Shadow plays a crucial role in creating depth and contrast in photography, enhancing the visual storytelling by adding dimension to your images. Mastering shadow techniques can transform ordinary scenes into captivating compositions with dramatic effects. Discover effective ways to use shadows to elevate your photography in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
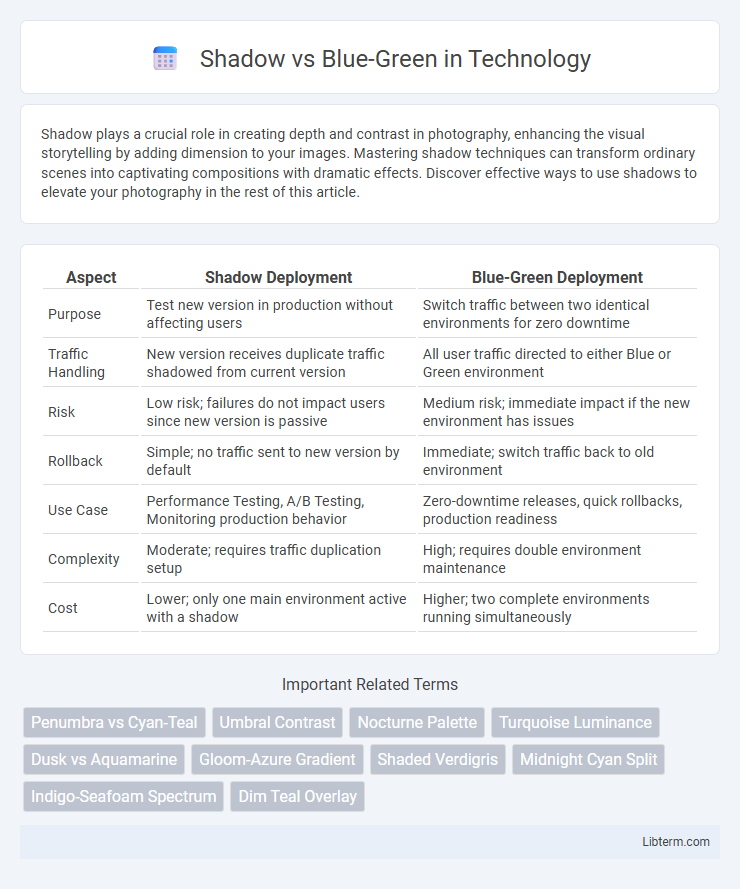
| Aspect | Shadow Deployment | Blue-Green Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Test new version in production without affecting users | Switch traffic between two identical environments for zero downtime |
| Traffic Handling | New version receives duplicate traffic shadowed from current version | All user traffic directed to either Blue or Green environment |
| Risk | Low risk; failures do not impact users since new version is passive | Medium risk; immediate impact if the new environment has issues |
| Rollback | Simple; no traffic sent to new version by default | Immediate; switch traffic back to old environment |
| Use Case | Performance Testing, A/B Testing, Monitoring production behavior | Zero-downtime releases, quick rollbacks, production readiness |
| Complexity | Moderate; requires traffic duplication setup | High; requires double environment maintenance |
| Cost | Lower; only one main environment active with a shadow | Higher; two complete environments running simultaneously |
Introduction to Shadow and Blue-Green Deployments
Shadow deployments involve running a new version of a service alongside the current version, duplicating real user traffic to monitor performance and detect issues without impacting users. Blue-Green deployments use two identical production environments--Blue (current) and Green (new)--allowing seamless switching by redirecting traffic from the Blue to the Green environment once the new version is validated. Both strategies minimize downtime and reduce risk during software releases by enabling testing in production-like conditions without disrupting end users.
Core Concepts: Understanding Shadow Deployment
Shadow deployment involves running a new software version alongside the current system without affecting live traffic, enabling real-world testing and performance analysis in production environments. This approach contrasts with blue-green deployment, where traffic is switched between two separate environments to minimize downtime during releases. Shadow deployments help detect issues early by mirroring user interactions, ensuring stability before full rollout.
Core Concepts: Understanding Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-Green deployment is a release management strategy that minimizes downtime by running two identical production environments: one active (Blue) and one idle (Green). Traffic is routed to the active environment while updates are applied to the idle environment, allowing for seamless switching and rollback without service interruption. This core concept enhances continuous delivery by enabling rapid, low-risk deployments and immediate failbacks.
Key Differences Between Shadow and Blue-Green Strategies
Shadow deployment involves releasing new features to a subset of production traffic without impacting user experience, enabling real-time testing against live conditions. Blue-Green deployment maintains two identical environments, shifting user traffic completely from the blue (current) to the green (new) environment for seamless updates and rollback. Key differences include Shadow's focus on parallel testing with live traffic versus Blue-Green's complete environment switch, impacting deployment risk and monitoring strategies.
Advantages of Shadow Deployment
Shadow deployment enables real-time testing of new features without impacting live user traffic, ensuring minimal risk and uninterrupted service. It facilitates comprehensive validation by running new code alongside the current version, capturing actual production data and performance metrics. This approach allows for early detection of issues and seamless rollback, enhancing overall system reliability and development agility.
Benefits of Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-Green Deployment minimizes downtime and reduces deployment risks by maintaining two identical production environments, enabling seamless switching between them. It facilitates faster rollback in case of issues, improving system reliability and uptime. This approach enhances continuous delivery workflows by allowing thorough testing in the blue environment before redirecting traffic from the green environment.
Limitations and Challenges of Shadow Deployments
Shadow deployments face limitations such as increased complexity in traffic duplication, which can lead to higher resource consumption and latency issues. Monitoring and debugging shadow environments pose challenges due to the lack of real user interaction, making it difficult to detect performance bottlenecks or errors that only occur under live conditions. Ensuring data consistency and security while routing duplicate traffic without impacting production systems remains a significant challenge in shadow deployments.
Risks and Drawbacks of Blue-Green Deployments
Blue-Green deployments risk prolonged resource consumption due to maintaining two full production environments simultaneously, increasing costs and complexity. Traffic routing errors between the blue and green environments can lead to inconsistent user experiences or downtime. Inadequate rollback strategies may cause delayed recovery during failures, undermining the deployment's reliability and business continuity.
Choosing the Right Deployment Strategy for Your Project
Selecting the optimal deployment strategy hinges on your project's risk tolerance, infrastructure complexity, and update frequency. Shadow deployment allows testing new features in the live environment with minimal user impact, ideal for early-stage validation and performance monitoring. Blue-Green deployment minimizes downtime by switching between two identical environments, making it suitable for high-availability systems requiring seamless rollbacks.
Best Practices for Shadow and Blue-Green Deployments
Shadow deployments best practices include directing real user traffic to a new service version while keeping the primary service active, ensuring thorough monitoring and logging for performance and error detection without impacting production. Blue-Green deployments focus on maintaining two identical production environments, switching traffic seamlessly from Blue (current) to Green (new) versions, enabling quick rollback and minimizing downtime. Both strategies emphasize robust automated testing, consistent environment configuration, and gradual traffic shift to ensure stability and reduce deployment risks.
Shadow Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com