Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys--public and private--to securely encode and decode information, ensuring data confidentiality and authenticity. This method is widely employed in secure communications, digital signatures, and key exchanges to protect sensitive data against unauthorized access. Explore the rest of the article to understand how asymmetric encryption can enhance your data security strategies.
Table of Comparison
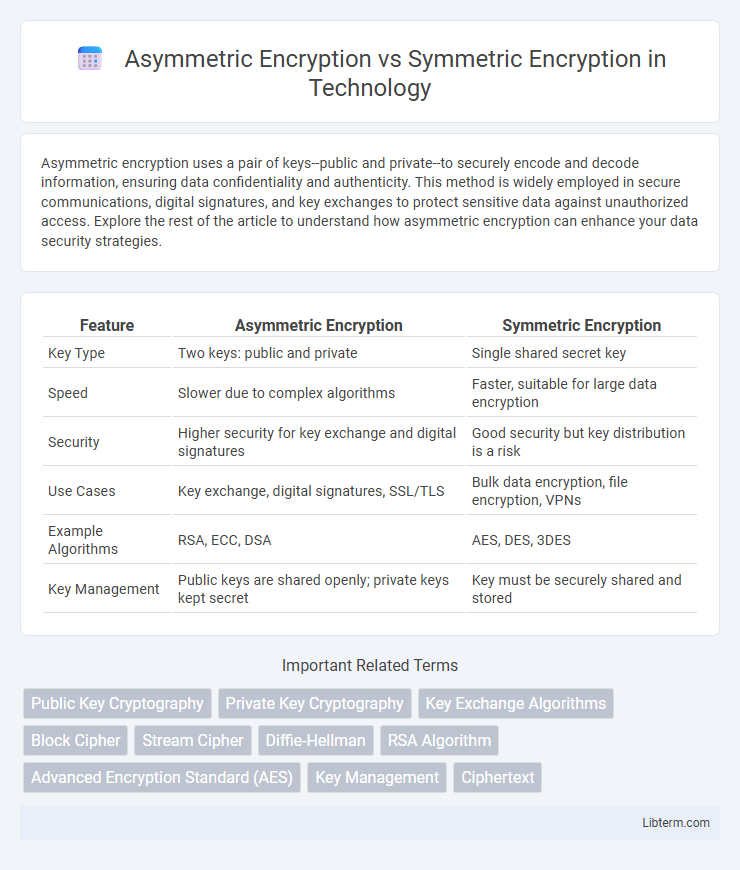
| Feature | Asymmetric Encryption | Symmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Key Type | Two keys: public and private | Single shared secret key |
| Speed | Slower due to complex algorithms | Faster, suitable for large data encryption |
| Security | Higher security for key exchange and digital signatures | Good security but key distribution is a risk |
| Use Cases | Key exchange, digital signatures, SSL/TLS | Bulk data encryption, file encryption, VPNs |
| Example Algorithms | RSA, ECC, DSA | AES, DES, 3DES |
| Key Management | Public keys are shared openly; private keys kept secret | Key must be securely shared and stored |
Introduction to Encryption Methods
Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys--public and private--for secure data transmission, ensuring confidentiality and authentication without sharing secret keys. Symmetric encryption relies on a single secret key for both encryption and decryption, offering faster processing but requiring secure key distribution. Both methods play crucial roles in modern cryptography, balancing speed, security, and key management based on application requirements.
What is Symmetric Encryption?
Symmetric encryption is a cryptographic method where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption of data, ensuring fast and efficient processing. It is widely applied in data transmission and storage to protect sensitive information, relying on secret keys shared between communicating parties. Common symmetric algorithms include AES, DES, and Blowfish, providing strong security with lower computational overhead compared to asymmetric encryption.
What is Asymmetric Encryption?
Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of mathematically related keys--a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption--ensuring secure communication without sharing secret keys. It enables secure key exchange, digital signatures, and authentication, commonly employed in protocols like SSL/TLS for internet security. This encryption method provides enhanced security over symmetric encryption by eliminating the need to distribute private keys, making it ideal for secure data transmission across untrusted networks.
Key Differences: Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses a single secret key for both encryption and decryption, making it faster and more efficient for processing large data volumes. Asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys--a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption--enhancing security through key distribution without sharing private keys. The key difference lies in key management: symmetric encryption requires secure key exchange, while asymmetric encryption provides secure communication channels without prior key sharing.
How Symmetric Encryption Works
Symmetric encryption works by using a single, shared secret key for both encryption and decryption, ensuring data confidentiality through fast and efficient cryptographic algorithms like AES or DES. The sender encrypts plaintext into ciphertext using the secret key, while the receiver uses the same key to revert ciphertext back to plaintext securely. This method is highly effective for encrypting large volumes of data but requires a secure key exchange mechanism to prevent unauthorized access.
How Asymmetric Encryption Works
Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of mathematically related keys--public and private--to secure data, where the public key encrypts the message and only the corresponding private key can decrypt it. This method ensures secure communication over untrusted networks by allowing anyone to encrypt data with the recipient's public key, while only the recipient can decrypt it using their private key. The security of asymmetric encryption relies on complex algorithms such as RSA or ECC, making key exchange and data confidentiality more robust compared to symmetric encryption.
Security Strength Comparison
Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys--public and private--offering enhanced security through complex mathematical algorithms that protect data in transit without sharing secret keys. Symmetric encryption relies on a single shared key, making it faster but more vulnerable to key distribution risks and potential interception. The security strength of asymmetric encryption is generally higher due to its ability to securely exchange keys and resist certain cryptographic attacks, while symmetric encryption remains efficient for encrypting large data volumes when key management is secure.
Performance and Speed Analysis
Symmetric encryption algorithms such as AES deliver high-speed performance due to their simpler mathematical operations and use of a single shared key, making them ideal for encrypting large volumes of data rapidly. Asymmetric encryption methods like RSA or ECC involve complex computations with public and private key pairs, resulting in slower processing times and higher computational overhead. Performance analysis consistently shows symmetric encryption outperforms asymmetric encryption in speed, which is why hybrid cryptographic systems use asymmetric encryption for key exchange and symmetric encryption for bulk data encryption.
Common Use Cases and Applications
Asymmetric encryption is widely used in secure communication protocols such as SSL/TLS for website security, email encryption with PGP, and digital signatures for authentication due to its use of public and private key pairs. Symmetric encryption excels in encrypting large datasets quickly, making it ideal for securing data at rest, such as in database encryption and disk encryption solutions like AES. Both encryption types complement each other in hybrid cryptosystems, where asymmetric encryption secures key exchange while symmetric encryption handles bulk data encryption.
Choosing the Right Encryption Method
Choosing the right encryption method depends on factors such as data sensitivity, performance requirements, and key management complexities. Symmetric encryption offers faster processing speeds ideal for encrypting large volumes of data but requires secure key distribution, while asymmetric encryption provides enhanced security through public-private key pairs, making it suitable for secure key exchange and authentication. Organizations often implement hybrid encryption to leverage the speed of symmetric algorithms alongside the security benefits of asymmetric methods.
Asymmetric Encryption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com