QR codes offer a quick and reliable way to share information instantly through a simple scan from your smartphone or device. These matrix barcodes store URLs, contact details, product information, and more, enhancing user convenience in marketing, payments, and authentication. Discover how QR codes can transform your interaction with technology by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
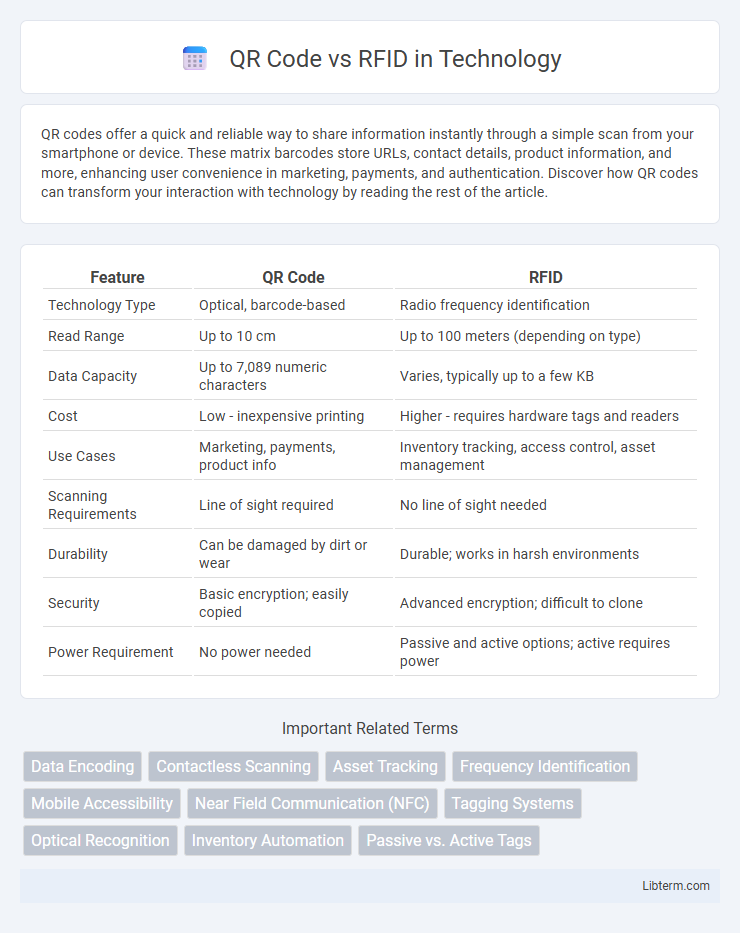
| Feature | QR Code | RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | Optical, barcode-based | Radio frequency identification |
| Read Range | Up to 10 cm | Up to 100 meters (depending on type) |
| Data Capacity | Up to 7,089 numeric characters | Varies, typically up to a few KB |
| Cost | Low - inexpensive printing | Higher - requires hardware tags and readers |
| Use Cases | Marketing, payments, product info | Inventory tracking, access control, asset management |
| Scanning Requirements | Line of sight required | No line of sight needed |
| Durability | Can be damaged by dirt or wear | Durable; works in harsh environments |
| Security | Basic encryption; easily copied | Advanced encryption; difficult to clone |
| Power Requirement | No power needed | Passive and active options; active requires power |
Introduction to QR Code and RFID Technologies
QR Code technology uses a matrix barcode readable by smartphones and scanners, enabling quick access to embedded information through optical recognition. RFID employs radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, offering contactless data exchange and real-time inventory management. Both technologies enhance data capture processes, with QR codes excelling in cost-effectiveness and easy deployment, while RFID provides superior range and automation capabilities.
How QR Codes Work: A Brief Overview
QR Codes store data in a matrix of black and white squares that can be scanned by smartphones or dedicated readers, quickly translating the pattern into information such as URLs, text, or contact details. The scanning process uses the device's camera to capture the QR Code image, then specialized decoding software interprets the pattern based on predefined algorithms to retrieve the embedded data. Unlike RFID, which relies on electromagnetic fields to communicate with tags wirelessly, QR Codes function through optical recognition and require a direct line of sight for scanning.
Understanding RFID: Key Concepts and Operation
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, enabling real-time data capture without direct line of sight. RFID systems comprise tags (active or passive), readers, and antennas operating at various frequencies (LF, HF, UHF) to facilitate communication and data exchange. Unlike QR codes that require visual scanning, RFID enhances inventory management and asset tracking through faster read rates and longer range capabilities.
Advantages of QR Codes
QR codes offer a cost-effective and easy-to-produce solution for quick scanning, requiring only a smartphone or camera without specialized equipment. Their visual nature supports direct human readability and allows encoding of rich information, including URLs, contact details, and product data. QR codes also provide enhanced flexibility in marketing and inventory management, enabling seamless integration with digital platforms and instant access to online content.
Advantages of RFID
RFID technology offers substantial advantages over QR codes, including rapid, contactless data scanning without requiring a direct line of sight, which significantly speeds up inventory management and asset tracking processes. RFID tags can store more data and are reusable, enhancing durability and reliability in harsh environments such as manufacturing and logistics. The automation potential of RFID reduces human error and labor costs, making it a superior choice for large-scale operations needing real-time visibility and efficient workflow integration.
QR Code vs RFID: Cost Comparison
QR Code technology offers a significantly lower cost solution compared to RFID, with QR code printing prices often under $0.10 per label, while RFID tags can range from $0.20 to several dollars depending on type and volume. QR Codes require no special hardware beyond a standard smartphone camera for scanning, whereas RFID systems demand costly readers and infrastructure, increasing initial investment and maintenance expenses. The affordability and ease of deployment make QR Codes a preferred choice for small to mid-sized businesses seeking efficient tracking without the high costs associated with RFID technology.
Security Considerations: QR Code vs RFID
RFID systems offer enhanced security features such as encryption and password protection, making them less vulnerable to cloning or unauthorized scanning compared to QR codes, which are easily replicated and do not inherently support encryption. QR codes rely solely on physical obscurity for security, exposing them to risks like phishing attacks and data manipulation when scanned by malicious apps. Organizations seeking robust authentication and data protection typically prefer RFID technology due to its advanced security protocols and ability to restrict unauthorized access.
Application Use Cases: QR Code and RFID
QR Code technology excels in retail, marketing, and logistics by providing cost-effective and easily deployable solutions for inventory tracking, product authentication, and consumer engagement through smartphone scanning. RFID is widely used in asset management, supply chain automation, and access control systems due to its ability to read multiple tags simultaneously and enable contactless identification over greater distances. Both technologies enhance operational efficiency but differ in application scope: QR Codes benefit customer interaction and static data display, while RFID supports real-time tracking and dynamic data collection in industrial environments.
Challenges and Limitations of QR Code and RFID
QR Codes face challenges such as limited data capacity, susceptibility to damage or dirt obscuring the code, and the need for line-of-sight scanning, which can slow down processes in high-volume environments. RFID technology encounters limitations including higher implementation costs, interference from metals or liquids affecting read accuracy, and concerns about security and privacy due to wireless data transmission. Both technologies require careful consideration of environmental factors and application requirements to optimize performance.
Choosing the Right Solution: QR Code or RFID
Selecting the right solution between QR Code and RFID depends on factors such as range, cost, and application environment. QR Codes offer a cost-effective, visual scanning option ideal for close-range identification and tracking, whereas RFID provides automated, long-range scanning capabilities suitable for inventory management and access control. Evaluating operational needs and budget constraints ensures optimal performance and efficiency in deployment.
QR Code Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com