BDD and unit testing are essential practices for ensuring your code behaves as expected by focusing on behavior and functionality at the smallest testable parts. BDD emphasizes writing tests from the user's perspective to clarify requirements, while unit testing verifies individual components in isolation for correctness. Discover how integrating these methods can enhance your development process and software quality in the full article.
Table of Comparison
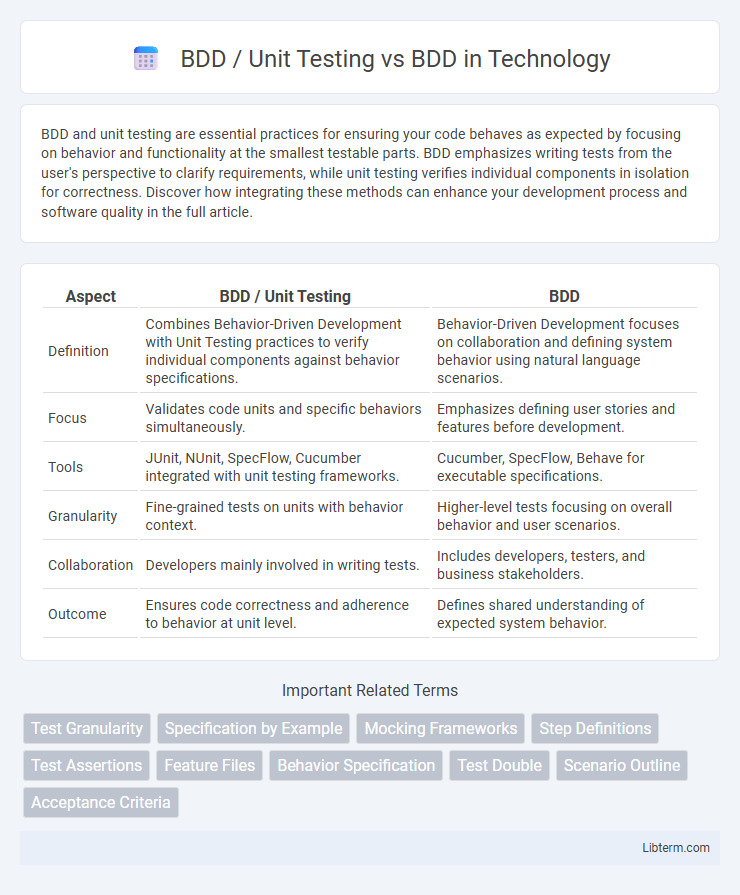
| Aspect | BDD / Unit Testing | BDD |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines Behavior-Driven Development with Unit Testing practices to verify individual components against behavior specifications. | Behavior-Driven Development focuses on collaboration and defining system behavior using natural language scenarios. |
| Focus | Validates code units and specific behaviors simultaneously. | Emphasizes defining user stories and features before development. |
| Tools | JUnit, NUnit, SpecFlow, Cucumber integrated with unit testing frameworks. | Cucumber, SpecFlow, Behave for executable specifications. |
| Granularity | Fine-grained tests on units with behavior context. | Higher-level tests focusing on overall behavior and user scenarios. |
| Collaboration | Developers mainly involved in writing tests. | Includes developers, testers, and business stakeholders. |
| Outcome | Ensures code correctness and adherence to behavior at unit level. | Defines shared understanding of expected system behavior. |
Introduction to Unit Testing and BDD
Unit Testing involves verifying individual components or functions of software to ensure they perform as expected, focusing on isolated code behavior. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) extends this approach by emphasizing collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to define software behavior using human-readable scenarios. BDD uses domain-specific language to create executable specifications that guide development and testing, improving communication and aligning software outcomes with business requirements.
Core Principles of Unit Testing
Unit testing centers on verifying individual components in isolation, emphasizing atomicity, repeatability, and quick execution to ensure code correctness at the granular level. Core principles involve testing a single function or method with controlled inputs to produce expected outputs, minimizing dependencies through mocking or stubbing. Behavioral-Driven Development (BDD) extends unit testing by framing tests around user behaviors and system outcomes, aligning technical tests with business requirements while maintaining the foundational unit test focus on method-level validation.
Fundamentals of Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) centers on collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to define software behavior using clear, domain-specific language, improving communication and requirement clarity. Unlike Unit Testing that focuses on verifying individual code components in isolation, BDD emphasizes testing behaviors and user stories from an end-user perspective, ensuring that software meets business needs. Core BDD tools like Cucumber or SpecFlow facilitate executable specifications that bridge the gap between technical implementation and business requirements.
Unit Testing Workflow and Practices
BDD emphasizes collaboration through user stories and scenarios, driving development from a behavior perspective to ensure software meets business requirements. Unit testing focuses on isolating and testing individual functions or methods, verifying code correctness at a granular level through automated tests executed frequently in the development workflow. The unit testing workflow includes writing test cases aligned with code units, running tests with frameworks like JUnit or NUnit, and integrating with CI/CD pipelines to catch regressions early and maintain code quality throughout the software lifecycle.
BDD Workflow and Practices
BDD workflow centers on collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to define clear, behavior-driven specifications using user stories and scenarios written in a natural language format. Practices emphasize writing executable specifications that guide development and serve as living documentation, enabling continuous feedback through automated tests that validate application behavior from the user's perspective. This contrasts with Unit Testing, which targets isolated code components and internal logic without explicit focus on user-centric behavior or collaborative specification.
Key Differences Between Unit Testing and BDD
Unit testing focuses on validating individual components of code in isolation, ensuring each function or method performs as expected. Behavior Driven Development (BDD) emphasizes collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to define application behavior through examples written in natural language. The key difference lies in BDD's user-centric approach that bridges technical implementation with business requirements, while unit testing is primarily a developer-oriented practice targeting code correctness.
Advantages of Unit Testing
Unit testing offers precise validation of individual code components, ensuring early detection of bugs and simplifying code refactoring in Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) environments. It enhances test coverage by isolating functions, leading to faster feedback loops compared to broader BDD scenarios. Unit tests improve maintainability and reliability of software by enforcing modular design and facilitating continuous integration pipelines in agile projects.
Benefits of BDD for Teams
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) improves team collaboration by promoting a shared understanding of requirements through clear, example-driven specifications that align business and technical stakeholders. Unlike traditional unit testing, BDD encourages writing test scenarios in natural language, enhancing communication and reducing misunderstandings. This approach accelerates feedback loops, ensures comprehensive coverage of user behaviors, and ultimately leads to higher-quality software delivered with greater confidence.
When to Choose Unit Testing vs BDD
Unit Testing is ideal for verifying individual components or functions, ensuring that specific code units work as intended in isolation. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) is best suited for validating overall system behavior by defining user-centric scenarios that bridge communication between developers, testers, and stakeholders. Choose Unit Testing when precise, low-level code validation is needed, and opt for BDD to align development with business requirements and improve collaboration across teams.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Approach
Selecting the best approach between BDD/Unit Testing and pure BDD depends on project goals and team collaboration needs. BDD/Unit Testing combines behavior-driven development's clear, user-focused scenarios with thorough unit-level code validation, ensuring both functionality and maintainability. Pure BDD emphasizes communication and shared understanding, ideal for aligning cross-functional teams but may require supplementing with unit tests for detailed code coverage.
BDD / Unit Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com