A Virtual Private Network (VPN) secures your internet connection by encrypting data and masking your IP address, providing enhanced privacy and protection against cyber threats. It enables access to restricted content and safe browsing on public Wi-Fi networks. Discover how a VPN can safeguard your online activities and improve your digital security further in this article.
Table of Comparison
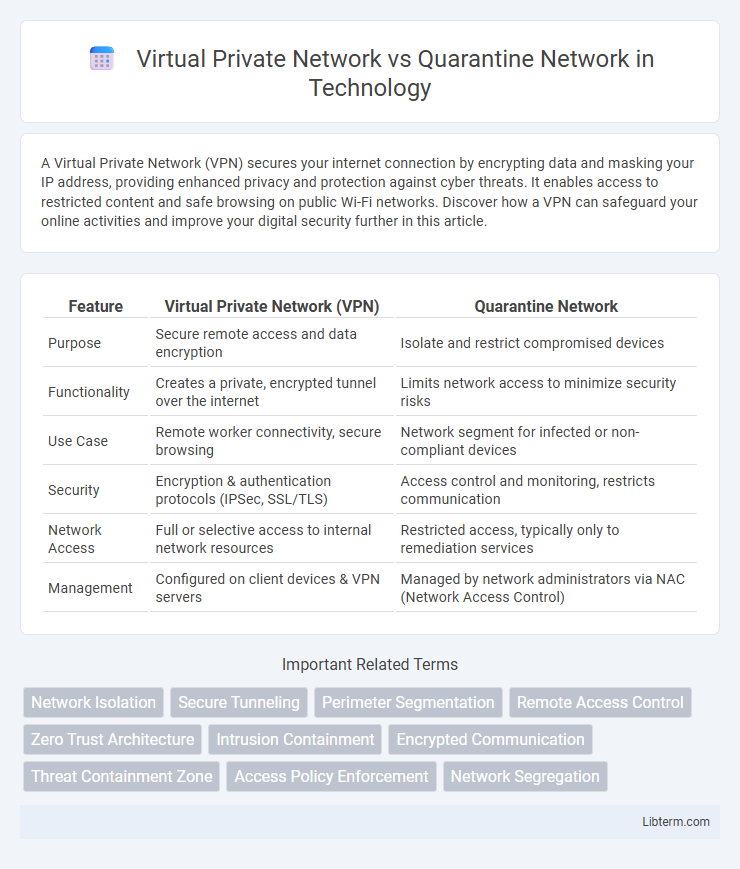
| Feature | Virtual Private Network (VPN) | Quarantine Network |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Secure remote access and data encryption | Isolate and restrict compromised devices |
| Functionality | Creates a private, encrypted tunnel over the internet | Limits network access to minimize security risks |
| Use Case | Remote worker connectivity, secure browsing | Network segment for infected or non-compliant devices |
| Security | Encryption & authentication protocols (IPSec, SSL/TLS) | Access control and monitoring, restricts communication |
| Network Access | Full or selective access to internal network resources | Restricted access, typically only to remediation services |
| Management | Configured on client devices & VPN servers | Managed by network administrators via NAC (Network Access Control) |
Introduction to Network Security Solutions
Virtual Private Network (VPN) and Quarantine Network are essential components in network security solutions, addressing data protection and threat containment respectively. VPN securely encrypts internet traffic, ensuring confidentiality and remote access, while Quarantine Network isolates suspicious devices to prevent malware spread within an enterprise. Effective network security architecture integrates VPN for secure communication and Quarantine Network to mitigate risks from compromised endpoints.
Defining Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) establish encrypted connections over public networks, enabling secure remote access to private data and resources. VPNs use tunneling protocols like OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, or WireGuard to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. Unlike quarantine networks that isolate compromised devices, VPNs prioritize secure communication for authorized users across diverse locations.
Understanding Quarantine Networks
Quarantine networks isolate devices suspected of security risks by restricting their access to critical resources, enabling administrators to conduct security assessments and enforce compliance before granting full network access. Unlike Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), which create encrypted tunnels for secure remote communication, quarantine networks serve as a containment and remediation layer to prevent potential threats from propagating. Implementing quarantine networks enhances organizational cybersecurity by ensuring only compliant and verified devices connect to the primary network environment.
Core Differences: VPN vs Quarantine Network
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between a user's device and the internet, allowing safe access to network resources and protecting data privacy. In contrast, a Quarantine Network isolates devices suspected of being infected or non-compliant with security policies, restricting their access to prevent potential threats from spreading within the main network. The core difference lies in VPN enabling secure remote access, while Quarantine Networks enforce security by limiting connectivity until devices meet compliance standards.
Use Cases for Virtual Private Networks
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) enable secure remote access to corporate resources by encrypting internet connections, making them ideal for telecommuting employees and protecting sensitive data on public Wi-Fi. VPNs also facilitate bypassing geographic restrictions and censorship, supporting global business operations and private browsing. In contrast, Quarantine Networks isolate potentially compromised devices to prevent malware spread, primarily serving security management rather than remote connectivity or privacy needs.
Applications of Quarantine Networks
Quarantine Networks isolate infected or non-compliant devices to prevent the spread of malware and protect critical infrastructure while allowing limited access for remediation and updates. Unlike Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) that secure remote access by encrypting data between user devices and corporate resources, Quarantine Networks focus on network segmentation and device compliance enforcement. Common applications of Quarantine Networks include managing endpoint security in corporate environments, mitigating risks during network onboarding processes, and ensuring regulatory compliance by controlling device access based on health status.
Security Benefits: VPN vs Quarantine Network
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts internet traffic, masking IP addresses and securing data transmissions to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. In contrast, a Quarantine Network isolates potentially compromised devices, preventing them from accessing the main network until security risks are mitigated, thus containing malware and limiting lateral movement. Both solutions enhance organizational security, with VPNs providing secure remote connections and Quarantine Networks enforcing strict access control for compromised endpoints.
Potential Risks and Limitations
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can expose users to potential risks such as data leakage, weak encryption protocols, and susceptibility to cyberattacks if improperly configured or using insecure servers. Quarantine Networks, designed to isolate suspicious or infected devices, face limitations including restricted network access that may hinder productivity and challenges in comprehensive threat detection without advanced monitoring tools. Both VPNs and Quarantine Networks require rigorous security policies and regular updates to mitigate vulnerabilities and ensure effective protection.
Choosing the Right Network Solution
Choosing the right network solution depends on organizational security needs and access control requirements. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide secure remote access by encrypting data and connecting users to trusted internal networks, ideal for remote work and confidential communications. Quarantine Networks isolate devices with potential security risks, restricting access until compliance or remediation is confirmed, making them essential for mitigating threats and maintaining network integrity.
Future Trends in Network Security
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) will continue evolving with advanced encryption protocols and AI-driven threat detection to enhance secure remote access, while Quarantine Networks are becoming more dynamic by integrating automated segmentation and real-time behavioral analysis to isolate compromised devices swiftly. Emerging trends emphasize zero-trust architectures that combine VPN encryption with quarantine capabilities, enabling granular access control and immediate containment of cyber threats. The convergence of VPN and quarantine technologies supports proactive defense strategies, leveraging machine learning for predictive security and adaptive network policies in increasingly complex IT environments.
Virtual Private Network Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com