with CI/CD pipelines, but GraphQL's schema-centric tools provide better introspection and type safety during development.
Use Cases and Best Scenarios
GraphQL is ideal for applications requiring precise data fetching and complex querying across multiple related resources, such as real-time dashboards and mobile apps with varying data needs. REST excels in scenarios with standardized CRUD operations and clear resource boundaries, making it suitable for publicly exposed APIs or systems with cacheable responses. Enterprises benefit from GraphQL when optimizing bandwidth and reducing over-fetching, while REST remains preferred for simpler, stateless APIs with mature tooling and widespread adoption.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right API Approach
Choosing the right API approach depends on the specific requirements of your project. GraphQL offers flexible, efficient data retrieval ideal for complex queries and reducing over-fetching, while REST provides simplicity and broad compatibility suited for straightforward CRUD operations. Evaluating factors like data complexity, development speed, and client needs ensures the optimal integration of either GraphQL or REST.
GraphQL Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com