A data mart is a focused subset of a data warehouse designed to meet the specific needs of a particular business unit or department, improving data accessibility and analysis efficiency. By streamlining data storage and retrieval, data marts enable quicker decision-making and targeted business insights. Explore the rest of the article to discover how data marts can enhance your organization's data strategy.
Table of Comparison
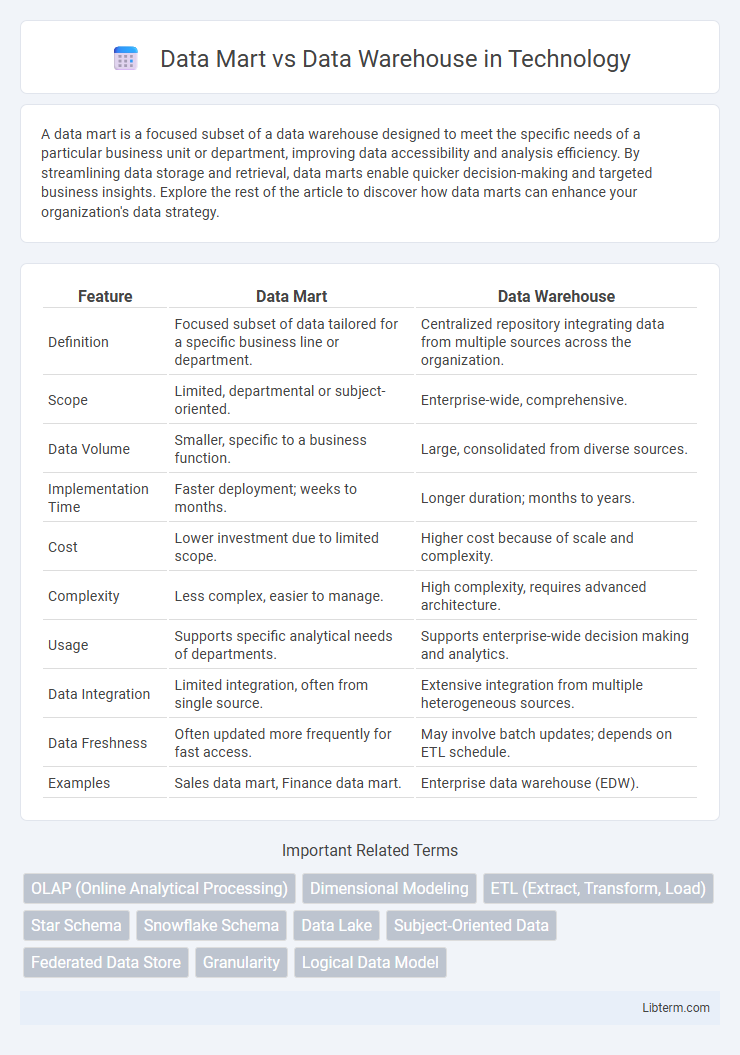
| Feature | Data Mart | Data Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focused subset of data tailored for a specific business line or department. | Centralized repository integrating data from multiple sources across the organization. |
| Scope | Limited, departmental or subject-oriented. | Enterprise-wide, comprehensive. |
| Data Volume | Smaller, specific to a business function. | Large, consolidated from diverse sources. |
| Implementation Time | Faster deployment; weeks to months. | Longer duration; months to years. |
| Cost | Lower investment due to limited scope. | Higher cost because of scale and complexity. |
| Complexity | Less complex, easier to manage. | High complexity, requires advanced architecture. |
| Usage | Supports specific analytical needs of departments. | Supports enterprise-wide decision making and analytics. |
| Data Integration | Limited integration, often from single source. | Extensive integration from multiple heterogeneous sources. |
| Data Freshness | Often updated more frequently for fast access. | May involve batch updates; depends on ETL schedule. |
| Examples | Sales data mart, Finance data mart. | Enterprise data warehouse (EDW). |
Introduction to Data Mart and Data Warehouse
Data Warehouse is a centralized repository that aggregates large volumes of data from multiple sources, designed for complex querying and extensive analytics across an entire organization. Data Mart is a smaller, subset database focused on specific business lines or departments, providing customized and faster access to relevant data. While Data Warehouses support broad data analysis and historical storage, Data Marts cater to targeted user groups requiring streamlined and domain-specific insights.
