Authoritative DNS servers provide the definitive answers to DNS queries by storing and managing DNS records for specific domains, ensuring accurate and reliable domain name resolution. These servers play a critical role in directing internet traffic to the correct IP addresses, enhancing both website performance and security. Explore the rest of the article to understand how authoritative DNS impacts your online presence and why proper configuration matters.
Table of Comparison
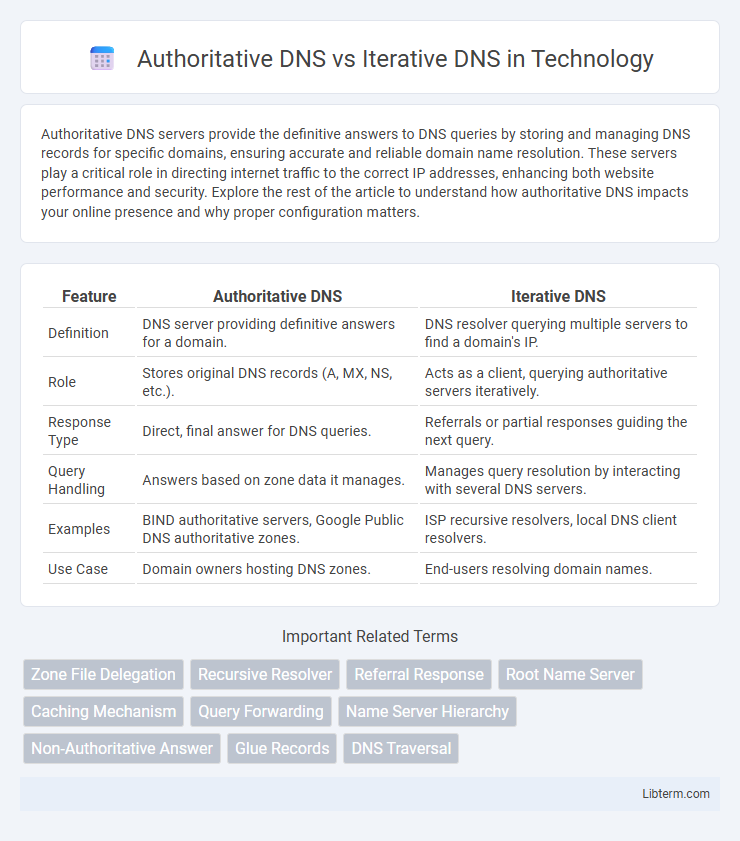
| Feature | Authoritative DNS | Iterative DNS |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | DNS server providing definitive answers for a domain. | DNS resolver querying multiple servers to find a domain's IP. |
| Role | Stores original DNS records (A, MX, NS, etc.). | Acts as a client, querying authoritative servers iteratively. |
| Response Type | Direct, final answer for DNS queries. | Referrals or partial responses guiding the next query. |
| Query Handling | Answers based on zone data it manages. | Manages query resolution by interacting with several DNS servers. |
| Examples | BIND authoritative servers, Google Public DNS authoritative zones. | ISP recursive resolvers, local DNS client resolvers. |
| Use Case | Domain owners hosting DNS zones. | End-users resolving domain names. |
Understanding DNS: The Backbone of the Internet
Authoritative DNS servers store complete domain name records and respond with definitive answers, ensuring accurate translation of domain names into IP addresses. Iterative DNS servers act as intermediaries, querying multiple authoritative servers step-by-step to resolve user requests efficiently. Together, they form the backbone of the internet's domain name system, enabling fast and reliable access to websites worldwide.
What is Authoritative DNS?
Authoritative DNS servers store and provide definitive answers for specific domain names, ensuring accurate and trusted resolution of DNS queries. These servers host original DNS records, including A, MX, and CNAME, allowing them to respond directly to requests without further queries. Authoritative DNS is essential for maintaining the integrity and reliability of domain name resolution within the internet's DNS hierarchy.
What is Iterative DNS?
Iterative DNS refers to the process where a DNS resolver queries multiple DNS servers sequentially to resolve a domain name, receiving referrals to other DNS servers until it finds the authoritative server with the answer. In this process, the resolver starts by querying the root DNS server, then follows the hierarchy through TLD servers and authoritative servers without the DNS servers performing full resolution themselves. Iterative DNS improves efficiency and reduces server load by distributing the resolution steps across various DNS servers rather than relying on a single server to provide the complete answer.
How Authoritative DNS Works
Authoritative DNS servers store complete domain name records, providing definitive answers to DNS queries by retrieving and returning the requested IP addresses directly from their local database. When a client requests a domain resolution, the authoritative DNS responds with the precise information without needing to query other servers. This direct response ensures faster and more accurate domain name resolution compared to iterative DNS processes that may require multiple queries across different servers.
How Iterative DNS Functions
Iterative DNS functions by clients querying DNS resolvers, which respond with the best possible answer they have or a referral to another DNS server closer to the authoritative source. Instead of resolving the full query themselves, iterative resolvers gradually navigate the DNS hierarchy, starting from root servers, then top-level domain servers, and finally authoritative name servers. This process reduces server load by distributing query resolution and ensures clients receive timely and accurate DNS information through step-by-step referrals.
Key Differences Between Authoritative and Iterative DNS
Authoritative DNS servers respond with definitive answers containing actual DNS records for a domain, managing and storing the original source data for zones. Iterative DNS servers, typically resolvers, query multiple DNS servers step-by-step to retrieve the final answer, often caching responses to improve efficiency. The primary difference lies in authoritative servers holding original data versus iterative servers facilitating domain name resolution by navigating the DNS hierarchy.
Security Implications of Authoritative vs Iterative DNS
Authoritative DNS servers provide definitive answers by directly hosting zone data, ensuring data integrity and reducing exposure to spoofed responses, which enhances overall security. Iterative DNS queries rely on multiple DNS servers to resolve a name, increasing potential attack surfaces such as cache poisoning and man-in-the-middle attacks due to reliance on intermediary servers. Protecting authoritative servers with DNSSEC and secure zone transfers is critical, while iterative resolution benefits from DNSSEC validation to mitigate risks associated with untrusted responses during recursive lookups.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Reliability
Authoritative DNS servers provide definitive answers by directly hosting domain records, resulting in faster and more reliable responses for end-users compared to iterative DNS queries, which require multiple lookups across various servers. Iterative DNS relies on a chain of referrals that can introduce latency and potential points of failure, impacting overall performance and response time. Consequently, authoritative DNS enhances speed and stability in domain resolution, crucial for high-traffic websites and critical applications.
Real-World Use Cases for Each DNS Type
Authoritative DNS servers store and provide definitive answers for domain name queries, making them essential for websites, email servers, and online services requiring accurate domain resolution. Iterative DNS servers handle domain name lookups by querying multiple authoritative servers, commonly used by ISPs and enterprise networks to efficiently resolve end-user requests. Real-world deployment sees authoritative DNS managing domain records directly, while iterative DNS optimizes query resolution speed and reduces network traffic within browsing and application environments.
Choosing the Right DNS Approach for Your Needs
Authoritative DNS servers store complete DNS records and respond with definitive answers, making them essential for managing domain-specific data and ensuring accurate resolution. Iterative DNS servers query multiple DNS servers in sequence until they find the final answer, optimizing speed and reducing load on authoritative servers. Selecting the right DNS approach involves evaluating factors like control over DNS records, response time requirements, and the complexity of your network infrastructure.
Authoritative DNS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com