Cloud computing transforms data storage and processing by delivering scalable resources over the internet, enabling businesses to reduce infrastructure costs while enhancing flexibility. It supports various models such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, each tailored to specific operational needs and workloads. Discover how embracing cloud computing can optimize your IT strategy by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
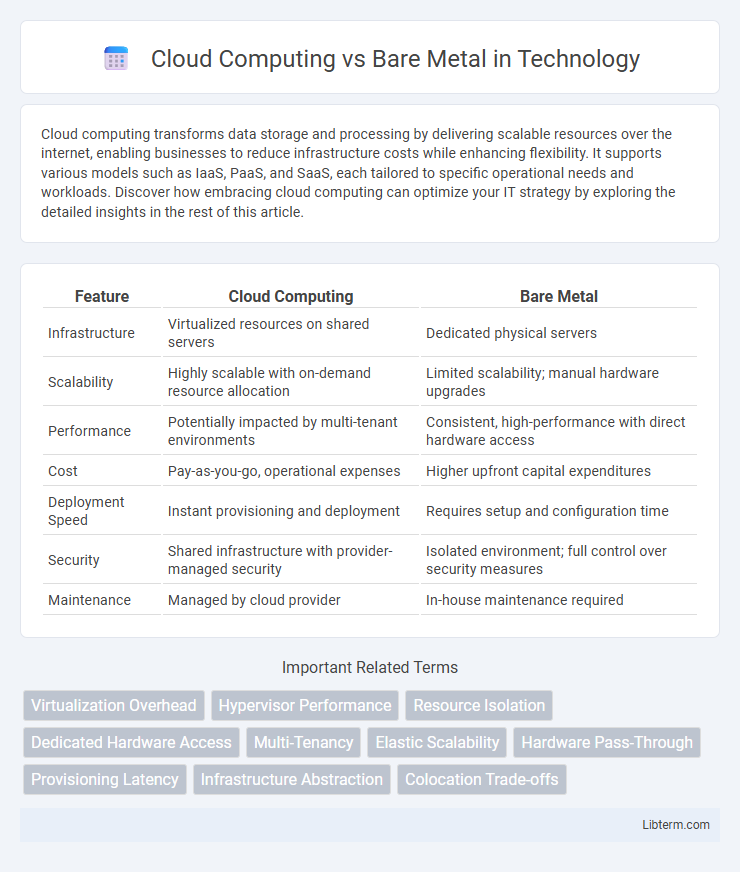
| Feature | Cloud Computing | Bare Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Virtualized resources on shared servers | Dedicated physical servers |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with on-demand resource allocation | Limited scalability; manual hardware upgrades |
| Performance | Potentially impacted by multi-tenant environments | Consistent, high-performance with direct hardware access |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go, operational expenses | Higher upfront capital expenditures |
| Deployment Speed | Instant provisioning and deployment | Requires setup and configuration time |
| Security | Shared infrastructure with provider-managed security | Isolated environment; full control over security measures |
| Maintenance | Managed by cloud provider | In-house maintenance required |
Introduction to Cloud Computing and Bare Metal
Cloud computing delivers scalable virtual resources via the internet, enabling on-demand access to servers, storage, and applications without physical hardware management. Bare metal refers to physical servers dedicated to a single tenant, offering direct access to hardware for maximum performance and customization. Key differences include virtualization, resource allocation, and management flexibility, with cloud computing emphasizing elasticity and bare metal prioritizing control and performance.
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing and Bare Metal
Cloud computing offers scalable virtualized resources managed by third-party providers, enabling flexible on-demand access and pay-as-you-go pricing models. Bare metal servers provide dedicated physical hardware with full control over performance, security, and customization, ideal for workloads requiring high computational power and predictable latency. Key differences include resource allocation, with cloud computing sharing infrastructure among multiple tenants, while bare metal ensures exclusive hardware use, impacting reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Performance Comparison: Cloud vs Bare Metal
Bare metal servers provide dedicated hardware resources offering superior performance, lower latency, and consistent input/output speeds compared to virtualized cloud instances. Cloud computing delivers scalable and flexible resource allocation but may experience variability in performance due to multi-tenancy and shared infrastructure. For high-performance computing tasks requiring deterministic throughput, bare metal remains the preferred choice, whereas cloud environments excel in dynamic workload management and rapid deployment.
Scalability and Flexibility Considerations
Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability and flexibility by enabling instant resource provisioning and seamless adjustments to workload demands through virtualized environments. Bare metal servers provide high performance with direct hardware access but lack the dynamic scalability and rapid adaptability inherent to cloud platforms. Organizations requiring swift scaling and agile resource management typically prefer cloud solutions, while workloads demanding consistent, predictable performance may opt for bare metal infrastructure.
Cost Analysis: Cloud Computing vs Bare Metal
Cloud computing typically offers lower upfront costs with pay-as-you-go pricing models that eliminate the need for significant capital expenditure on hardware, making it ideal for scalable workloads. Bare metal servers require a higher initial investment due to dedicated physical hardware costs but can deliver better performance and predictable monthly expenses, which may reduce long-term operational costs for steady workloads. Analyzing total cost of ownership (TCO) reveals cloud computing's flexibility advantages, while bare metal often excels in cost-effectiveness for consistent, resource-intensive applications.
Security Implications of Both Approaches
Cloud computing offers enhanced security through automated updates, robust encryption, and shared responsibility models, yet it faces risks like multi-tenant vulnerabilities and potential data breaches due to external access. Bare metal servers provide dedicated hardware with complete control over security configurations, minimizing risks of co-tenant attacks but requiring extensive in-house expertise for patch management and physical security. Organizations must weigh cloud provider compliance certifications against bare metal's customizable firewall and intrusion detection capabilities to address specific regulatory and risk requirements.
Use Cases: When to Choose Cloud or Bare Metal
Cloud computing excels in scalable web applications, big data analytics, and development environments requiring rapid provisioning and flexible resources. Bare metal is ideal for performance-intensive workloads such as high-frequency trading, large databases, or applications with stringent compliance and security requirements. Organizations choose cloud for cost-effective scalability and bare metal when maximum control, dedicated hardware, and predictable performance are critical.
Deployment and Management Complexity
Cloud computing offers simplified deployment and management through automated provisioning, scalable resources, and centralized control panels, reducing the need for manual configuration. Bare metal servers require direct hardware access, manual setup, and ongoing maintenance, resulting in higher management complexity and longer deployment times. Enterprises prioritize cloud solutions to streamline operations and accelerate time-to-market by minimizing infrastructure overhead.
Future Trends in Infrastructure Choices
Future trends in infrastructure choices indicate a growing convergence between cloud computing and bare metal solutions, driven by demands for enhanced performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Hybrid architectures integrating bare metal servers with cloud platforms enable organizations to optimize workloads, benefiting from bare metal's dedicated resources and cloud's elasticity. Advances in edge computing and AI workloads further accelerate the adoption of customizable infrastructure that leverages both bare metal speed and cloud automation for next-generation digital transformation.
Making the Right Decision for Your Business
Choosing between cloud computing and bare metal depends on your business's specific needs for scalability, control, and cost-efficiency. Cloud computing offers flexible resource allocation and reduced maintenance overhead, ideal for variable workloads and rapid deployment. Bare metal provides dedicated hardware with maximum performance and security, preferred for latency-sensitive applications and workloads requiring full customization.
Cloud Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com