Key Definitions: Data Mart and Data Warehouse
A Data Mart is a focused subset of a Data Warehouse designed for specific business lines or departments, providing specialized data tailored for quick access and analysis. A Data Warehouse is a centralized repository that aggregates large volumes of data from multiple sources, enabling comprehensive data analysis across the entire organization. Both structures support decision-making, but Data Warehouses offer broad data integration whereas Data Marts emphasize targeted, user-specific data retrieval.
Core Differences Between Data Mart and Data Warehouse
Data marts and data warehouses both store organizational data but differ primarily in scope and purpose; data warehouses consolidate data from multiple sources for enterprise-wide analysis, while data marts focus on specific business lines or departments, offering a more tailored dataset. Data warehouses typically handle larger volumes of data and support complex queries across the entire organization, whereas data marts prioritize faster access and simplified data structures for niche user groups. This distinction influences data integration, storage costs, and query performance, making data marts suitable for tactical decision-making and data warehouses ideal for strategic analytics.
Structure and Architecture Comparison
Data marts are focused, subject-oriented repositories designed to serve specific business lines or departments, featuring a simplified architecture with faster query performance due to smaller data volume. Data warehouses integrate and store large volumes of enterprise-wide data, employing a complex, centralized architecture that supports advanced analytics, historical data consolidation, and cross-functional reporting. While data marts streamline access and improve responsiveness for targeted users, data warehouses provide comprehensive data governance, consistency, and scalability across diverse organizational needs.
Use Cases: When to Use Data Mart vs Data Warehouse
Data marts are ideal for targeted departmental analysis, providing quick access to specific business units like sales or marketing with tailored data subsets. Data warehouses support enterprise-wide data integration, enabling comprehensive reporting and advanced analytics across multiple departments and large datasets. Organizations use data marts for focused, agile decision-making, while data warehouses serve as centralized repositories for strategic insights and long-term data storage.
Advantages of Data Marts
Data marts offer targeted data storage solutions designed to meet the specific needs of individual departments, improving query performance by reducing data volume compared to enterprise-wide data warehouses. Their streamlined architecture enables faster deployment and lower costs, making them ideal for organizations requiring agile decision support systems. By isolating relevant datasets, data marts enhance user accessibility and simplify data management without compromising security or data integrity.
Benefits of Data Warehouses
Data warehouses consolidate large volumes of data from multiple sources, enabling comprehensive analytics and business intelligence with high data quality and consistency. They support complex queries and historical data analysis, providing a single source of truth for strategic decision-making across an entire organization. Enhanced scalability and centralized data governance in data warehouses streamline data management and improve overall organizational efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations
Data marts face challenges with data integration and consistency due to their limited scope, often leading to data silos and duplication when multiple marts exist independently. Data warehouses encounter limitations in handling large-scale data processing and real-time analytics, which can result in slower query performance and increased maintenance complexity. Both systems require robust data governance and metadata management strategies to overcome issues of data quality, scalability, and user accessibility.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Selecting between a data mart and a data warehouse depends on business scale, data complexity, and specific departmental needs. Data marts offer focused, faster access to relevant data for individual business units, improving efficiency with lower cost and simpler management. Data warehouses provide integrated, comprehensive enterprise-wide data solutions optimal for complex analytics and long-term strategic decision-making.
Future Trends in Data Storage Solutions
Data marts and data warehouses will increasingly integrate with cloud-native technologies, enabling scalable storage and real-time analytics for enterprise data. Advances in AI and machine learning will drive automation in data management, optimizing ETL processes and enhancing data quality within both architectures. The adoption of hybrid cloud models and edge computing will shape future data storage solutions, offering more flexible and faster access to localized data for business intelligence.
Data Mart Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com