Agile methodology revolutionizes project management by emphasizing flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback to deliver high-quality results efficiently. Its iterative approach allows teams to adapt to changes quickly, ensuring that project goals align closely with business needs and stakeholder expectations. Discover how Agile can transform Your project workflows and drive success by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
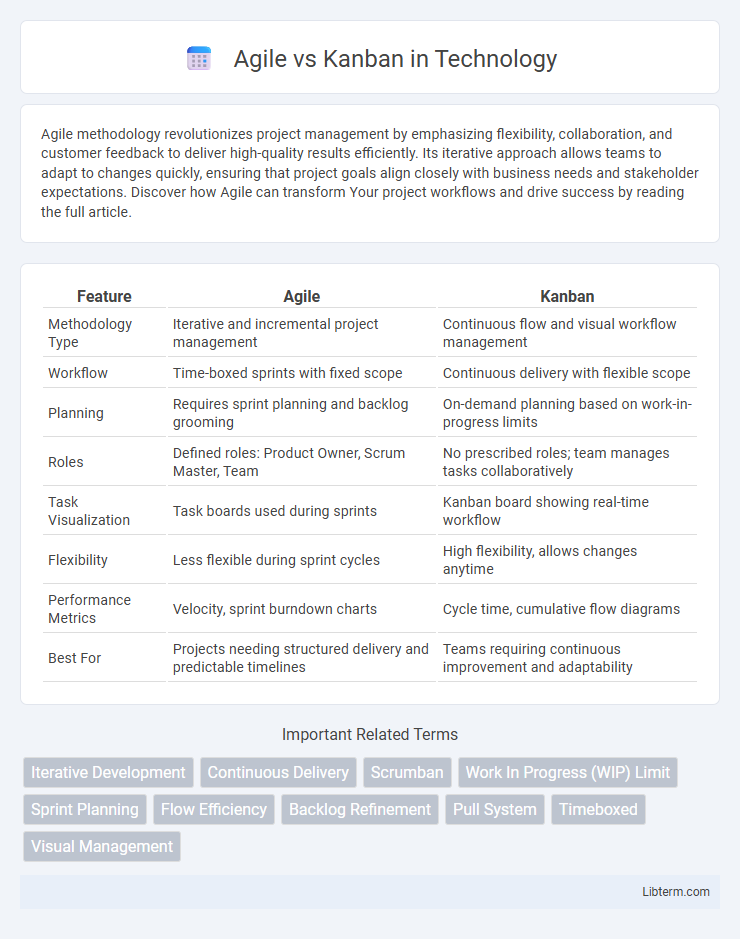
| Feature | Agile | Kanban |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology Type | Iterative and incremental project management | Continuous flow and visual workflow management |
| Workflow | Time-boxed sprints with fixed scope | Continuous delivery with flexible scope |
| Planning | Requires sprint planning and backlog grooming | On-demand planning based on work-in-progress limits |
| Roles | Defined roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Team | No prescribed roles; team manages tasks collaboratively |
| Task Visualization | Task boards used during sprints | Kanban board showing real-time workflow |
| Flexibility | Less flexible during sprint cycles | High flexibility, allows changes anytime |
| Performance Metrics | Velocity, sprint burndown charts | Cycle time, cumulative flow diagrams |
| Best For | Projects needing structured delivery and predictable timelines | Teams requiring continuous improvement and adaptability |
Introduction to Agile and Kanban
Agile is a flexible project management methodology emphasizing iterative development, customer collaboration, and adaptive planning to deliver high-quality products efficiently. Kanban, a visual workflow management tool originating from Lean manufacturing, focuses on continuous delivery by limiting work in progress and visualizing tasks on a board. Both Agile and Kanban improve team productivity and responsiveness but differ in structure and implementation focus.
Core Principles of Agile
Agile core principles emphasize iterative development, customer collaboration, and responding to change over rigid planning, fostering flexibility and continuous improvement in project management. Agile promotes self-organizing teams, delivering working software frequently, and valuing individuals and interactions to enhance productivity and product quality. Unlike Kanban, which centers on workflow visualization and limiting work in progress, Agile encompasses broader values and practices that drive adaptive and incremental delivery.
Core Principles of Kanban
Kanban centers on visualizing work, limiting work in progress (WIP), and managing flow to improve efficiency and reduce bottlenecks. It emphasizes continuous delivery without overloading team members, allowing for flexibility and adaptability in project management. This method relies on real-time communication of capacity and workflow, enabling teams to respond swiftly to changing priorities.
Key Differences Between Agile and Kanban
Agile is a broad project management philosophy emphasizing iterative development and customer collaboration, while Kanban is a specific Agile framework focused on visualizing work and managing flow. Agile uses time-boxed sprints with predefined tasks, whereas Kanban employs continuous delivery without fixed iterations. Agile teams plan work in batches, contrasting with Kanban's pull system that limits work in progress for optimizing efficiency.
When to Choose Agile
Choose Agile when project requirements are evolving, complex, or unclear, requiring iterative development and frequent delivery of functional software. Agile is ideal for teams seeking continuous feedback, flexibility in scope changes, and strong collaboration among cross-functional members. Projects with a need for rapid prototyping, adaptive planning, and incremental value delivery benefit significantly from Agile methodologies.
When to Use Kanban
Kanban is ideal for projects requiring continuous delivery without overloading team capacity, particularly in environments with fluctuating priorities. It excels in maintenance and support teams where work items need to be visualized across stages to improve flow and limit work in progress (WIP). Use Kanban when flexibility and incremental improvements are prioritized over fixed iterations or sprints common in Agile Scrum.
Advantages and Challenges of Agile
Agile offers significant advantages such as increased flexibility, faster delivery of products, and enhanced collaboration among cross-functional teams, which leads to improved customer satisfaction. However, Agile presents challenges including the need for strong team discipline, potential scope creep due to iterative processes, and difficulties in accurately estimating timelines and resources. Organizations adopting Agile must invest in continuous training and adapt their culture to fully realize its benefits while managing these complexities.
Advantages and Challenges of Kanban
Kanban offers significant advantages such as enhanced workflow visualization, improved flexibility in task management, and continuous delivery without the need for fixed iterations, which helps teams adapt quickly to changing priorities. Key challenges include potential for workflow bottlenecks if WIP (Work In Progress) limits are not strictly enforced, difficulty in measuring progress compared to time-boxed methods like Scrum, and the risk of less structured planning leading to scope creep. Effective implementation of Kanban requires disciplined use of visual boards, WIP limits, and regular review to optimize productivity and maintain project control.
Real-World Use Cases and Examples
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, excel in software development projects requiring iterative planning, frequent stakeholder feedback, and adaptive sprint cycles to deliver incremental value. Kanban offers real-world efficiency in manufacturing and support environments by visualizing workflow, limiting work in progress, and enabling continuous delivery without fixed iterations. Companies like Spotify leverage Agile for rapid product innovation, while Toyota uses Kanban to streamline production and improve operational flow.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the right approach between Agile and Kanban depends on project requirements and team dynamics, with Agile offering structured iteration cycles and Kanban providing continuous workflow optimization. Agile suits projects needing flexibility in scope with regular feedback loops, while Kanban excels in environments prioritizing visual task management and steady delivery. Evaluating factors such as project complexity, team size, and deadline sensitivity ensures alignment with organizational goals for optimal productivity and value delivery.
Agile Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com